Question
This question is about copper and copper compounds.
(a) Describe how you could prepare a pure sample of crystals of hydrated copper(II) sulfate using dilute sulfuric acid and an excess of copper(II) oxide.[3]
(b) Anhydrous copper(II) sulfate is used to test for water.
(b) Anhydrous copper(II) sulfate is used to test for water.
$
\begin{aligned}
& \mathrm{CuSO}_4+5 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O} \rightleftharpoons \mathrm{CuSO}_4 \cdot 5 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O} \\
& \text { anhydrous hydrated } \\
& \text { copper(II) sulfate copper(II) sulfate } \\
&
\end{aligned}
$
(i) What is meant by the symbol $\rightleftharpoons$ ?[1]
(ii) How can hydrated copper(II) sulfate be changed into anhydrous copper(II) sulfate?[1]
(c) Complete the table to calculate the relative formula mass of anhydrous copper(II) sulfate, $\mathrm{CuSO}_4$. Use your Periodic Table to help you.

relative formula mass = …………………………. [2]
(d) Complete the table to show the number of electrons, protons and neutrons in the sulfur atom and copper ion shown.

(e) Alloys of copper are used to make coins.
(i) What is meant by the term alloy?[1]
(ii) Suggest why an alloy of copper is used to make coins instead of using pure copper.[1] [Total: 13]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
a) any three from:
• heat copper oxide with sulfuric acid
• filter off (excess) copper oxide
• heat filtrate to point of crystallisation / heat (copper sulfate) solution to point of crystallisation
• dry between filter papers / dry in drying oven
(b)(i) reversible reaction 1
(b)(ii) heat / warm 1
(c) 160 (2 marks)
if 2 marks not scored 1 mark for S = (1 × 32) = 32 OR O (= 4 × 16) = 64
(d) electrons in S = 16 (1)
electrons in Cu 2+ = 27 (1)
neutrons in S = 18 AND neutrons in Cu 2+ = 34 (1)
protons in S = 16 (1)
(e)(i) mixture of metal and other elements 1
(e)(ii) (alloy) more resistant to wear / stronger / harder / more resistant to corrosion ORA for copper
Question
(a) The table shows the percentage by mass of the elements on Earth and in the Universe.
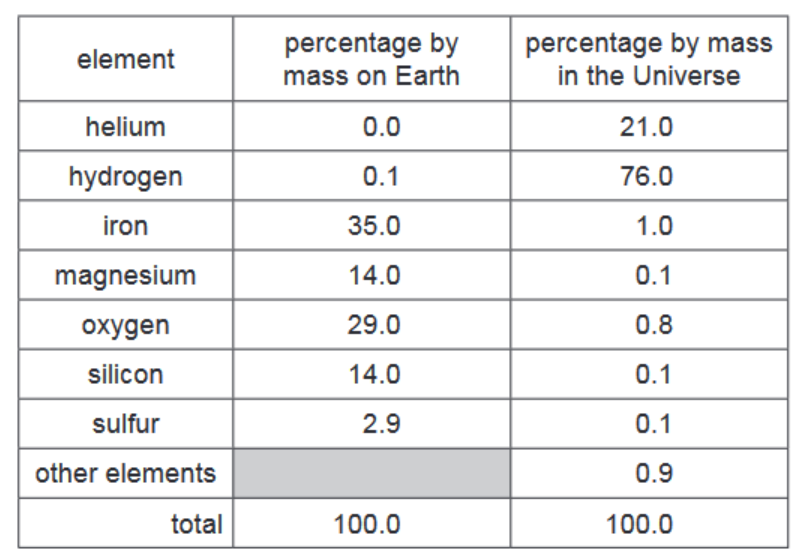
Answer these questions using only the information in the table.
(i) Deduce the percentage by mass of other elements present on Earth.$\%[1]$
(ii) Which non-metallic element is present on Earth in the greatest percentage by mass?[1]
(iii) Give two major differences in the percentage by mass of the elements on Earth and in the Universe.[2]
1
5
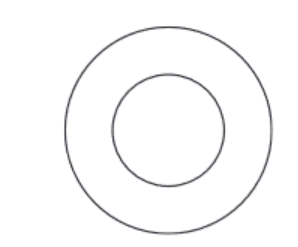
(b) Complete the diagram to show the electron arrangement in an oxygen atom.
(c) Helium, neon and argon are noble gases.
(i) Explain, in terms of the electronic structure, why neon is unreactive.[1]
(ii) State one use of argon.[1] [Total: 7]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a)(i) 5.0%
3(a)(ii) oxygen
3(a)(iii) any two from:
• more hydrogen in Universe (or reverse argument)
• more helium in Universe (or reverse argument)
• more oxygen on Earth (or reverse argument)
• more magnesium on Earth (or reverse argument)
• more iron on Earth (or reverse argument)
• more silicon on Earth (or reverse argument)
• more sulfur on Earth (or reverse argument)
(b) 2 electrons in inner shell AND 6 electrons in outer shell AND no additional shells of electrons
(c)(i) has complete outer (electron) shell / has full outer (electron) shell / outer shell cannot gain or lose electron(s)
(c)(ii) lamps / inert atmosphere (in metal extraction)
Question
This question is about Group IV elements and their compounds.
(a) The changes of state of lead are shown.

Name the changes of state represented by A and B.[2]
A
B
(b) Use the kinetic particle model to describe the differences between liquid lead and lead gas in terms of:[4]
-
- the separation of the particles
- the motion of the particles.
(c) Lead is extracted from lead(II) oxide by heating with carbon.
PbO + C → Pb + CO
Describe how this equation shows that lead(II) oxide is reduced.[1]
(d) Lead is a pollutant of the air.
(i) State one source of lead in the air.[1]
(ii) State one adverse effect of lead on health.[1]
(e) Diamond is a form of carbon.
The structure of diamond is shown.

(i) Choose the word which best describes the structure of diamond.
Draw a circle around your chosen answer.[1]
giant ionic metallic simple
(ii) Name the type of bonding in diamond.[1]
(iii) Give one use of diamond.[1]
(iv) Deduce the electronic structure of carbon.
Use the Periodic Table to help you.[1] [Total: 13]
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
a) A: freezing (1)
B: boiling (1)
b) separation:
liquid: close together / some touching (1)
gas: far apart (1)
motion:
liquid: sliding over each other / restricted movement (1)
gas: moving freely (1)
(c) lead oxide has lost oxygen
(d)(i) (leaded) petrol / paints
(d)(ii) poisonous / toxic / harms nerves / harms brain
(e)(i) giant
(e)(ii) covalent
(e)(iii) cutting tools / for cutting / drill tips / jewelry
(e)(iv) 2,4