Question
Which statement about members of a homologous series is correct?
A They are elements with the same chemical properties.
B They are compounds with the same functional group.
C They are atoms with the same number of outer electrons.
D They are molecules with the same boiling point.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:B
A homologous series refers to a group of organic compounds that have the same general formula and similar chemical properties because they share the same functional group.
Question
The structure of an organic molecule is shown.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
It has -OH (alcohol), C=C(alkene) and -COOH(carboxylic acid) functional groups.
Question
Which compounds belong to the same homologous series?
A ethane and propane
B ethanoic acid and ethanol
C methane and ethene
D propene and ethanoic acid
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
The homologous series of alkanes all have the same functional group (-CH3) and follow the general formula CnH2n+2. As you move from one member to the next in the series, the number of carbon atoms (n) increases by one, and the number of hydrogen atoms (2n+2) also increases accordingly.
Ethane is C2H6 and propane is C3H8 .
Question
Part of the structure of a very large molecule is shown.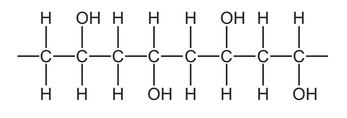
Which term describes the small unit used to make this molecule?
A hydrocarbon
B monomer
C polymer
D saturated
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
The small unit used to make a molecule in the context of organic chemistry is called a “monomer.” A monomer is a single molecule that can join with other monomers through chemical reactions, such as polymerization, to form a larger molecule known as a “polymer.”Here, -CH2-CHOH- is the monomer unit.
Question
Which type of compound is a member of a homologous series?
A carbonate
B carboxylic acid
C halogen
D hydroxide
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Carboxylic acids are a member of a homologous series. Carboxylic acids have the general molecular formula of RCOOH, where R represents an alkyl or aryl group. The functional group in a carboxylic acid is the carboxyl group (-COOH).