Question
This question is about Group IV elements and their compounds.
(a) The changes of state of lead are shown.

Name the changes of state represented by A and B.[2]
A
B
(b) Use the kinetic particle model to describe the differences between liquid lead and lead gas in terms of:[4]
-
- the separation of the particles
- the motion of the particles.
(c) Lead is extracted from lead(II) oxide by heating with carbon.
PbO + C → Pb + CO
Describe how this equation shows that lead(II) oxide is reduced.[1]
(d) Lead is a pollutant of the air.
(i) State one source of lead in the air.[1]
(ii) State one adverse effect of lead on health.[1]
(e) Diamond is a form of carbon.
The structure of diamond is shown.

(i) Choose the word which best describes the structure of diamond.
Draw a circle around your chosen answer.[1]
giant ionic metallic simple
(ii) Name the type of bonding in diamond.[1]
(iii) Give one use of diamond.[1]
(iv) Deduce the electronic structure of carbon.
Use the Periodic Table to help you.[1] [Total: 13]
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
a) A: freezing (1)
B: boiling (1)
b) separation:
liquid: close together / some touching (1)
gas: far apart (1)
motion:
liquid: sliding over each other / restricted movement (1)
gas: moving freely (1)
(c) lead oxide has lost oxygen
(d)(i) (leaded) petrol / paints
(d)(ii) poisonous / toxic / harms nerves / harms brain
(e)(i) giant
(e)(ii) covalent
(e)(iii) cutting tools / for cutting / drill tips / jewelry
(e)(iv) 2,4
Question
Aqueous ammonia is an alkali.
(a) Complete the dot-and-cross diagram to show the electron arrangement in a molecule of ammonia.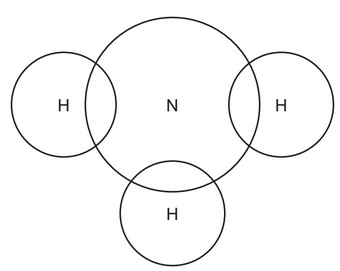
Complete the word equation for the reaction of aqueous ammonia with dilute hydrochloric acid.
(c) Describe the colour change when excess aqueous ammonia is added to an acidified solution of methyl orange.
from ………………………………………………………. to ……………………………………………………….
(d) Aqueous ammonia reacts with aqueous copper(II) ions to produce compound B.
The formula of compound B is \(CuN_4H_{16}O_2\).
Complete the table to calculate the relative molecular mass of compound B.
relative molecular mass = …………………………
(e) Ammonia is used in the production of fertilisers.
State why farmers put fertilisers on the soil where crops are to be grown.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a) bonding pair of electrons between each H and N AND no other electrons on H (1)
2 non-bonded electrons on N (1)
(b) ammonium chloride (1)
(c) red / pink to yellow (1)
(d) 168 (2 marks)
if 2 marks not scored, 1 mark for :
(16 × 1) = 16 OR (2 × 16) = 32 (on the appropriate line)
(e) makes plants grow faster / increases yield
Question
This question is about nitrogen and compounds of nitrogen.
(a) When nitrogen is cooled to below –196°C it changes state from gas to liquid.
(i) Name the change of state from gas to liquid.
(ii) Use the kinetic particle theory to describe the differences between nitrogen gas and liquid
nitrogen in terms of:
● the separation of the particles
● the motion of the particles.
(b) Oxides of nitrogen are pollutants in the air.
(i) State one source of oxides of nitrogen in the air.
(ii) Oxides of nitrogen contribute to acid rain.
Give one adverse effect of acid rain on buildings.
(c) Nitric acid contains the nitrate ion.
(i) Use words from the list to complete the sentences to describe the test for nitrate ions.
aluminium ammonia chloride copper
hydroxide iron oxygen sulfate
Put the sample in a test-tube then add aqueous sodium ……………………. .
Then add ……………………. .
Warm gently. A gas is produced. The name of this gas is …………………….
(ii) Nitric acid reacts with calcium carbonate.
Complete the word equation for this reaction.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a) (i) condensation
(ii)
separation:
liquid: particles close together (1)
gas: far apart (1)
motion:
liquid: sliding over each other / limited motion / restricted motion (1)
gas: particles have rapid motion / particles have random motion (1)
(b) (i) car engines
(ii) chemical weathering / chemical erosion
(c) (i) hydroxide (1)
aluminium (1)
ammonia (1)
(ii) calcium nitrate (1)
carbon dioxide (1)
water (1)