Question
(a) Sulfur dioxide is a pollutant in the air.
(i) State one source of sulfur dioxide in the air………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. [1]
(ii) Sulfur dioxide is oxidised to sulfur trioxide in the air.
Oxides of nitrogen act as catalysts for this reaction.
What is meant by the term catalyst?…………………………………………… [1]
(iii) Sulfur trioxide dissolves in rainwater to form acid rain.
Which one of the following pH values could be the pH of acid rain?
Draw a circle around the correct answer.[1]
pH 4 pH 7 pH 9 pH 13
(iv) State one adverse effect of acid rain on buildings.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… [1]
(b) Sulfur dioxide melts at –73 °C and boils at –10 °C.
What is the physical state of sulfur dioxide at –20 °C?
Explain your answer…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. [2]
(c) Excess sulfuric acid reacts with ammonia to make a salt which can be used as a fertiliser.
State the name of the salt formed when excess sulfuric acid reacts with ammonia…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. [1]
(d) The table shows some observations about the reactivity of four metals with dilute sulfuric acid.

Use the information in the table to put the four metals in order of their reactivity. Put the least reactive metal first.

▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a)(i) burning fossil fuels / volcanoes / heating (sulfide) ores
(a)(ii) substance which speeds up a reaction / substance which increases the rate of reaction
(a)(iii) pH4
(a)(iv) erodes buildings (made of carbonate rocks) / wears away buildings (made of carbonate rocks) / reacts with mortar / corrodes iron
work / corrodes metal
(b) liquid (1)
–20 °C is between the melting and boiling point / –20 °C is above melting point but lower than boiling point (1)
(c) ammonium sulfate
(d) tungsten < nickel < iron < magnesium (2)
if 2 marks not scored 1 mark for one consecutive pair reversed
Question
The table shows the masses of some of the ions in 1000\(cm^3\) of fruit juice.
(a) Answer these questions using only the information in the table.
(i) State which negative ion has the highest mass in 1000\(cm^3\) of fruit juice.
(ii) Give the formulae of the ions in ammonium sulfate.
………………………………………………………. and ………………………………………………………
(iii) Calculate the mass of sodium ions in 200\(cm^3\) of fruit juice.
mass = ………………………… mg
(b) Describe a test for lithium ions.
test ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
observations ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(c) Ions of the element potassium, K, are present in most fertilisers.
State the names of two other elements that are in most fertilisers.
1 ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
2 ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(d) Orange juice is acidic.
Draw a circle around the pH of orange juice.
pH 4 pH 7 pH 10 pH 13
(e) Some soils are acidic.
Give the names of two compounds that are used to make soils less acidic.
1 ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
2 ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(f) Hydrogen chloride is an acidic gas produced when concentrated hydrochloric acid evaporates.
(i) Describe the arrangement and separation of the molecules in hydrogen chloride gas.
arrangement ………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
separation ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(ii) A long glass tube is set up as shown.
At first, the blue litmus paper does not turn red.
After a short time, the litmus paper turns red.
Explain these observations using the kinetic particle model.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a)(i) Cl – / chloride
(ii) \(NH_4^+ AND SO_4^{2-}\)
(iii) 24 (mg)
(b) flame test / description of flame test (1)
(flame coloured) red (1)
(c) nitrogen (1)
phosphorus (1)
pH 4 circled
(e) 1 mark each for any 2 of :
- calcium carbonate
- calcium oxide
- calcium hydroxide
(f)(i) arrangement: random (arrangement)/ no fixed arrangement / no pattern / no fixed position (1)
separation: far apart / far away (from each other) / distant (from each other) (1)
(ii) 1 mark each for any 3 of :
- (HCl) molecules escape form solution
- diffusion
- molecules in (constant) movement / molecules collide/ molecules travel
- (movement of) molecules is random/ haphazard/ in every direction
- molecules spread out/ molecules mix
- (molecules spread) from high (er) concentration to low(er) concentration
- molecules hit the litmus paper/ molecules
Question
Aqueous ammonia is an alkali.
(a) Complete the dot-and-cross diagram to show the electron arrangement in a molecule of ammonia.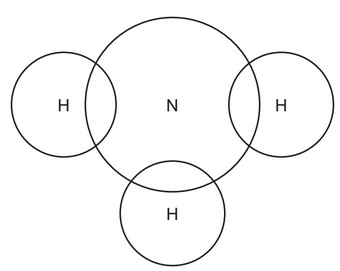
Complete the word equation for the reaction of aqueous ammonia with dilute hydrochloric acid.
(c) Describe the colour change when excess aqueous ammonia is added to an acidified solution of methyl orange.
from ………………………………………………………. to ……………………………………………………….
(d) Aqueous ammonia reacts with aqueous copper(II) ions to produce compound B.
The formula of compound B is \(CuN_4H_{16}O_2\).
Complete the table to calculate the relative molecular mass of compound B.
relative molecular mass = …………………………
(e) Ammonia is used in the production of fertilisers.
State why farmers put fertilisers on the soil where crops are to be grown.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a) bonding pair of electrons between each H and N AND no other electrons on H (1)
2 non-bonded electrons on N (1)
(b) ammonium chloride (1)
(c) red / pink to yellow (1)
(d) 168 (2 marks)
if 2 marks not scored, 1 mark for :
(16 × 1) = 16 OR (2 × 16) = 32 (on the appropriate line)
(e) makes plants grow faster / increases yield