Question
Coal gas is made by heating coal in the absence of air. The list shows the main gases present in coal gas.
carbon dioxide
carbon monoxide
ethene
hydrogen
methane
nitrogen
(a) (i) Which one of these gases is an alkane?……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… [1]
(ii) Draw the structure of a molecule of ethene. Show all of the atoms and all of the bonds.[1]
(iii) Describe how aqueous bromine can be used to tell the difference between methane andethene.……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… [2]
(b) Ethene molecules react with each other to form poly(ethene).
(i) What is the name given to this type of chemical reaction?……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… [1]
(ii) Which one of the following words describes the ethene molecules in this reaction?
Draw a circle around the correct answer.
elements mixtures monomers polymers[1]
(iii) Poly(ethene) is a non-biodegradable plastic.
What is meant by the term non-biodegradable?……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… [1]
(iv) Describe one pollution problem caused by non-biodegradable plastics.……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… [1]
(c) Ethanol can be made from ethene and one other reactant.
● Name the other reactant.………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
● State the conditions needed to make ethanol from ethene.………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….[3][Total: 11]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a)(i) methane
(a)(ii)

(a)(iii) with methane (aqueous) bromine remains orange (1)
with ethene (aqueous) bromine decolourised (1)
(b)(i) polymerisation / addition
(b)(ii) monomers
(b)(iii) cannot be decomposed by organisms / cannot be broken down by bacteria / cannot be broken down by fungi
(b)(iv) gets stuck in gullets of birds / gets stuck in gullets of animals / blocks drains
(c) steam (1)
high temperature (1)
catalyst (1)
Question
The structure of malic acid is shown.
(a) (i) On the structure draw a circle around the alcohol functional group.
(ii) Deduce the formula of malic acid to show the number of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen atoms.
(b) When malic acid is heated it forms compound F.
The structure of compound F is shown.
Explain why compound F is described as unsaturated.
(c) Compound F can form polymers.
(i) State the meaning of the term polymer.
(ii) State the name of the polymer formed when ethene is polymerised.
(d) Ethanoic acid is a carboxylic acid.
Describe the observations made when dilute ethanoic acid reacts with:
magnesium ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
litmus solution. ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(e) The graph shows how the pH changes when dilute ethanoic acid is added slowly to aqueous sodium hydroxide.
(i) Deduce the pH of the aqueous sodium hydroxide before the addition of dilute ethanoic acid.
pH = …………………………
(ii) Deduce the volume of dilute ethanoic acid added when the pH is neutral.
………………………… \(cm^3\)
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a) (i) OH alcohol group cicled
(ii) \(C_4H_{6}O_5\)
(b) it has a C = C double bond
(c) (i) large molecules / long chain molecules / macromolecules (1)
built up from (many) small units / made from monomers (1)
(ii) poly(ethene)
(d) with Mg: fizzes / bubbles / effervescence (1)
litmus: turns red / turns pink (1)
(e) (i) pH 13
(ii) 18 (\(cm^3\))
Question
The table shows the structures of some organic compounds.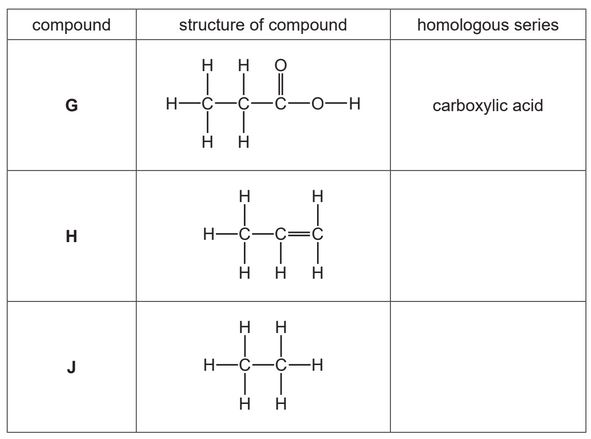
(a) Complete the table by naming the homologous series.
The first one has been done for you.
(b) Draw the structure of a compound containing two carbon atoms which belongs to the same homologous series as compound H.
Show all of the atoms and all of the bonds.
(c) State which compound in the table is an unsaturated hydrocarbon.
Explain your answer.
(d) State which compound in the table reacts with aqueous sodium hydroxide.
Explain your answer.
(e) State the names of the two compounds formed during the complete combustion of compound J.
…………………………………………………………. and ………………………………………………………….
(f) Compound H can be polymerised.
(i) State the general name given to the small units which join together to form a polymer.
(ii) Terylene is also a polymer.
Give one use of Terylene.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a) H: alkene (1)
J: alkane (1)
(b) ![]()
(c) H AND has a C=C double bond
(d) G AND acids react with alkalis / G AND acids react with bases / carboxylic acids react with alkalis / carboxylic acids react
with bases (1)
(e) carbon dioxide (1)
water (1)
(f) (i) monomer(s)
(ii) clothing