Question
Compound X is dissolved in water and two separate samples of the solution are tested. The results of the tests are shown.
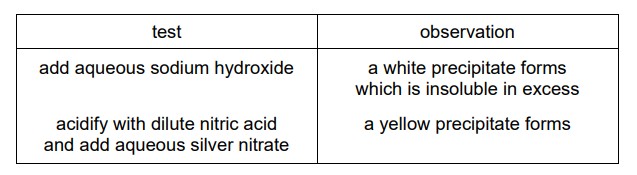
What is compound X?
A. calcium chloride
B. calcium iodide
C. zinc chloride
D. zinc iodide
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
B
Calcium hydroxide is sparingly soluble in water and tends to form a white solid precipitate. The reaction between calcium iodide and sodium hydroxide results in the formation of this white precipitate. The formation of a white precipitate confirms the presence of calcium ions in the reaction mixture. This precipitation reaction is often used as a qualitative test for the presence of calcium ions.
Calcium iodide reacts with nitric acid to form calcium nitrate and hydrogen iodide (HI) as a byproduct. Then, when silver nitrate is added, it reacts with hydrogen iodide to form silver iodide (AgI) and nitric acid. The yellow precipitate observed is the silver iodide.
Silver iodide is sparingly soluble in water and has a characteristic yellow color, which gives rise to the yellow precipitate. This reaction is often used as a test for the presence of iodide ions in a solution, as the formation of the yellow precipitate confirms the presence of iodide ions.
Question
A student carries out an experiment to prepare pure magnesium sulfate crystals.
The diagram shows the first stage of the preparation.

He adds magnesium carbonate until no more reacts.
Which process should he use for the next stage?
A crystallisation
B evaporation
C filtration
D neutralisation
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:B
In the next stage after adding magnesium carbonate until no more reacts is evaporation, then the student should perform the process of evaporation for further preparation of pure magnesium sulfate crystals. As the solution is heated, the acid content will gradually evaporate, leaving behind more concentrated magnesium sulfate solution. Continue heating and evaporating until a desired concentration is achieved.
Question
When pink crystals of cobalt(II) chloride are heated, steam is given off and the colour of the solid changes to blue.
$
\mathrm{CoCl}_2 \cdot 6 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O} \rightleftharpoons \mathrm{CoCl}_2+6 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}
$
What happens when water is added to the blue solid?

▶️Answer/Explanation
AnsB
The resulting solution is pink in color. This is due to the formation of cobalt(II) chloride ions in the aqueous solution. The pink color indicates the presence of the hydrated cobalt(II) chloride species.
The dissolution of some salts, including cobalt(II) chloride, is an exothermic process, meaning it releases heat energy. In such cases, the dissolution can lead to a slight increase in temperature.
Question
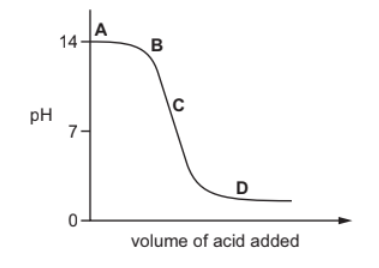
The graph shows how the $\mathrm{pH}$ of a solution changes as an acid is added to an alkali.
$
\text { acid }+ \text { alkali } \rightarrow \text { salt }+ \text { water }
$
Which letter represents the area of the graph where both acid and salt are present?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:D
D occurs after neutralization. At D, pH is well below 7. Here, both acid and salt are present.
Question
P is a hydrated metal salt with a blue colour. When P is heated, water is given off, leaving solid Q.
R is a hydrated metal salt with a pink colour. When R is heated, water is given off, leaving solid S.
Which row gives the name of P and the colour of S?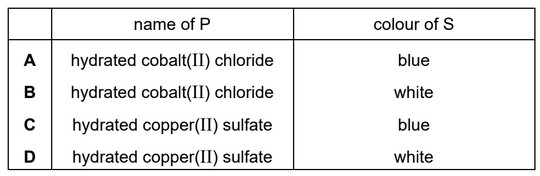
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
When hydrated copper sulfate is heated, water molecules are driven off, resulting in the formation of anhydrous copper sulfate as a solid residue. This process is known as dehydration.
Cobalt(II) chloride hexahydrate is a pink-colored compound due to the presence of water molecules within its crystal lattice. When heated, the water molecules are released, resulting in the formation of an anhydrous form of cobalt(II) chloride, which appears as a blue residue.