Question
What is part of the definition of transpiration?
-
-
the loss of water vapour from plant leaves by evaporation of water at the surfaces of the mesophyll cells
-
the movement of molecules into the cells of the organism where they are used
-
the movement of particles through a cell membrane from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration
-
the transport of mineral ions from the roots into the stem and leaves
Answer/Explanation
A
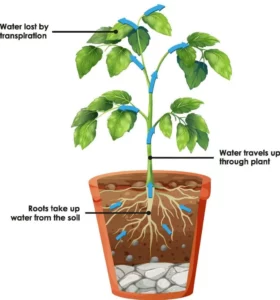
The correct definition of transpiration is: The loss of water vapor from plant leaves by evaporation of water at the surfaces of the mesophyll cells.
Transpiration specifically refers to the process by which water vapor exits the leaves of a plant through tiny openings called stomata. This process is driven by factors such as temperature, humidity, and the concentration of water vapor inside and outside the leaf. Transpiration plays a crucial role in plant physiology, as it helps in the absorption of water and nutrients from the soil, the regulation of temperature, and the transport of minerals throughout the plant.
-
Question
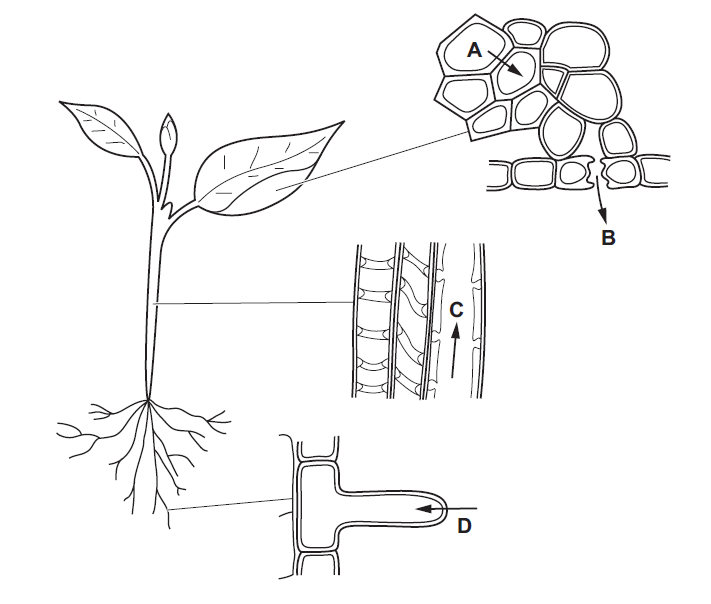
The diagrams show stages in the passage of water through a plant.
Which arrow shows water moving in the form of water vapour?
 Answer/Explanation
Answer/Explanation
B
In a plant, water moves in the form of water vapor through a process called transpiration. Transpiration occurs primarily through tiny openings called stomata, which are found on the surface of leaves, stems, and other aerial parts of the plant.
During transpiration, water is lost from the plant through the stomata in the form of water vapor. Stomata open and close to regulate the exchange of gases, including the release of water vapor. As the stomata open, water molecules on the surface of the cells within the leaves evaporate into the surrounding air spaces. These water molecules then diffuse out of the stomata and into the atmosphere.
Water vapor moves from areas of higher concentration (inside the leaf) to areas of lower concentration (the surrounding air), driven by the difference in water vapor pressure. This movement is referred to as water vapor diffusion. As water vapor is lost from the plant, more water is drawn up through the xylem, a system of specialized tissues in the plant responsible for transporting water and nutrients from the roots to the rest of the plant.
The process of transpiration helps in the transport of water and nutrients from the roots to the upper parts of the plant. It also plays a role in regulating temperature and maintaining the plant’s structure.
Question
By which process does oxygen pass out of a leaf?
A diffusion
B osmosis
C translocation
D transpiration
▶️Answer/Explanation
D
Transpiration is the process by which water vapor is lost from the surfaces of plant leaves, stems, and other aerial parts. During transpiration, water evaporates from the cells of the leaf and exits through small openings called stomata, which are mainly located on the underside of the leaf. While water vapor is being released, oxygen also diffuses out of the leaf through the stomata into the surrounding atmosphere.
Question
The diagram shows a plant shoot and the same shoot six hours later.
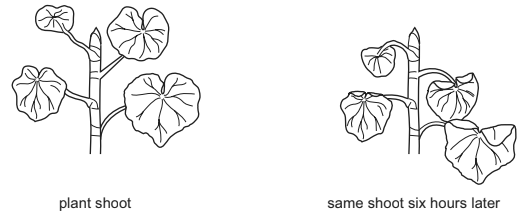
Which change in environmental conditions could cause this change in the shoot?
A a decrease in available water
B a decrease in light intensity
C a decrease in wind speed
D an increase in humidity
 Answer/Explanation
Answer/Explanation
A
Among the options provided, the most likely factor that could lead to the observed change in the shoot within a relatively short time frame is a decrease in available water, which corresponds to option A.
Plants require an adequate water supply to carry out essential physiological processes, including photosynthesis and maintaining turgidity in their cells. Water is a crucial component for various metabolic reactions and helps transport nutrients and minerals throughout the plant. When there is a decrease in available water, plants may experience water stress, which can lead to visible changes such as wilting, drooping leaves, and a decrease in overall plant vigor as shown in the diagram.
Therefore, option A, a decrease in available water, explain the observed changes in the plant shoot within the given time frame.
