Question
(a) Fig. 3.1 shows the digestive system.
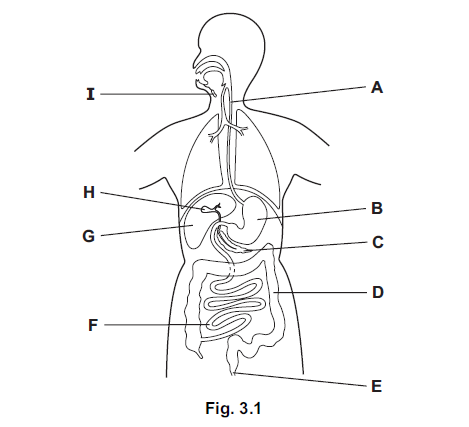
Use the letters from Fig. 3.1 to identify one place where each process occurs.
(b) Enzymes are involved in chemical digestion.
Describe the function of the enzyme lipase.

(c) The teeth are involved in physical digestion.
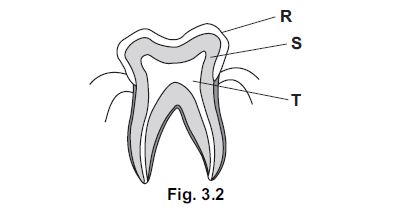
Fig. 3.2 shows a section through a tooth.
(i) Name a mineral that is required for the development of healthy teeth.
![]()
(ii) Name the parts labelled R, S and T as shown on Fig. 3.2.

(iii) Describe how dental decay is caused.

Answer/Explanation
Ans:
Question
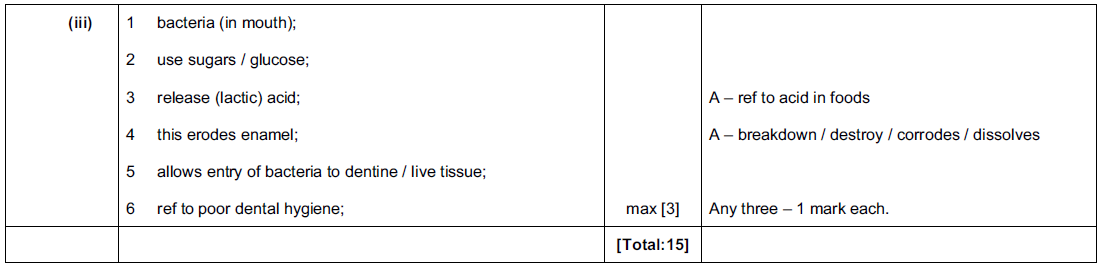
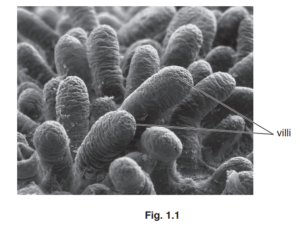
Fig. 1.1 and Fig. 1.2 show two images of villi.
Fig. 1.1 shows a surface view of many villi viewed through a scanning electron microscope.
Fig. 1.2 shows a section of one villus viewed through a light microscope.
Villi are found in the small intestine.
(a) State the function of villi.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
absorption (of digested food / water) / movement of (small) molecules (from small
intestine) into blood ;
Question
(b) Identify and describe two of the labelled components of a villus.
Use the letters in Fig. 1.2 in your answer.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
1 goblet cells labelled P ;
2 shaped described / produces mucus ;
3 lacteal / lymph vessel / lymphatic vessel, labelled Q ;
4 description / transports fatty acids / fats;
5 capillaries / blood vessel, labelled R ;
6 thin / one cell thick, walls / carries products of digestion ;
7 microvilli / epithelia labelled S ;
8 for microvilli accept – large surface area / thin, for diffusion / absorption ;
Question
(c) Some infections in the small intestine can cause diarrhoea.
(i) Describe the effects of diarrhoea on the body.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
watery faeces / AW ;
dehydration / described ;
loss of, salts / ions / electrolytes ;
cramps / stomach pain ;
death ;
Question
(ii) State the treatment for the effects of severe diarrhoea.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
oral rehydration therapy ;
Question
(d) (i) Blood transports nutrients.
State the component of the blood that transports nutrients.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(blood) plasma ;
Question
(ii) The nutrients in the blood can be used to become part of cells.
State the name of this process.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
assimilation ;
Question
(iii) Amino acids are an example of a type of nutrient transported in the blood.
State two examples of larger molecules found in cells that are made from amino acids.
1 ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
2 ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
protein ;
named proteins ;;
Question
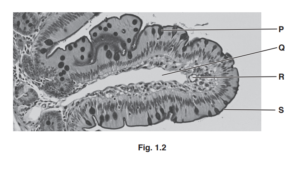
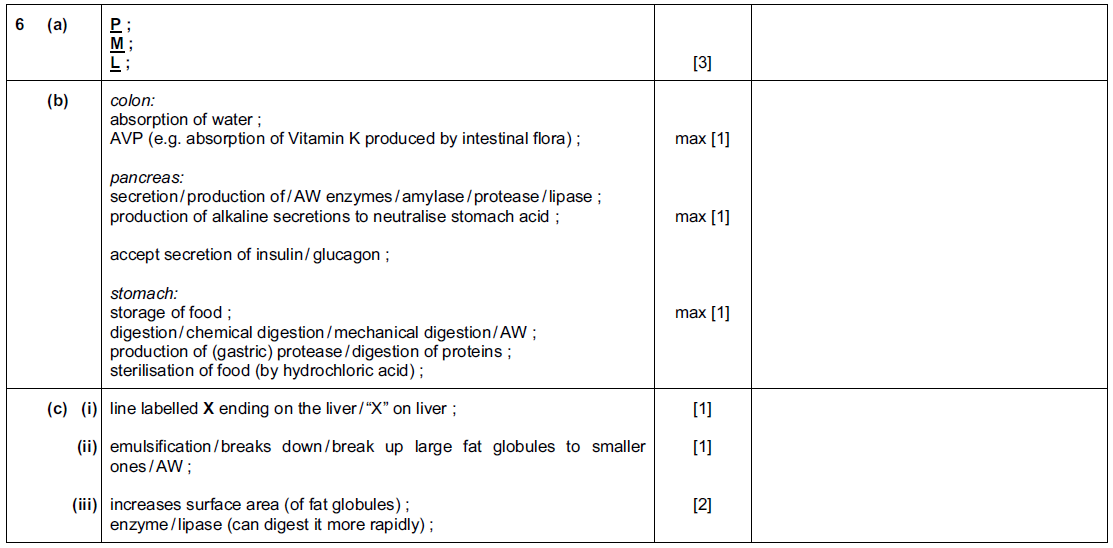
Fig. 6.1 shows a diagram of the alimentary canal.
(a) Use the letters on Fig. 6.1 to identify:
the colon, ………………
the pancreas, ………………
the stomach. ………………
[3]
(b) State one function for each of these parts of the alimentary canal.
colon ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
pancreas …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
stomach ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
[3]
(c) (i) On Fig. 6.1 draw a line to show where bile is made.
Label it X.
[1]
(ii) State the action that bile has on fats in the small intestine.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. [1]
(iii) Explain how this action speeds up the digestion of fats.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. [2]
(d) Digested food is absorbed as it passes along the small intestine.
Explain how this absorption takes place.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. [3]
Answer/Explanation
Ans:

Question
Fig. 6.1 shows the human digestive system.
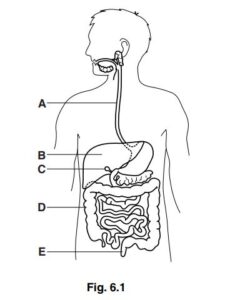
(a) (i) State the letter of the organ that makes bile.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………[1]
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B;
(ii) Name the organ that stores bile.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………[1]
Answer/Explanation
Ans: gall bladder;
(iii) The bile duct can become blocked.
Explain why this causes problems with the digestion of fats.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………[2]
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(bile is) necessary to emulsify fats / AW;
(emulsification) needed to increase surface area; for the action
of lipase;
(b) Table 6.1 shows information about some parts of the human digestive system
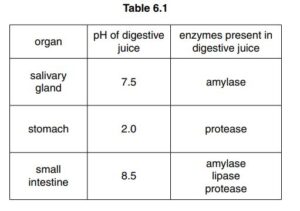
(b) Table 6.1 shows information about some parts of the human digestive system

(c) (i) The material entering the colon is liquid, but the faeces are usually much more solid.
State how this happens.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………[1]
Answer/Explanation
Ans: water is removed / reabsorbed (into bloodstream);
(ii) Name the component of a balanced diet which is necessary for the correct formation of
faeces.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………[1]
Answer/Explanation
Ans: fibre / roughage;
(iii) Name a disorder which can result from a shortage of the component identified in (c)(ii).
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………[1]
[Total: 11]
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
constipation;
diverticulitis;
colon / bowel cancer;
