Question
How do carbon dioxide and oxygen move in and out of a mesophyll cell?
A active transport
B diffusion
C respiration
D transpiration
▶️Answer/Explanation
B
Carbon dioxide and oxygen move in and out of a mesophyll cell through diffusion.
Diffusion is the process by which molecules move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. In the case of mesophyll cells, carbon dioxide and oxygen diffuse in and out of the cell through small pores called stomata located on the surface of the leaves.
During photosynthesis, carbon dioxide enters the mesophyll cells through the stomata. Inside the cell, carbon dioxide is converted into sugars through the process of photosynthesis. Oxygen, which is a byproduct of photosynthesis, is released from the mesophyll cells and exits through the stomata.
Therefore, the correct answer is B: diffusion.
Question
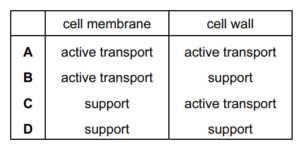
Which row matches the cell membrane and cell wall of a palisade cell to their functions?
▶️Answer/Explanation
B
In the context of a palisade cell, the correct matching of functions is:
Cell membrane: Active transport
Cell wall: Support
1. Cell membrane: The cell membrane, also known as the plasma membrane, is responsible for controlling the movement of substances into and out of the cell. It regulates the transport of ions, nutrients, and waste products through various mechanisms, including active transport. Active transport refers to the process by which the cell uses energy to move molecules against their concentration gradient, requiring specific carrier proteins embedded in the membrane.
2. Cell wall: The cell wall is a rigid structure that surrounds the cell membrane in plant cells. It provides support and protection to the cell, helping it maintain its shape and resist mechanical stress. The cell wall is composed of cellulose and other polysaccharides, providing strength and rigidity to the cell.
Question
Active transport is the movement of
A molecules from a region of their higher concentration to a region of their lower concentration.
B particles from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration using
energy from respiration.
C urine by relaxation of a sphincter muscle in the bladder.
D water through a partially permeable membrane from a more dilute to a more concentrated
solution.
▶️Answer/Explanation
B
The correct answer is B: particles from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration using energy from respiration.
Active transport is the process by which cells move molecules or ions against their concentration gradient, from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration. This movement requires the expenditure of energy, typically in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate), which is generated through cellular respiration. Active transport is essential for various physiological processes in living organisms, such as nutrient uptake, ion transport, and maintaining the electrochemical balance across cell membranes.
Question
Which substance, needed for protein synthesis, is carried into a leaf from the stem?
A carbon dioxide
B nitrate
C oxygen
D starch
▶️Answer/Explanation
B
The correct answer is B) nitrate.
Nitrate is the substance needed for protein synthesis that is carried into a leaf from the stem. Nitrate is an essential nutrient for plants and is absorbed from the soil through the plant’s roots. It is then transported upward through the stem to the leaves, where it is utilized in the process of protein synthesis.
Carbon dioxide (A) is another essential component required for photosynthesis in plants, but it enters the leaves directly from the atmosphere through small openings called stomata.
Oxygen (C) is produced as a byproduct of photosynthesis and is released from the leaves into the atmosphere.
Starch (D) is a complex carbohydrate that serves as a storage form of energy in plants. It is synthesized in the leaves through the process of photosynthesis and is typically transported to other parts of the plant, such as the stem or storage organs, rather than being carried from the
Question
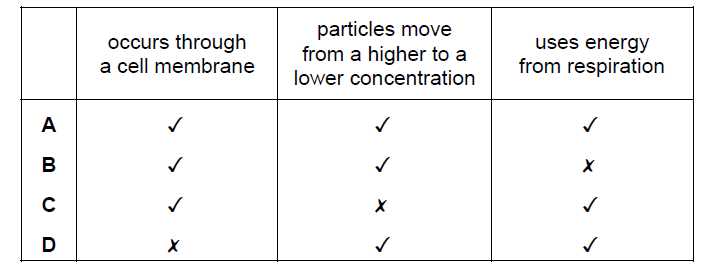
What are the features of active transport?
▶️Answer/Explanation
C
Active transport is a biological process that enables the movement of molecules or ions across a cell membrane against their concentration gradient, from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration. This process requires the expenditure of energy to overcome the natural tendency of molecules to diffuse down their concentration gradient. Features of active transport:
Occurs through a cell membrane: Active transport takes place across cell membranes, which separate the interior of the cell from the extracellular environment. It is essential for maintaining proper concentrations of ions and molecules within the cell.
Uses Energy from respiration: Unlike passive transport mechanisms (such as diffusion or facilitated diffusion), active transport requires the input of energy. This energy is typically obtained from the breakdown of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the primary energy currency of cells, generated through cellular respiration or other energy-producing processes.