Question
The table shows the structures of some organic compounds.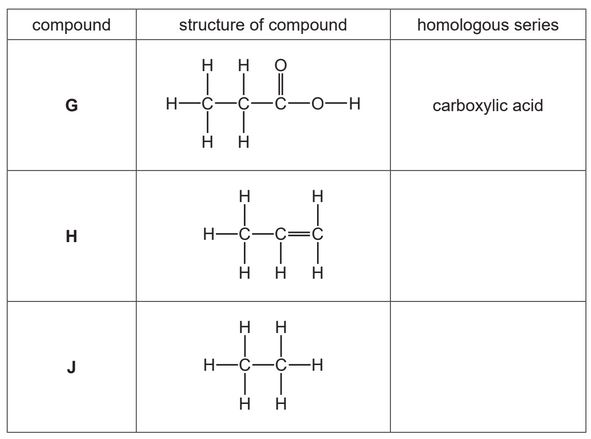
(a) Complete the table by naming the homologous series.
The first one has been done for you.
(b) Draw the structure of a compound containing two carbon atoms which belongs to the same homologous series as compound H.
Show all of the atoms and all of the bonds.
(c) State which compound in the table is an unsaturated hydrocarbon.
Explain your answer.
(d) State which compound in the table reacts with aqueous sodium hydroxide.
Explain your answer.
(e) State the names of the two compounds formed during the complete combustion of compound J.
…………………………………………………………. and ………………………………………………………….
(f) Compound H can be polymerised.
(i) State the general name given to the small units which join together to form a polymer.
(ii) Terylene is also a polymer.
Give one use of Terylene.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a) H: alkene (1)
J: alkane (1)
(b) ![]()
(c) H AND has a C=C double bond
(d) G AND acids react with alkalis / G AND acids react with bases / carboxylic acids react with alkalis / carboxylic acids react
with bases (1)
(e) carbon dioxide (1)
water (1)
(f) (i) monomer(s)
(ii) clothing
Question
Angelic acid and ethanoic acid are both carboxylic acids.
The structure of angelic acid is shown.
(a) (i) On the structure of angelic acid, draw a circle around the functional group that shows that it is a carboxylic acid.
(ii) Deduce the formula of angelic acid to show the number of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen atoms.
(iii) Angelic acid is an unsaturated compound.
Describe a chemical test to distinguish between an unsaturated and a saturated compound.
test ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
result with unsaturated compound …………………………………………………………………………..
result with saturated compound ………………………………………………………………………………
(b) The formula of ethanoic acid is \(C_2H_4O_2\).
Complete the table to calculate the relative molecular mass of ethanoic acid.
Use the Periodic Table to help you.
relative molecular mass = …………………………
(c) Ethanoic acid can be reduced to ethanol.
Complete the structure of ethanol to show all of the atoms and all of the bonds.
(d) Ethanol can be manufactured by fermentation.
Describe the process of fermentation to include:
● the names of the reactants and catalyst
● the conditions required
● the name of the process used to separate the ethanol from the rest of the reaction mixture.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a) (i) circle round COOH group
(ii) \(C_5H_8O_2\)
(iii) aqueous bromine / bromine water / bromine (1)
unsaturated: decolourises / goes colourless / loses its colour (1)
saturated: remains red-brown / remains brown / remains orange / no change (in colour) (1)
(b) 60 (2)
if two marks not scored, one mark for (4 × 1) = 4 OR (2 ×16) = 32
(c) 
(d) 1 mark each for any two of:
• glucose / sugar
• in aqueous solution / in water
• yeast / enzymes / zymase
1 mark each for any two of:
• no oxygen / no air / anaerobic
• pH neutral
• room temperature / stated temperature between 5°C and 40°C (inclusive)
1 mark for:
• (fractional) distillation
Question
The structure of myrcene is shown.

(a) Deduce the formula of myrcene to show the number of atoms of carbon and hydrogen. ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. [1]
(b) Myrcene is found in some plants.
The coloured compounds in plant leaves can be separated by chromatography.
Complete the diagram by putting the correct labels in the boxes.

(c) Myrcene is an unsaturated hydrocarbon.
Describe a chemical test to distinguish between a saturated and an unsaturated hydrocarbon.
test ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
observations with saturated hydrocarbon ……………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
observations with unsaturated hydrocarbon…………………[3]
(d) Butane is a saturated hydrocarbon.
To which homologous series does butane belong?
Draw a circle around the correct answer.
alcohol alkane alkene carboxylic acid [1]
(e) Large hydrocarbons can be cracked to form smaller hydrocarbons.
Complete the chemical equation for cracking tridecane, $\mathrm{C}_{13} \mathrm{H}_{28}$, to form an alkene and one other hydrocarbon.
$
\mathrm{C}_{13} \mathrm{H}_{28} \rightarrow \mathrm{C}_3 \mathrm{H}_6+\ldots \ldots \ldots \ldots
$
(f) Ethene is an alkene.
Draw the structure of ethene showing all of the atoms and all of the bonds. [1]
(g) Complete the sentences about the separation of hydrocarbons from petroleum using words from the list.
bitumen combustion condense crystallisation distillation
evaporate gasoline kerosene melt
Hydrocarbons are separated in a fractionating column by fractional ……………………… .
Hydrocarbons with lower boiling points move further up the column. When the temperature
in the column falls below the boiling points of the hydrocarbons they ……………………… . The
fraction at the bottom of the column which is used for making roads is called ……………………… . [3] [Total: 12]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a) $\mathrm{C}_{10} \mathrm{H}_{16}$
(b) top box: chromatography paper / filter paper
bottom box: solvent / named solvent e.g. alcohol
(c) bromine / bromine water / aqueous bromine
with saturated hydrocarbon: no colour change / stays orange
with unsaturated hydrocarbon: decolourised / (goes) colourless
(d) alkane
(e) $\mathrm{C}_{10} \mathrm{H}_{22}$
(f)

g) distillation
condense
bitumen