Question
A sequence of changes involving sulfur is shown.
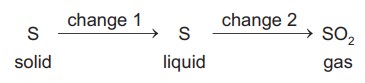
Which row describes the changes?
▶️Answer/Explanation
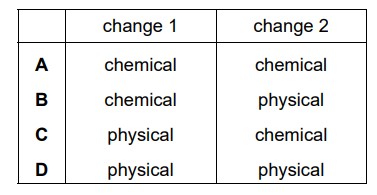
Ans:
C
The change from solid sulfur to liquid sulfur is a physical change, specifically a change of state or phase change.
The change from liquid sulfur to sulfur dioxide gas (SO2) is a chemical change. During this process, the chemical composition of the substance changes as sulfur undergoes a chemical reaction to form sulfur dioxide.
Question
Which process involves a physical change?
A heating calcium carbonate
B burning wood
C melting an ice cube
D mixing an acid and a base
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
The melting of an ice cube represents a physical change, specifically a phase change, as it involves the transformation of a solid (ice) into a liquid (water) without any alteration in chemical composition.
Question
Which diagram represents a chemical change?

▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:D
D represents a chemical change due to the alteration in chemical composition and the formation of a new substance.
Question
When sulfur is heated it undergoes a ……1…… change as it melts.
Further heating causes the sulfur to undergo a ……2…… change and form sulfur dioxide.
Which words complete gaps 1 and 2?
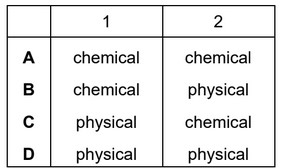
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
The change from solid sulfur to liquid sulfur is a physical change, specifically a change of state or phase change.
The change from liquid sulfur to sulfur dioxide gas (SO2) is a chemical change. During this process, the chemical composition of the substance changes as sulfur undergoes a chemical reaction to form sulfur dioxide.
Question
When zinc carbonate is mixed with dilute hydrochloric acid a change, M, takes place.
When carbon is heated with copper(II) oxide a change, N, takes place.
Which row describes changes M and N?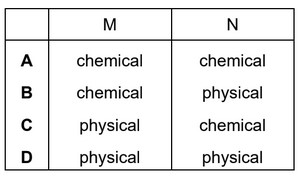
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
When zinc carbonate is mixed with dilute hydrochloric acid, a chemical change occurs, resulting in the formation of new substances, including water, carbon dioxide, and zinc chloride.
When carbon is heated with copper(II) oxide, a chemical change occurs, resulting in the formation of new substances, including copper and carbon dioxide.