Question
Which reaction can be easily reversed?
A dissolving zinc in hydrochloric acid
B fermenting glucose with yeast
C heating hydrated cobalt(II) chloride
D the rusting of an iron nail
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
When the hydrated cobalt(II) chloride is heated, it undergoes a process called dehydration, where the water molecules are removed, leaving behind the anhydrous cobalt(II) chloride. This reaction can be reversed by adding water back to the anhydrous cobalt(II) chloride, resulting in the reformation of the hydrated cobalt(II) chloride.
The dehydration and rehydration processes are reversible because they involve only physical changes and do not involve any chemical reactions. The addition or removal of water molecules does not alter the chemical composition of cobalt(II) chloride.
Question
The diagram shows the change from an anhydrous salt to its hydrated form.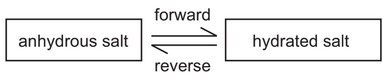
Which statement is correct?
A The forward reaction requires heat and water.
B The forward reaction requires water only.
C The reverse reaction requires heat and water.
D The reverse reaction requires water only.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
The forward reaction requires water only as it is a hydration reaction.
The reverse reaction requires heat only as it is a dehydration reaction.
Question
When blue-green crystals of nickel(II) sulfate are heated, water is produced and a yellow solid remains. When water is added to the yellow solid, the blue-green colour returns. Which process describes these changes?
A. combustion
B. corrosion
C. neutralisation
D. reversible reaction
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
D
The dehydration and rehydration processes are reversible because they involve only physical changes and do not involve any chemical reactions. The addition or removal of water molecules does not alter the chemical composition of nickel(II) sulfate.
Question
Which reaction is reversible?
- Cu + ZnSO4 → CuSO4 + Zn
- CuO + H2SO4 → CuSO4 + H2O
- CuO + H2 → Cu + H2O
- CuSO4•5H2O → CuSO4 + 5H2O
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
D
The dehydration and rehydration processes are reversible because they involve only physical changes and do not involve any chemical reactions. The addition or removal of water molecules does not alter the chemical composition of copper sulfate.
Question
Which reaction is reversible?
A $\mathrm{CuCO}_3+2 \mathrm{HCl} \rightarrow \mathrm{CuCl}_2+\mathrm{CO}_2+\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}$
B $\mathrm{CuSO}_4 .5 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O} \rightarrow \mathrm{CuSO}_4+5 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}$
C $2 \mathrm{Na}+2 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O} \rightarrow 2 \mathrm{NaOH}+\mathrm{H}_2$
D $\mathrm{NaOH}+\mathrm{HCl} \rightarrow \mathrm{NaCl}+\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}$
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:B
The dehydration and rehydration processes are reversible because they involve only physical changes and do not involve any chemical reactions. The addition or removal of water molecules does not alter the chemical composition of copper sulfate.