Question
Mammals have a double circulation system.
(a) Explain what is meant by a double circulation system.
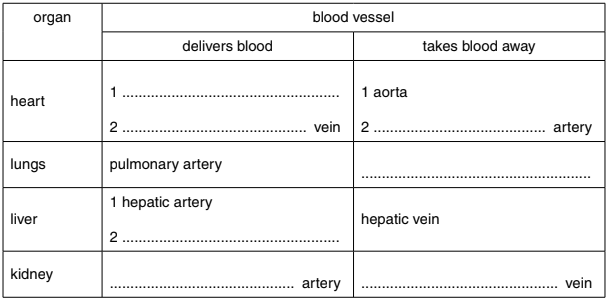
(b) Table 5.1 shows some of the main organs in a mammal and the vessels that deliver blood and take it away.
Complete the table.
Table 5.1
(c) Table 5.2 shows the blood pressure in the different blood vessels that supply and drain a muscle in the leg.
Table 5.2
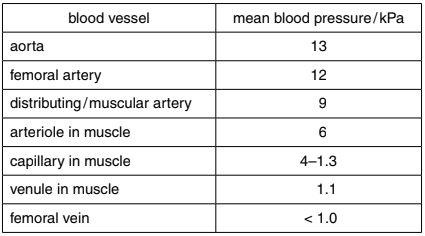
(i) The table shows that the mean blood pressure decreases from 13 kPa in the aorta to 6 kPa in the arterioles.
Explain why blood pressure must decrease in the arterioles before entering the capillaries.
(ii) Explain how blood returns to the heart in the femoral vein against the pull of gravity.
(d) Fig. 5.1 shows a section across part of an artery.
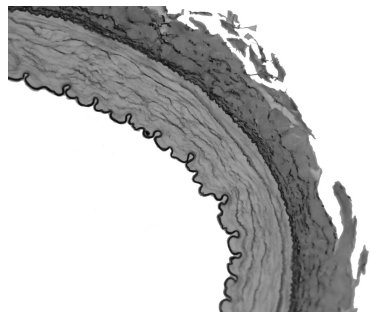
Fig. 5.1
With reference to Fig. 5.1, explain how the structure of an artery is related to its function.
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a) idea that
blood travels through the heart twice during one complete circuit (of the body) ;
or
pulmonary circulation / to the lungs and systemic circulation / described ;
(b) 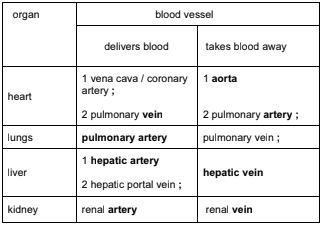
(c) (i) high pressure would, burst/ damage, capillaries /AW ;
capillaries / capillary walls, are, thin/ fragile/weak / delicate/ narrow ;
wall/ lining, (of capillary) is one cell thick ;
(ii) contraction of muscles (in the legs)/ movement of legs ;
pushing/ squeezing, blood ;
(semi-lunar) valves, ensure blood flows towards heart/ prevents backflow ;
negative pressure in the, chest/thorax /right atrium/ atria/ heart ;
idea of residual pressure from the heart ;
(d) thick wall ;
withstands /AW, (blood) pressure ;
muscular (tissue) ;
(vaso)constriction/(vaso)dilation/resisting rupture/withstands pressure ;
elastic (tissue) ;
stretches to allow blood surge/AW or recoils to maintain (blood)
pressure/ smooths out blood flow ;
folded / crinkly, endothelium/ lining ;
allows artery to stretch/ allow larger volume of blood to flow/AW ;
small lumen ;
maintains (blood) pressure ;
fibrous (tissue) ;
maintains shape/ prevents bursting ;
Question
An investigation was carried out into the blood flow in different parts of the body when resting and
during mild exercise.
Fig. 5.1 shows the results for the skeletal muscles, the skin and the alimentary canal.
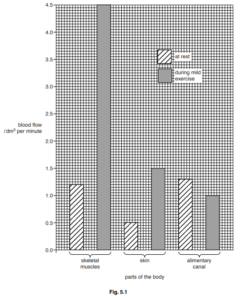
(a) (i) Use Fig. 5.1 to state the blood flow to the skeletal muscles when at rest.
…………………………… dm3 per minute [1]
(ii) Use Fig. 5.1 to state the difference in blood flow to the skeletal muscles between rest and
during mild exercise.
Show your working.
…………………………… dm3 per minute [2]
(b) Suggest why increased blood flow to the skeletal muscles is necessary during mild exercise. [3]
(c) At rest, the blood flow to the skin is 0.5 dm3 per minute. During mild exercise this increases to
1.5 dm3 per minute.
(i) Calculate the percentage increase in blood flow to the skin during mild exercise.
Show your working.
……………………………………………….% [2]
(ii) Outline the reason for this increased blood flow to the skin. [3]
(d) Suggest why the blood flow to the alimentary canal decreases during mild exercise. [1]
(e) The blood flow to the brain stays the same during rest and exercise.
Suggest two reasons for this unchanged blood flow. [2]
[Total: 14]
Answer/Explanation
Ans
5 (a) (i) 1.2(dm3 per min);
(ii) (ecf)
3.3(dm3 per min);;
(b) muscles contract;
need more energy;
muscles respire more;
need more oxygen;
need more glucose;
produce more carbon dioxide;
ref to oxygen/ glucose/ carbon dioxide carried by blood;
(c) (i) (1.5 – 0.5 = 1.0)
1.0 / 0.5 × 100
= 200 (%);;
(ii) heat/energy release;
from respiration;
heat carried by blood;
heat lost from skin surface/AW;
by sweat;
evaporation of;
more sweat required/ref to liquid coming from blood;
ref to homeostasis;
AVP;
(d) blood needed in the muscles / at skin surface/AW;
digestion not immediately essential/AW;
AVP;
(e) brain (cell) function has to be constant/ cells cannot reduce their
energy requirement / AW;
brain cells do not require extra energy during exercise / AW;
AVP;
