Question
Limonene is a volatile liquid which smells of oranges.
(a) A teacher placed a beaker of limonene at the front of a classroom.
At first, the students at the back of the classroom could not smell the limonene.
After two minutes, the smell of limonene had spread throughout the classroom.
The air in the classroom was still and calm.
(i) Explain these observations using the kinetic particle model. [3]
(ii) The melting point of limonene is –74°C.
The boiling point of limonene is 176°C.
What is the physical state of limonene at –80°C?
Explain your answer.[2]
(b) An enzyme present in peppermint plants is a catalyst for the oxidation of limonene.
State what is meant by the terms:
(i) catalyst [1]
(ii) oxidation [1]
(c) Limonene can be made from a colourless compound called α-terpineol.
The structure of α-terpineol is shown.
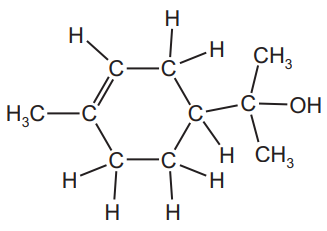
(i) What feature of the structure of the α-terpineol molecule shows that it is an unsaturated compound?[1]
(ii) Describe how the colour of aqueous bromine changes when an excess of α-terpineol is added to it.
from ___ to ___ [2] [Total: 10]
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a)(i) One mark each for any 3 of:
- (limonene) particles go from liquid to vapour
- diffusion
- random movement of particles / particles move anywhere / particles move in all directions
- spreading out of particles / intermingling of particles / mixing of particles / particles collide / particles bounce off each other / particles go all over
- (bulk) movement of particles from higher to lower concentration / movement of particles down concentration gradient
(a)(ii) solid
- 80 ºC is below the melting point / it is below the melting point / it has not yet reached its melting point / melts above – 80 ºC
(b)(i) (substance which) speeds up a reaction / substance which increases the rate of reaction
(b)(ii) addition of oxygen (to a substance) / loss of electrons / increase in oxidation number
(c)(i) C=C bond
(c)(ii) orange / red-brown / brown
to colourless