Question
The table shows diagrams of three types of cell found in a leaf.
Which row correctly identifies each cell type?
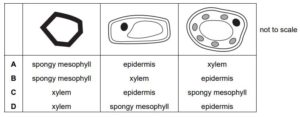
▶️Answer/Explanation
C
Diagrams of three types of cells found in a leaf:
Xylem cells: Xylem is a vascular tissue responsible for transporting water and minerals from the roots to the rest of the plant, including the leaves. Xylem cells are specialized for conducting water, and they are typically elongated, hollow, and thick-walled. They form part of the leaf’s vascular system.
- Epidermis: These are the outermost layer of cells that cover the upper and lower surfaces of the leaf. They form a protective barrier and are typically transparent to allow light penetration. The epidermal cells on the upper surface often have a waxy cuticle to prevent excessive water loss.
- Spongy mesophyll : These cells are found in the lower part of the leaf, beneath the palisade mesophyll cells. They are more loosely arranged and have air spaces between them. Spongy mesophyll cells also contain few chloroplasts. The air spaces within this layer allow for the exchange of gases, such as carbon dioxide and oxygen, during photosynthesis and respiration.
Together, these three types of cells contribute to the leaf’s structure and function in photosynthesis, gas exchange, and protection.
Question
The diagram shows a cross-section of a leaf as seen under a microscope.
Which structure is a palisade mesophyll cell?
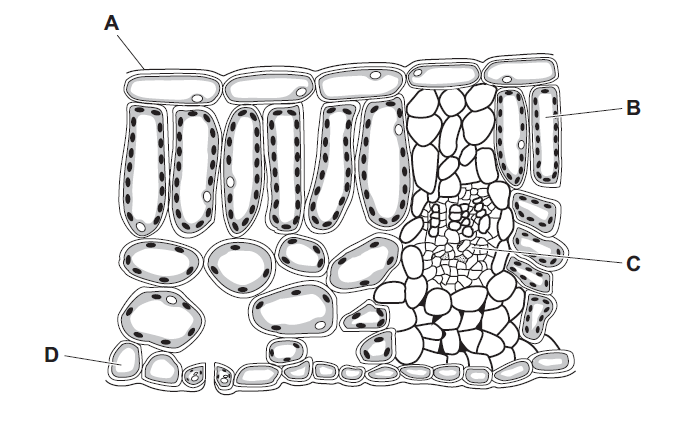
▶️Answer/Explanation
B
Structure B is palisade mesophyll cell which is a specialized type of plant cell found in the leaves of plants. It is located in the upper layer of the leaf within the mesophyll tissue. The palisade mesophyll cells are elongated and tightly packed, arranged vertically or perpendicular to the leaf surface.
These cells contain a large number of chloroplasts, which are responsible for photosynthesis. The chloroplasts in the palisade mesophyll cells capture light energy and convert it into chemical energy through photosynthesis, producing sugars that the plant uses for growth and energy. The arrangement of palisade mesophyll cells allows for efficient light absorption as the vertically oriented cells can maximize the exposure of chloroplasts to sunlight. This adaptation helps plants optimize the process of photosynthesis by capturing as much light energy as possible for efficient production of glucose.
Question
The diagram shows a leaf as seen in cross-section under the microscope.
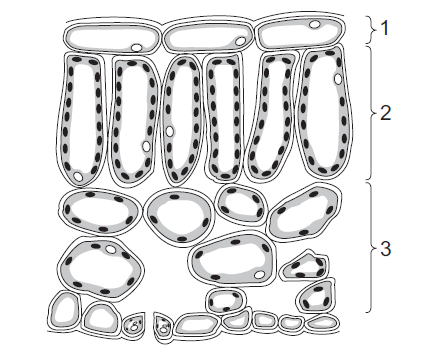
What are tissues 1, 2 and 3?
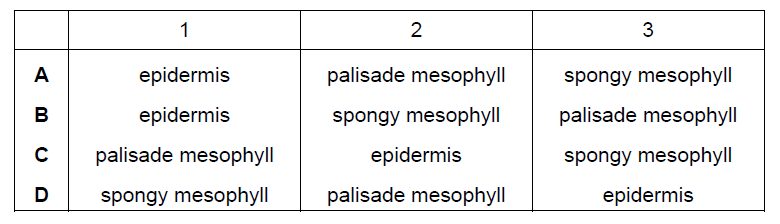
▶️Answer/Explanation
A
Tissue 1,2 , and 3 are Epidermis, palisade mesophyll cells, and spongy mesophyll cells which are commonly found in a leaf.
1. Epidermal cells: These are the outermost layer of cells that cover the upper and lower surfaces of the leaf. They form a protective barrier and are typically transparent to allow light penetration. The epidermal cells on the upper surface often have a waxy cuticle to prevent excessive water loss.
2. Palisade mesophyll cells: These cells are located in the upper part of the leaf, just below the epidermis. They are elongated and closely packed together, forming a layer of cells. Palisade mesophyll cells contain many chloroplasts, which are responsible for photosynthesis, making this region the primary site for capturing sunlight and converting it into chemical energy.
3. Spongy mesophyll cells: These cells are found in the lower part of the leaf, beneath the palisade mesophyll cells. They are more loosely arranged and have air spaces between them. Spongy mesophyll cells also contain chloroplasts, although they are fewer in number compared to the palisade mesophyll cells. The air spaces within this layer allow for the exchange of gases, such as carbon dioxide and oxygen, during photosynthesis and respiration.
Together, these three types of cells contribute to the leaf’s structure and function in photosynthesis, gas exchange, and protection.
Question
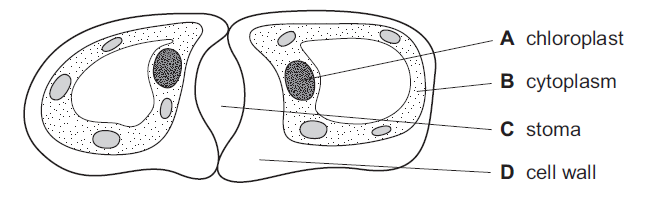
The diagram shows a student’s drawing of guard cells.
Which label is not correct?
▶️Answer/Explanation
A
Label A is not chloroplast, It is nucleaus.
Guard cells are specialized cells found in the epidermis of plant leaves and stems. They are responsible for controlling the opening and closing of stomata, which are tiny pores on the surface of plant tissues. The two guard cells surround each stomatal pore and are shaped like kidney beans or dumbbells. Guard cells have a rigid cell wall made up of cellulose. The cell wall provides structural support and protection to the cell. The interior of the guard cell contains cytoplasm, which consists of various organelles such as nucleus, mitochondria, Golgi apparatus, and endoplasmic reticulum.
The structure of the nucleus in guard cells is enclosed by a double membrane called the nuclear envelope, which separates the contents of the nucleus from the cytoplasm
Guard cells possess chloroplasts, which are responsible for photosynthesis. The presence of chloroplasts gives guard cells their green color. Structurally, chloroplasts are oval-shaped double-membrane organelles. The outer membrane encloses the entire organelle, while the inner membrane forms a system of folded membranes called thylakoids, which are stacked together to form structures known as grana.
Question
The diagram shows the structure of a palisade cell.
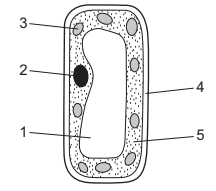
Which features are also found in a liver cell?
A 1 and 2 B 2 and 5 C 3 and 4 D 4 and 5
▶️Answer/Explanation
B
The features that are also found in a liver cell are provided in option B. 2 and 5. Both the nucleus and cytoplasm are found in both palisade cells and liver cells.
The nucleus is a membrane-bound organelle present in most eukaryotic cells, including both plant cells (such as palisade cells) and animal cells (such as liver cells). It contains the cell’s genetic material, including DNA.
Cytoplasm refers to the fluid-like substance that fills the cell, excluding the nucleus. It is present in all types of cells, including palisade cells and liver cells. The cytoplasm contains various organelles, such as mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and ribosomes, which are involved in different cellular processes and functions.
