Question
The structure of myrcene is shown.

(a) Deduce the formula of myrcene to show the number of atoms of carbon and hydrogen. ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. [1]
(b) Myrcene is found in some plants.
The coloured compounds in plant leaves can be separated by chromatography.
Complete the diagram by putting the correct labels in the boxes.

(c) Myrcene is an unsaturated hydrocarbon.
Describe a chemical test to distinguish between a saturated and an unsaturated hydrocarbon.
test ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
observations with saturated hydrocarbon ……………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
observations with unsaturated hydrocarbon…………………[3]
(d) Butane is a saturated hydrocarbon.
To which homologous series does butane belong?
Draw a circle around the correct answer.
alcohol alkane alkene carboxylic acid [1]
(e) Large hydrocarbons can be cracked to form smaller hydrocarbons.
Complete the chemical equation for cracking tridecane, $\mathrm{C}_{13} \mathrm{H}_{28}$, to form an alkene and one other hydrocarbon.
$
\mathrm{C}_{13} \mathrm{H}_{28} \rightarrow \mathrm{C}_3 \mathrm{H}_6+\ldots \ldots \ldots \ldots
$
(f) Ethene is an alkene.
Draw the structure of ethene showing all of the atoms and all of the bonds. [1]
(g) Complete the sentences about the separation of hydrocarbons from petroleum using words from the list.
bitumen combustion condense crystallisation distillation
evaporate gasoline kerosene melt
Hydrocarbons are separated in a fractionating column by fractional ……………………… .
Hydrocarbons with lower boiling points move further up the column. When the temperature
in the column falls below the boiling points of the hydrocarbons they ……………………… . The
fraction at the bottom of the column which is used for making roads is called ……………………… . [3] [Total: 12]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a) $\mathrm{C}_{10} \mathrm{H}_{16}$
(b) top box: chromatography paper / filter paper
bottom box: solvent / named solvent e.g. alcohol
(c) bromine / bromine water / aqueous bromine
with saturated hydrocarbon: no colour change / stays orange
with unsaturated hydrocarbon: decolourised / (goes) colourless
(d) alkane
(e) $\mathrm{C}_{10} \mathrm{H}_{22}$
(f)

g) distillation
condense
bitumen
Question
(a) Magnesium is manufactured by the electrolysis of molten magnesium chloride.
(i) The negative electrode is made of iron.
Suggest a non-metal which could be used for the positive electrode.
Give a reason for your answer.[2]
(ii) Predict the products of the electrolysis of molten magnesium chloride at:[2]
the positive electrode
the negative electrode.
(b) The following statements are about the procedure for making crystals of hydrated magnesium chloride from magnesium and dilute hydrochloric acid.
-
- Leave the mixture until no more bubbles are seen.
- Leave the mixture at room temperature to form more crystals.
- Add an excess of magnesium to dilute hydrochloric acid.
- Warm the filtrate to the point of crystallization.
- Filter off the crystals and dry between filter papers.
- Filter off the excess magnesium.
Put the statements A, B, C, D, E and F in the correct order.
The first one has been done for you.

(c) Magnesium is a metal in Group II of the Periodic Table.
Copper is a transition element.
Copper has a higher melting point and a higher boiling point than magnesium.
Describe two other properties of copper which are different from those of magnesium.[2]
1
2
(d) Chromatography can be used to separate a mixture of ions from different transition element compounds.
Four samples, R, S, T and U, each containing transition element ions, were placed on a piece of chromatography paper.
Two solutions, Y and Z, each containing only one type of transition element ion were also placed on the same piece of chromatography paper.
The results of the chromatography are shown.

(i) Which sample, R, S, T or U, contains the same ions as both solution Y and solution Z?[1]
(ii) Which sample, R, S, T or U, does not contain the same ions as either solution Y or solution Z?[1]
(iii) In which sample, R, S, T or U, has the greatest number of transition element ions been separated?[1] [Total: 11]
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a)(i) graphite (1)
conducts electricity / inert (1)
(a)(ii) positive electrode: chlorine (1)
negative electrode: magnesium (1)
b) (C), A, F, D, B, E (2)
if 2 marks not scored 1 mark for 1 consecutive pair reversed
(c) 1 mark each for any two of:
-
- high density ORA for Mg
- forms coloured compounds ORA for Mg
- forms ions with different charges / has variable oxidation number ORA for Mg
- forms complex ions ORA for Mg
- copper is catalyst ORA for Mg
- reference to difference in chemical properties e.g. magnesium reacts with dilute acid / copper does not react with dilute acid
(d)(i) R
(d)(ii) T
(d)(iii) R
Question
The structures of some organic compounds are shown.
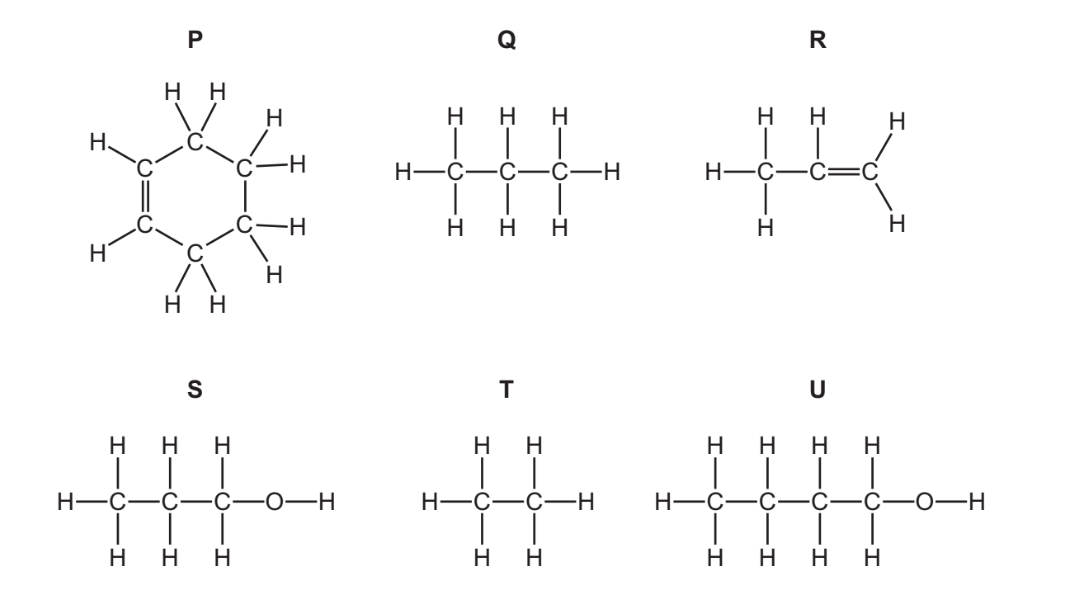
(a) (i) Which two of these compounds are alcohols?
Explain your answer.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. [2]
(ii) Which two of these compounds are saturated hydrocarbons?
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. [1]
(b) Methanol and ethanol are alcohols in the same homologous series.
Complete the following sentence about a homologous series using words from the list.
alcohols chemical compounds elements
functional mixtures physical
A homologous series is a family of similar …………………………………… with similar
…………………………………… properties due to the same …………………………………… group.[3]
(c) Ethene is an alkene.
(i) Draw the structure of ethene showing all atoms and all bonds.[1]
(ii) Describe how aqueous bromine is used to show that ethene is an unsaturated compound.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. [2]
Ethene is manufactured by cracking.
(iii) State the conditions needed for cracking.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. [1]
Complete the chemical equation for the cracking of hexadecane, C16H34 , to form propene and one other hydrocarbon.
\(C_16H_34 \rightarrow C_3H_6+………………..\)
(d) Three dye mixtures, J, K and L, were spotted onto a piece of chromatography paper. Three pure dyes, X, Y and Z, were also spotted onto the same piece of paper
The diagram shows the results of this chromatography.
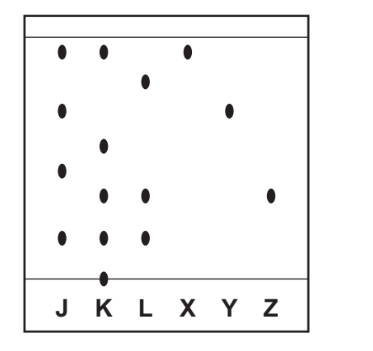
(i) Suggest why the base line was drawn in pencil and not in ink.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. [1]
(ii) Which dye mixture, J, K or L, contains a dye which did not move during this chromatography?
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. [1]
(iii) Which dye mixture, J, K or L, contains both dye X and dye Y?
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. [1]
(iv) Which dye mixture, J, K or L, does not contain dye Z?
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. [1]
[Total: 12]
Answer/Explanation
(a)(i)
S and U;
both have OH (group);
(a)(ii) Q and T; 1
(b)
compounds;
chemical;
functional;
(c)(i)

(c)(ii)
aqueous bromine is added to (test tube of) ethene/ aqueous bromine is orange; aqueous bromine turns colourless / solution turns colourless;
(c)(iii) high temperature/ heat; 1
(c)(iv) \(C_13H_28\);
Question
A list of techniques used to separate mixtures is given below.
- filtration
- diffusion
- fractional distillation
- simple distillation
- crystallisation
- chromatography
From this list, choose the most suitable technique to separate the following mixtures.
A technique may be used once, more than once or not at all.
(a) butane from a mixture of propane and butane …………………………………………………..
(b) oxygen from liquid air …………………………………………………………………………………….
(c) water from aqueous magnesium sulfate ……………………………………………………………
(d) potassium chloride from aqueous potassium chloride …………………………………………
(e) silver chloride from a mixture of silver chloride and water ……………………………………
(f) glucose from a mixture of glucose and maltose …………………………………………………
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a) diffusion or fractional distillation;
(b) fractional distillation;
(c) simple distillation;
(d) crystallisation;
(e) filtration;
(f) chromatography;