Question
Magnesium is added to dilute hydrochloric acid. 25 \(cm^{3}\) of gas is given off in the first 30 s of the reaction. The experiment is repeated at a lower temperature. All other reaction conditions are the same. Which volume of gas is produced in the first 30 s of this reaction?
A. 15 \(cm^{3}\) B. 25 \(cm^{3}\) C. 30 \(cm^{3}\) D. 50 \(cm^{3}\)
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
A
When temperature is reduced, rate of reaction also gets reduced. Thus, for same time interval of 30 seconds, less than 25 \(cm^{3}\) of gas will be produced.
Question
The rate of reaction between magnesium and hydrochloric acid is investigated. The volume of hydrogen given off at different times is measured. The results are shown.

Which conclusions are correct?
1 The rate is fastest between 0 and 20 seconds.
2 The maximum volume of hydrogen given off is $22 \mathrm{~cm}^3$.
3 At 40 seconds, $20 \mathrm{~cm}^3$ of hydrogen is given off.
A 1 and 2 only
B 1 and 3 only
C 2 and 3 only
D 1,2 and 3
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:A
Slope of the curve is constant and maximum upto t=30 sec, after which, it decreases. Hence, the rate is fastest between 0 and 20 seconds.
At y axis, the volume of hydrogen becomes constant at the peak value of $22 \mathrm{~cm}^3$. Hence, it is the maximum volume of hydrogen given off.
From the graph, At 40 seconds, $19 \mathrm{~cm}^3$ of hydrogen is given off.
Question
Zinc reacts with an acid to form a gas. The volume of gas produced is measured at intervals. The results are shown as curve Z.
The reaction is repeated in the presence of a catalyst.
Which curve shows the results for the catalysed reaction?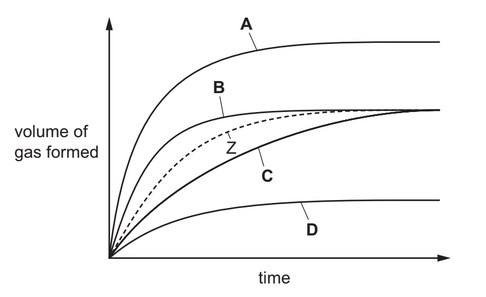
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
A catalyst only increases the rate of reaction and has no affect on final volume of product formed.
Curve B has more slope than curve Z and final volume of gas formed is also same as Z.
Question
Solid copper(II) carbonate reacts with dilute sulfuric acid.
\(CuCO_3 + H_2SO_4 → CuSO_4 + CO_2 + H_2O\)
The rate of the reaction can be changed by varying the conditions.
Which changes always increase the rate of this chemical reaction?
1 increasing the concentration of sulfuric acid
2 increasing the size of the pieces of copper(II) carbonate
3 increasing the temperature
4 increasing the volume of sulfuric acid
A 1, 3 and 4 B 1 and 3 only C 2 and 3 D 3 and 4 only
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Increasing the concentration of the acid provides more reactant particles per unit volume, leading to more frequent collisions and an increased reaction rate.
Raising the temperature of the reaction increases the kinetic energy of the particles, resulting in more frequent collisions and a higher reaction rate due to an increased number of successful collisions.
Breaking the solid into smaller pieces or using a powdered form increases the surface area exposed to the acid. This allows for more acid molecules to come into contact with the solid, resulting in an increased rate of reaction.
Question
Marble chips (calcium carbonate) react with hydrochloric acid in an exothermic reaction.
calcium carbonate + hydrochloric acid → calcium chloride + water + carbon dioxide
When excess marble chips are added to dilute hydrochloric acid the rate of the reaction starts off
fast, then gets slower until the reaction stops.
Why does the reaction rate get slower?
A The concentration of the hydrochloric acid is decreasing.
B The concentration of calcium chloride is increasing.
C The calcium carbonate is completely used up.
D The temperature of the mixture decreases.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
As the reaction progresses, the concentration of hydrochloric acid decreases because it is being consumed in the reaction. The concentration of the reactants affects the rate of reaction according to the rate equation. With a decrease in reactant concentration, the frequency of collisions between acid particles and the marble chips decreases, resulting in a slower rate of reaction.