Question
Lactase is a human enzyme that catalyses the breakdown of lactose in milk.
At which temperature does lactase work fastest?
A 0°C B 18°C C 37°C D 100°C
▶️Answer/Explanation
C
The optimal temperature for lactase activity is typically around 37°C (Celsius). At this temperature, the enzyme functions most efficiently and achieves its maximum rate of lactose breakdown.
Extreme temperatures can denature or deactivate the enzyme. In the case of lactase, temperatures significantly above 37°C, such as 100°C, would likely denature the enzyme and render it nonfunctional. Similarly, lower temperatures, such as 0°C, can slow down the enzyme’s activity, although it may still retain some functionality.
Therefore, option C, 37°C, is the most suitable temperature for lactase to work at its fastest.
Question
The graph shows the effect of pH on a particular enzyme-controlled reaction.
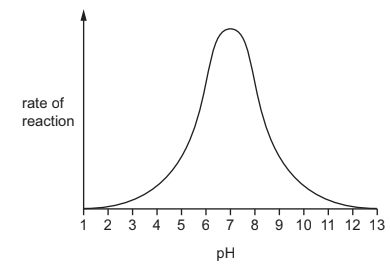
When is the enzyme not active?
A at pH 1 and pH 13
B at pH 3 and pH 11
C at pH 5 and pH 9
D at pH 7
▶️Answer/Explanation
A
In the given graph showing the effect of pH on an enzyme-controlled reaction, it is observed that the enzyme is not active at pH 1 and pH 13.
Enzymes are biological catalysts that facilitate and regulate chemical reactions in living organisms. They are highly sensitive to changes in their environment, including pH. Enzymes have an optimal pH range in which they exhibit maximum activity, and deviations from this range can lead to a decrease or loss of enzymatic activity.
At extremely acidic conditions, such as pH 1, the enzyme’s structure can become denatured. Denaturation refers to the alteration of an enzyme’s three-dimensional structure, which is essential for its proper functioning. The extreme acidity disrupts the delicate balance of electrostatic interactions within the enzyme, causing it to lose its shape and, consequently, its activity.
Similarly, at highly alkaline conditions, such as pH 13, the enzyme can also become denatured. The high alkalinity interferes with the enzyme’s structure and disrupts its active site, where the substrate binds and the catalytic reaction occurs. As a result, the enzyme loses its ability to effectively interact with the substrate, rendering it inactive.
Question
Which enzyme in a biological washing powder will help remove fatty stains?
A amylase
B lipase
C pectinase
D protease
▶️Answer/Explanation
B
The correct answer is B) lipase. Lipases are enzymes that help break down and remove fatty stains, such as oil and grease, from fabrics. They catalyze the hydrolysis of fats and oils into smaller components, such as fatty acids and glycerol, which are more easily removed during the washing process. Therefore, lipases are commonly included in biological washing powders to enhance their stain-removing capabilities.
Question
What is the correct definition of the term enzyme?
A carbohydrates that act as biological catalysts
B carbohydrates that act as substrates
C proteins that act as biological catalysts
D proteins that act as substrates
▶️Answer/Explanation
C
The correct definition of the term enzyme is C: proteins that act as biological catalysts. Enzymes are proteins that accelerate chemical reactions in living organisms by lowering the activation energy required for the reactions to occur. They facilitate biochemical reactions by binding to specific molecules called substrates and converting them into products. Enzymes are not carbohydrates and they are not typically substrates themselves; instead, they facilitate the conversion of substrates into products.
Question
Which graph shows the effect of pH on enzyme activity?
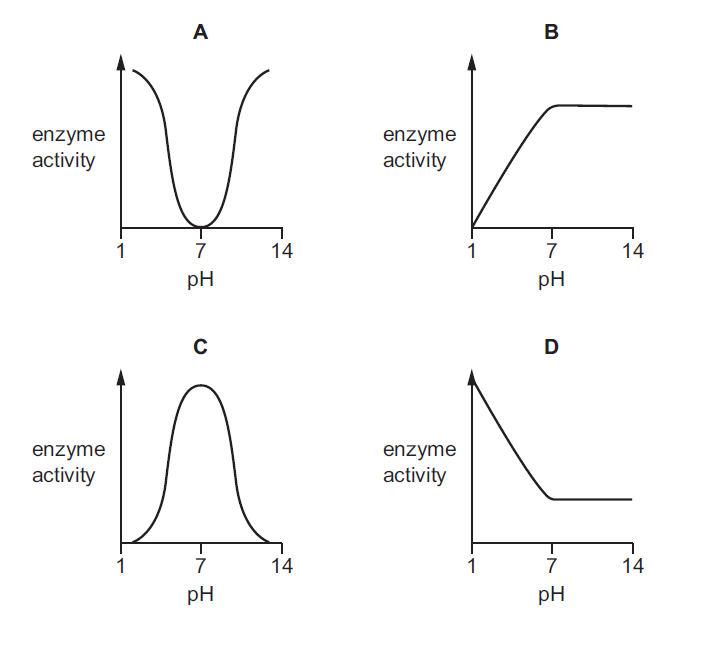
▶️Answer/Explanation
C
The graph that typically shows the effect of pH on enzyme activity is called an “enzyme activity versus pH” graph or an “enzyme activity profile.” This graph plots the rate of enzyme activity (measured as either reaction rate or product formation) on the y-axis and the pH values on the x-axis.
The graph generally shows a bell-shaped curve, known as the pH optimum curve, which represents the optimal pH at which the enzyme activity is highest. As the pH deviates from the optimum, the enzyme activity gradually decreases.
The enzyme is inactive or exhibits very low activity at pH 1 and pH 14. Extreme pH values, whether highly acidic (pH 1) or highly basic (pH 14), can denature proteins, including enzymes. Denaturation involves the disruption of the enzyme’s structure, rendering it non-functional.
At pH 7, which is considered neutral, the enzyme exhibits maximum activity. This pH value represents the optimal pH for the particular enzyme being studied. Enzymes often have an optimal pH that corresponds to the pH of their natural environment or the specific biological process they are involved in.
