Question
Figure shows changes in the global human population between 1910 and 2010.
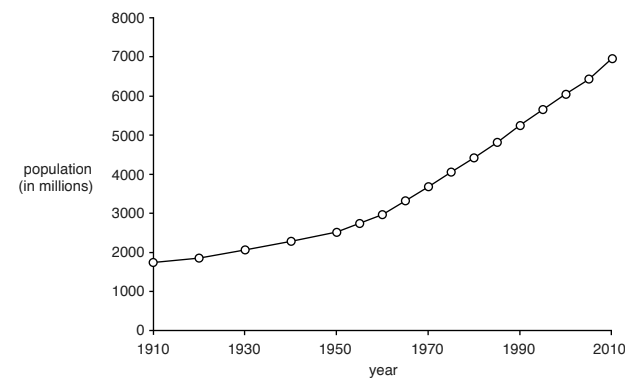
(a) Improved food production has contributed to the increase in the human population.
(i) State and explain two ways in which modern technology has resulted in increased food production.
(ii) State one reason, other than food production, why the human population has increased so rapidly between 1910 and 2010.
(b) In view of the increasing human population, people are sometimes encouraged to eat less meat and more fruit and vegetables, to improve the energy efficiency of their food supply. Explain why
eating less meat and more fruit and vegetables is more energy efficient.
(c) As the human population has increased, forests have been cleared for farming. Outline the effects of deforestation on the environment.
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a) (i) selective breeding qualified with feature e.g. increase in crop yield ;
agricultural machinery, to work larger fields /AW ;
fertilisers, to increase plant growth/ provide mineral ions / salts / (named) nutrient ;
pesticides / insecticides to kill pests to prevent crop destruction ;
herbicides to kills weeds to reduce competition ;
fungicides, to kill fungi to stop disease/reduce crop destruction ;
genetic engineering qualified with a correct feature ;
use of antibiotics to increase yield (in livestock) ;
AVP ;
(ii) better/AW, medical care/ medicine/ drugs / antibiotics ;
clean/ treated, water ;
drainage/ sewage treatment/ sanitation ;
vaccination ;
improved housing conditions ;
improved food, storage/ transport/ availability ;
(b) 1 shorter food chain/ plants at first trophic level/ plants are producers / animals are at a higher trophic level ;
2 energy lost, at each trophic level/along food chain ;
3 energy from plants goes (directly) to humans instead of via animals ;
4 animals / named animal, use up energy so less available ;
5 example of energy loss from animals in food chain ;
(c) 1 soil erosion ;
2 flooding ;
3 landslides ;
4 leaching/ loss of nutrients ;
5 drought ;
6 desertification ;
7 increase in, frequency / severity of storms ;
8 loss of habitat ;
9 extinction/endangerment of species / loss of biodiversity ;
10 disruption of, food chains /food webs ;
11 burning of trees increases carbon dioxide in the atmosphere ;
12 decreased photosynthesis so, increased carbon dioxide/ decreased oxygen, in atmosphere ;
Question:
Figure shows a species of bacterium, Lactobacillus bulgaricus.

(a) List two features that distinguish bacteria from other groups of organisms.
1 ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
2 …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(b) L. bulgaricus are added to milk to make yoghurt.
Figure shows the changes in a population of L. bulgaricus during fermentation to make yoghurt.
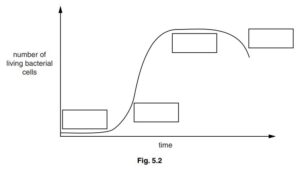
(i) Name the stages shown on Fig. 5.2. Write your answers in the boxes on Fig. 5.2.
(ii) Explain why the population of L. bulgaricus does not continue to increase during the
fermentation to make yoghurt.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(c) The curve shown in Fig. 5.2 is a sigmoid population growth curve.
Define the term growth.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(d) Bacteria, such as L. bulgaricus, can reproduce rapidly.
Name the process of reproduction in bacteria.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
(e) Sometimes food additives are added to yoghurt. Some people suggest that it is healthier to
eat yoghurt without additives.
Suggest the advantages and disadvantages of putting food additives into yoghurt.
advantages ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
disadvantages ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a) cell wall, peptidoglycan/murein;
no nucleus/no nuclear membrane/have nucleoid;
loop of DNA;
no mitochondria;
no chloroplasts;
no vacuoles;
smaller ribosomes;
have pili;
have capsule;
small/1–2µm; A correct reference to size
(b) (i) lag (phase);
log/exponential (phase);
stationary/plateau (phase);
death (phase);
(ii) no longer reproducing/death rate greater than or equal to ‘birth’ rate;
ref to limiting factor(s);
no/less, (named) nutrients;
no/less, space;
no/less, oxygen;
build-up of (named) waste;
waste is toxic;
idea that pH could change to be unsuitable;
(c) increase in, size/length/mass / volume/AW;
increase in dry mass;
increase in cell number;
ref to permanent;
(d) Ans: asexual (reproduction) / binary fission;
(e) advantages:
longer shelf-life/ stop foods going off;
stop/reduce, growth of (unwanted) bacteria/fungi/microbes;
prevent food poisoning;
improve/give, taste/flavor;
give colour/improve appearance;
give texture;
emulsify/ stabilise, food components;
disadvantages:
hyperactivity (in children);
allergies;
vomiting/nausea/headache;
asthma;
possible link with cancer;
AVP;