Question
Fig. 5.1 shows the different types of human teeth.
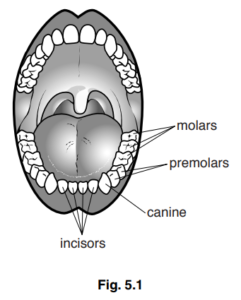
(a) Describe the functions of the canine and molar teeth. [2]
(b) Fig. 5.2 shows the skulls of a tiger and a rabbit.
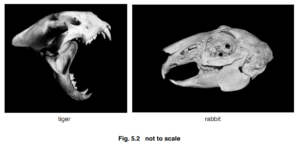
(i) State two ways in which the teeth of a tiger differ from the teeth of a rabbit, using evidence
from Fig. 5.2. [2]
(ii) Suggest one feature visible in Fig. 5.2 that indicates the tiger is a carnivore. [1]
(c) Omnivores are animals that eat both animals and plants. Scientists use the number and types
of teeth to classify animals as carnivores, herbivores or omnivores.
Table 5.1 shows examples of different types of mammals and their teeth.
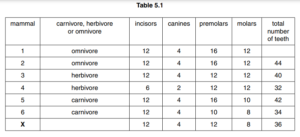
(i) Calculate the number of molars as a percentage of the total number of teeth for
mammal 1.
Show your working.
Give your answer to the nearest whole number.
…………………………………………………….%
[2]
(ii) The skull of an unidentified mammal, X, is likely to be a carnivore.
Discuss the evidence in Table 5.1 for and against classifying mammal X as a carnivore.
(d) Mechanically digested food travels from the mouth to the stomach. The gastric juice in the
stomach contains hydrochloric acid, giving a low pH environment.
Explain why it is important to have a low pH in the stomach. [3]
(e) Products of digestion are absorbed through the villi in the small intestine.
Explain how villi are adapted for absorption. [3]
(f) Coeliac disease is caused by a reaction to a protein called gluten. The villi become damaged
causing a reduction in the absorption of nutrients.
Suggest possible effects on the body of a reduction in the absorption of nutrients. [3]
[Total: 20]
Answer/Explanation
Ans
5 (a) canine
piercing/ tearing the food ;
molar
chewing/ grinding the food ;
(b) (i) 1 tiger has more pointed incisors /rabbit has less pointed incisors ;
2 tiger has canines /rabbit has no canines ;
3 tiger has jagged, premolars / molars ;
4 tiger has fewer molars /rabbits have more molars ;
5 rabbit has a diastema/(larger) gap between incisors and pre molars ;
(ii) canines ;
jagged, premolars / molars ;
eyes positioned at the front of the skull ;
pointed ridge / crest, on skull ;
(c) (i) 12/ 44 × 100
27 ;;
(ii) arguments for carnivore:
1 has same number of incisors as, other carnivores / 5/ 6 ;
2 has same number of canines as, other carnivores 5/ 6 ;
3 has same number of molars as, 6/ a carnivore ;
arguments against carnivore:
4 same number of premolars as, herbivores / 3/ 4;
5 1/ 2/3/ some herbivores / omnivores, also have 12 incisors ;
6 1/ 2/3/ some herbivores / omnivores, also have 4 canines ;
(d) 1 denatures enzymes in microorganisms ;
2 kills, microorganisms /(named) pathogens ;
3 optimum pH for pepsin activity ;
4 proteins are digested/ broken down, to (poly)peptides /amino acids ;
(e) 1 villi lining/epithelium, only one cell thick / thin ;
2 good blood supply / many capillaries ;
3 microvilli ;
4 large surface area ;
5 lacteal for fats / fatty acid, absorption ;
6 protein channels ;
7 mitochondria for active transport ;
(f) 1 weight loss / poor growth/ lack of energy / stomach pain/abdominal pain/
cramps / diarrhoea/weaker immune system ;
2 malnutrition/ deficiency disease ;
3,4 named, nutrient deficiency /effect, with deficient nutrient ;;;
&5 e.g. anaemia → iron/ vitamin B12
kwashiorkor → protein ;
marasmus → all nutrients
scurvy → vitamin C
night blindness →vitamin A/retinol
Question
(a) Fig. 3.1 shows the digestive system.
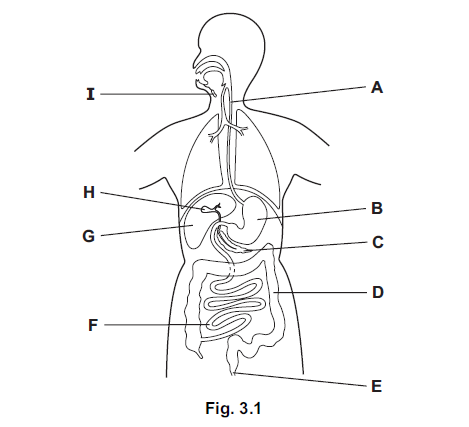
Use the letters from Fig. 3.1 to identify one place where each process occurs.
(b) Enzymes are involved in chemical digestion.
Describe the function of the enzyme lipase.

(c) The teeth are involved in physical digestion.
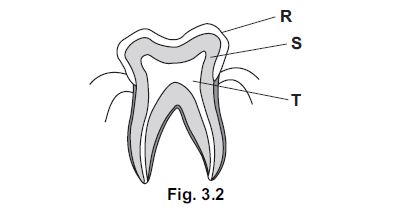
Fig. 3.2 shows a section through a tooth.
(i) Name a mineral that is required for the development of healthy teeth.
![]()
(ii) Name the parts labelled R, S and T as shown on Fig. 3.2.

(iii) Describe how dental decay is caused.

Answer/Explanation
Ans:
Question
(a) (i) Sometimes teeth develop dental decay.
Describe how dental decay develops.
(ii) Table 2.1 states three methods of caring for the teeth to prevent dental decay.
Complete Table 2.1 by describing why each method is effective.
Table 2.1

(b) (i) There are four types of teeth.
State the functions of each of the following when food is being eaten.
incisors ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
canines ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
premolars and molars …………………………………………………………………………………………..
(ii) Suggest how the tongue helps in the process of chewing.
(c) Describe two reasons why solid food is chewed before it is swallowed.
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a) (i) bacteria (in mouth) ;
(bacteria) change or respire sugar/ named sugar (in food) ;
(sugar) to acid/ lactic acid ;
acid dissolves /attacks, enamel/ teeth/ dentine/top layer/AW ;
anaerobic respiration ;
(ii) brushing: dislodges, plaque/ bacteria/ food (particles)/ sugars (from mouth) ;
rinsing: removes, plaque/bacteria/ food (particles)/ sugars (from mouth) ;
not eating sweet foods between meals: bacteria have, less sugar/ food (to respire/ use) bacteria respire less / less acid produced ;
(b) (i) incisors: chop/ cut / bite /AW ;
canines: pierce/ tear/grip/AW ;
premolars and molars: grind/ crush/ chew/AW ;
(ii) moves food (between teeth)/AW ;
mixes food with saliva/ amylase ;
helps form a bolus ;
(c) food small enough (to be swallowed) ora ;
increases surface area ;
for more rapid enzyme action/ digestion ;
food mixed with, enzyme/ amylase ;
food mixed with saliva/ mucus (to make swallowing easier) ;
prepares stomach for receiving food / AW ;
Question
Fig. 7.1 shows the human alimentary canal and some of the organs associated with it.

(a) Use letters from Fig. 7.1 to identify which structure carries out a particular function. Write your answers in Table 7.1.
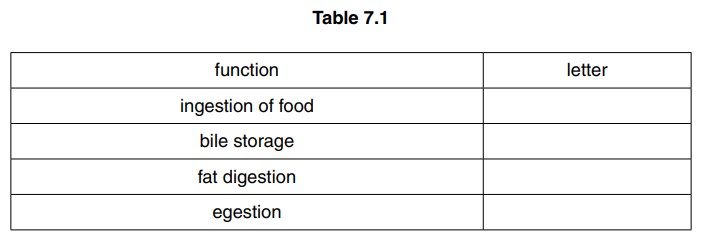
(b) Name the process which moves food from D to F.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(c) A student investigated the digestion of fats by the enzyme lipase. He found that as lipase digested the fats, the pH of the solution changed from pH 8 to pH 6.
(i) Explain why the digestion of fats changed the pH of the solution.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(ii) Fig. 7.2 shows three test-tubes that were set up for this experiment.
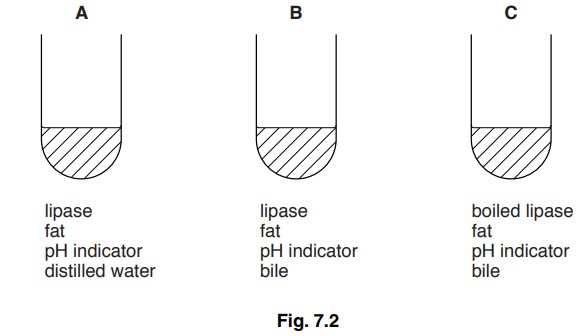
The time taken for the indicator to change colour after the lipase was added was measured. The results are shown in Table 7.2.
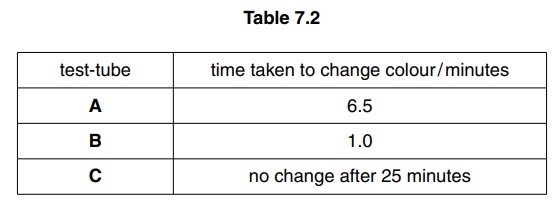
Explain why the indicator in test-tube B changes colour much faster than the indicator in test-tube A.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
(d) Some biological washing powders contain lipase. Instructions on the packet state that biological washing powders should be used in warm water but not in very hot water. Explain why warm water should be used instead of very hot water. Use Fig. 7.2 and Table 7.2 to help with your answer.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(e) Eating too much fat can be harmful. State one way in which too much fat can be harmful to human health.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a) 
(b) peristalsis;
(c) (i) fat digestion produces fatty acids (and glycerol);
fatty acids lower pH;
(ii) (B contains bile) which emulsifies fats;
increases surface area for enzyme/ lipase action/AW;
(so) fatty acids are produced more quickly / more rapid fat digestion;
colour of indicator changes more quickly;
(d) hot water could denature the enzyme;
changes the shape of active site of enzyme/ enzyme
inactive;
tube C shows that boiled enzyme does not digest fats;
(e) obesity;
(which) leads to joint damage;
blockage of blood vessels / heart disease/CHD/atherosclerosis / cardiac arrest;
high blood pressure;
type 2 diabetes;
cancer;
AVP;
