Question
A leafy shoot is placed in a solution of a red dye.
After 30 minutes, which part of a leaf from this shoot will contain the red dye?
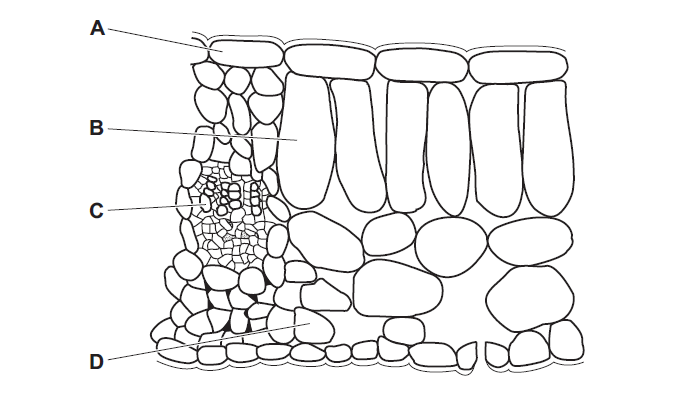
▶️Answer/Explanation
C
If a leafy shoot is placed in a solution of a red dye, the dye will be transported through the xylem vessels, which are responsible for the upward movement of water and dissolved substances from the roots to the rest of the plant. Consequently, after 30 minutes, the red dye will likely be present in the veins of the leaf.
Xylem vessels are interconnected throughout the leaf, providing a network for the movement of water and dissolved substances. These vessels are most concentrated in the leaf veins, which consist of xylem and phloem tissues. The xylem vessels transport water and nutrients absorbed by the roots to the leaf cells, while the phloem vessels transport sugars and other organic molecules produced during photosynthesis to other parts of the plant.
Therefore, due to the transportation system in plants, the red dye would be expected to be primarily present in the veins of the leaf after 30 minutes of exposure to the dye solution.
Question
A celery stalk was placed into a beaker of blue dye. When the dye reached the leaves, the stalk
was taken out and a section was cut, as shown in the diagram.
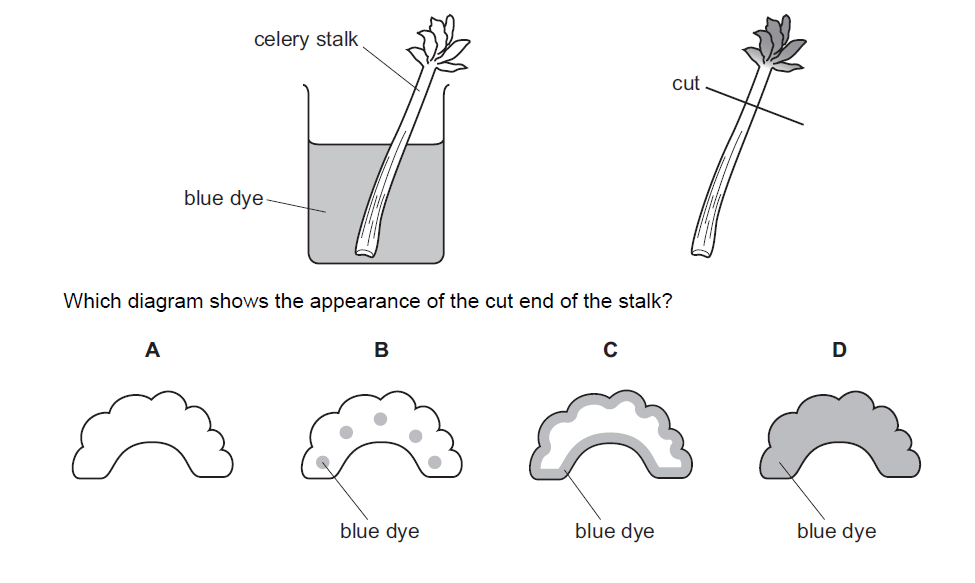
▶️Answer/Explanation
B
When the celery stalk is placed into a beaker of blue dye, the dye will be drawn up through the xylem vessels of the celery stalk via capillary action. The xylem vessels are responsible for transporting water and nutrients from the roots to the leaves of the plant. In a cut section of a celery stalk, there are small, scattered dots or streaks throughout the cross-section. These dots or streaks represent the cut ends of xylem vessels. They can vary in size and may appear as fine lines or larger, more distinct structures, depending on the thickness of the celery stalk.
As the blue dye reaches the leaves of the celery stalk, it will also reach the cells in the vascular tissue, including the xylem vessels. The cut end of the celery stalk will likely show the blue coloration from the dye that has been transported through the xylem vessels.
Question
Potted plants are left for a week in a tank of water as shown.
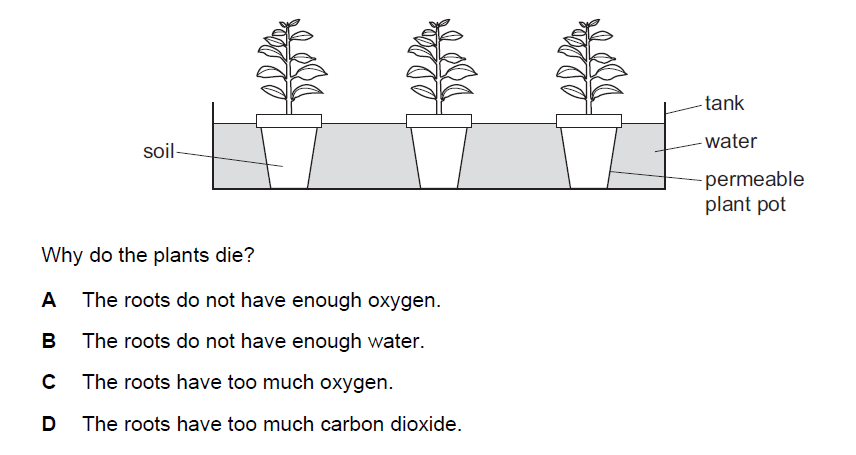
▶️Answer/Explanation
A
Plants require a certain amount of oxygen to survive, and their roots play a crucial role in obtaining oxygen from the surrounding environment. When permeable plant potted plants are left in water tank for an extended period several factors contribute to the lack of oxygen supply to the roots, leading to their death.
Plants need access to atmospheric oxygen for respiration. When the permeable pots are submerged in water continuously, they are deprived of contact with air. The water restricts the exchange of gases, preventing the roots from taking in sufficient oxygen. Also, Oxygen enters the root system primarily through tiny air spaces in the soil or growing medium. These air spaces provide a pathway for oxygen to reach the root cells. However, when the medium is consistently saturated with water, these air spaces become filled with water, impeding oxygen diffusion. As a result, the roots receive inadequate oxygen supply and plant leads to death.
Question
The diagrams show cross-sections through four roots.
Which root is best adapted for absorbing water from the soil?
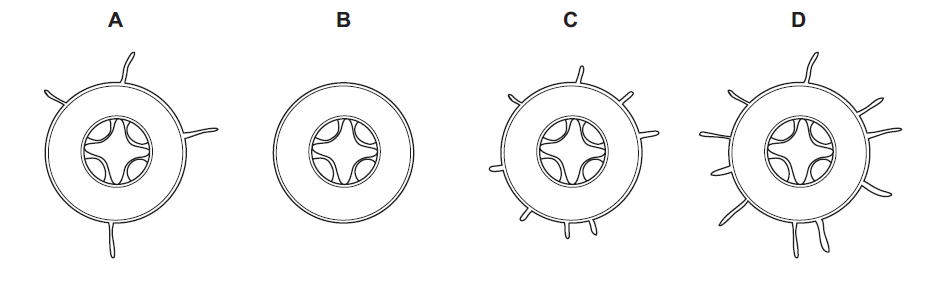
▶️Answer/Explanation
C
The root D, with more root hairs, is best adapted for absorbing water from the soil. Root hairs are tiny, finger-like projections that increase the surface area of the root, enhancing its ability to absorb water and nutrients from the soil. By having more root hairs, a root can significantly increase its surface area, thereby maximizing its capacity to absorb water.
It’s important to note that root hairs are primarily responsible for water absorption, while other root structures, such as the root cap, root cortex, and vascular tissues, play different roles in plant physiology. However, in the context of water absorption, a larger number of root hairs generally indicates a greater adaptation for this particular function.
Question
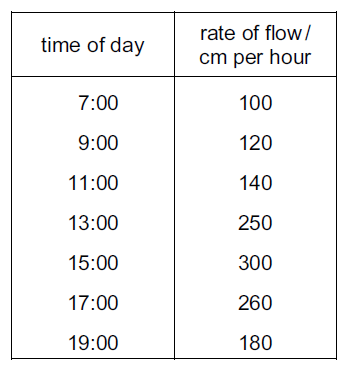
The table shows the rate of water flow through a tree over a 12 hour period.
 /
/
What conclusion can be drawn from the table?
A Between 7:00 and 17:00 hours the rate of flow continuously increases.
B The greatest increase in rate of flow in a two-hour period is between 11:00 and 13:00 hours.
C Water does not flow up through a tree at night.
D Water flow is affected by humidity.
▶️Answer/Explanation
B
The greatest increase in the rate of water flow through a tree between 11:00 and 13:00 hours is likely due to environmental factors such as sunlight and temperature.
During this time period, the sun is typically at its peak intensity, providing ample light and heat to the tree. Sunlight is essential for photosynthesis, the process by which trees convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen. As a result, photosynthesis increases, leading to an increased demand for water by the tree.
The increase in temperature during these hours enhances the transpiration process. Transpiration is the loss of water vapor from the leaves and stems of plants, and it plays a crucial role in pulling water up from the roots through the xylem vessels. As the temperature rises, the rate of transpiration also increases, creating a greater demand for water uptake by the roots.
The combination of heightened photosynthesis and increased transpiration during this two-hour period results in a higher rate of water flow through the tree. The tree’s vascular system, specifically the xylem, works to transport water from the roots to the leaves, meeting the increased demand caused by the metabolic processes occurring within the tree.
