Question
This question is about halogens and halogen compounds.
(a) Deduce the number of electrons, neutrons and protons in one atom of the isotope of chlorine shown.[3]
\(_{17}^{37}\textrm{Cl }\)
number of electrons
number of neutrons
number of protons
(b) State why chlorine is used in water treatment.[1]
(c) Aqueous chlorine reacts with aqueous potassium iodide.
(i) Complete the chemical equation for this reaction. [2]
Cl2 + …..KI → …..KCl + I2
(ii) Explain in terms of the reactivity of the halogens why aqueous iodine does not react with aqueous potassium chloride.[1]
(d) The table shows some properties of four halogens.

(i) Complete the table by predicting:
-
- the boiling point of fluorine
- the density of liquid chlorine at its boiling point. [2]
(ii) Predict the physical state of chlorine at –105°C.
Give a reason for your answer.[2] [Total: 11]
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a) electrons: 17 (1)
neutrons: 20 (1)
protons: 17 (1)
(b) to kill bacteria (1)
(c)(i) 2 (KI) (1)
2 (KCl) (1)
(c)(ii) chlorine is more reactive than iodine / iodine is less reactive than chlorine
(d)(i) boiling point of fluorine:
values between – 40 and – 210 (inclusive of these values) (1)
density of chlorine:
values between 1.6 and 3.0 (inclusive of these values) (1)
(d)(ii) solid (1)
–105 °C is lower than the melting point / the melting point is above –105 °C (1)
Question
This question is about water.
(a) The water in rivers often contains pollutants such as acids.
Describe how universal indicator paper can be used to determine the pH value of the water.
(b) The diagram shows some of the stages in water treatment.
(i) Air is blown through the aeration tank.
Name the two gases that make up most of the air.
………………………………………………………. and ………………………………………………………
(ii) After aeration, the water still contains large insoluble particles.
The filter is made up of fine sand and stones.
Explain how the filter helps purify the water.
(iii) Explain why chlorine is used in water treatment.
(c) Anhydrous cobalt(II) chloride is used to test for water.
State the colour change in this test.
from ………………………………………………………. to ……………………………………………………….
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a) dip indicator paper in to water (and record the colour) (1)
compare the colour with (universal indicator) colour chart
match colour with colour chart (1)
(b) (i) nitrogen (1)
oxygen (1)
(ii)
large(r) particles cannot get through (the small gaps in) the filter / large(r) particles get trapped in the filter / large(r) particles
too big to get through (filter) (1)
water passes through (1)
(iii) to kill bacteria / to kill micro-organisms
(c) (from) blue (1)
(to) pink (1)
Question
Water is essential for many industrial processes.
(a) State one use of water in industry.
(b) What is the pH of pure water?
Draw a circle around the correct answer.
pH 0 pH 6 pH 7 pH 14
(c) Filtration and chlorination are two of the steps used in water treatment.
Describe the purpose of each of these steps.
filtration ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
chlorination ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
(d) The changes of state of water are shown.
Give the names of the changes of state represented by A and B.
A ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
B ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(e) The table compares the reactions of four metals with both steam and dilute hydrochloric acid.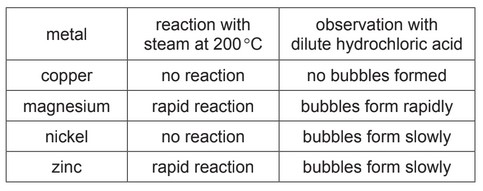
Put the four metals in order of their reactivity.
Put the least reactive metal first.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a) coolant / cooling / solvent / for dissolving
(b) pH 7
(c) filtration: to remove solids / to remove insoluble materials / to separate solids from liquids (1)
chlorination: to kill bacteria / to disinfect (the water) / to kill (harmful) microorganisms (1)
(d) A: melting / fusion (1)
B: condensing / condensation (1)
(e) copper <nickel <zinc <magnesium (2)
if two marks not scored one mark for one consecutive pair reversed / all reversed