Question
A student investigates the rate of reaction of small pieces of calcium carbonate with an excess of hydrochloric acid of concentration $1 \mathrm{~mol} / \mathrm{dm}^3$.
$
\mathrm{CaCO}_3(\mathrm{~s})+2 \mathrm{HCl}(\mathrm{aq}) \rightarrow \mathrm{CaCl}_2(\mathrm{aq})+\mathrm{CO}_2(\mathrm{~g})+\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}(\mathrm{l})
$
(a) Name the salt formed when calcium carbonate reacts with hydrochloric acid.
[1]
(b) The graph shows how the mass of the reaction mixture changes with time.
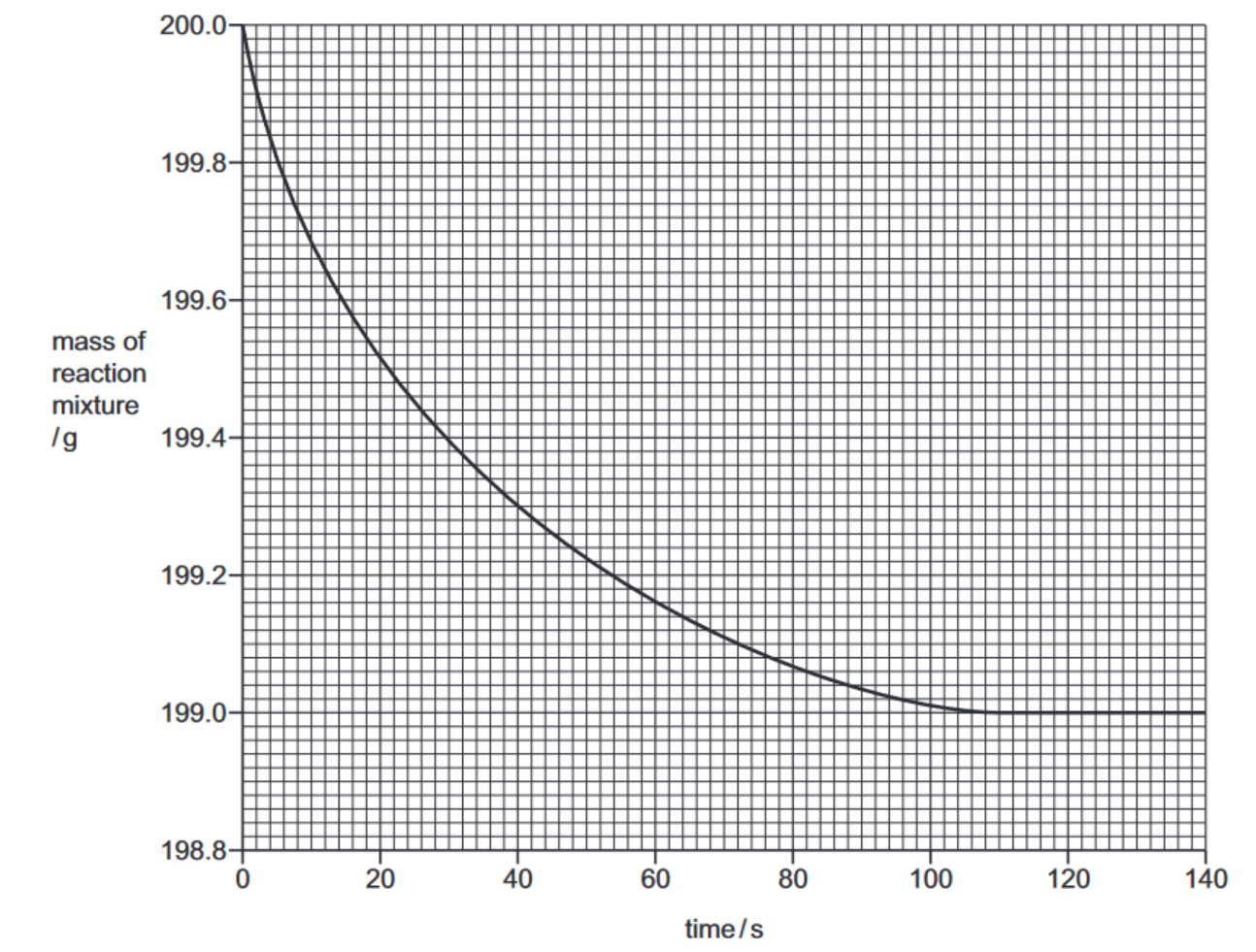
(i) State why the reaction mixture decreases in mass.[1]
(ii) Calculate the loss in mass during the first 40 seconds of the experiment.$g[1]$
(iii) The experiment is repeated using hydrochloric acid of concentration $2 \mathrm{~mol} / \mathrm{dm}^3$. All other conditions are kept the same.
Draw a line on the grid for the experiment using hydrochloric acid of concentration $2 \mathrm{~mol} / \mathrm{dm}^3$.
(iv) In the experiment, when $2.00 \mathrm{~g}$ of calcium carbonate is used, the loss in mass of the reaction mixture is $0.88 \mathrm{~g}$.
All other conditions are kept the same.
Calculate the loss in mass when $0.50 \mathrm{~g}$ of calcium carbonate is used.
loss in mass = ………………………… g [1]
(v) The experiment is repeated using the same mass of different sized pieces of calcium carbonate.
All other conditions are kept the same.
The sizes of the pieces of calcium carbonate are:
- powder
- small pieces
- large pieces.
Complete the table by writing the sizes of the pieces of calcium carbonate in the first column.

▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans
(a) calcium chloride
(b)(i) gas released / gas escapes / gas lost
(b)(ii) 0.7 (g) 1
(b)(iii) line steeper than original and starting from 0 and 200.0 g (1)
line ends up at same final mass AND levels off at or before 104 s (1)
(b)(iv) 0.22 (g) 1
(b)(v) large pieces → 0.005
small pieces → 0.030
powder → 0.100
Question
This question is about iodine and compounds of iodine.
(a) Use the kinetic particle model to describe the separation between the molecules and the type of motion of the molecules in:
- solid iodine
- iodine gas. [4]
(b) The graph shows how the volume of iodine gas changes with pressure. The temperature is kept constant.

Describe how the volume of iodine gas changes with pressure.[1]
(c) (i) Complete the word equation to show the halogen and halide compound which react to form the products iodine and potassium bromide.

(ii) Explain, in terms of the reactivity of the halogens, why aqueous iodine does not react with aqueous potassium chloride
(d) lodine reacts with aqueous sodium thiosulfate, $\mathrm{Na}_2 \mathrm{~S}_2 \mathrm{O}_3$.
(i) Balance the chemical equation for this reaction.
$
\mathrm{Na}_2 \mathrm{~S}_2 \mathrm{O}_3+\mathrm{I}_2 \rightarrow \mathrm{Na}_2 \mathrm{~S}_4 \mathrm{O}_6+\ldots . . \mathrm{NaI}
$
(ii) The energy level diagram for this reaction is shown.

Explain how this diagram shows that the reaction is exothermic [1]
(e) Describe a test for iodide ions.
test
observations[2]
(f) Molten sodium iodide is electrolysed.
Predict the product at the positive electrode.[1][Total: 14]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a) solid:
particles touching / particles close together (1)
particles (only) vibrating / not moving from place to place (1)
gas:
particles far apart (1)
particles moving fast / particles moving randomly / particles moving in any direction (1)
4(b) increasing the pressure decreases the volume / decreasing the pressure increases the volume / the higher the volume, the lower
the pressure
4(c)(i) bromine (1)
potassium iodide (1)
Question
This question is about acids, bases and salts.
(a) Sodium hydroxide is a base.
(i) Name the products formed when sodium hydroxide reacts with dilute nitric acid.[2]
(ii) Describe the effect of sodium hydroxide on a named indicator.[2]
(iii) Complete the word equation for the reaction of sodium hydroxide with ammonium chloride.

(b) Describe how to prepare pure, dry crystals of the salt zinc sulfate from an aqueous solution of zinc sulfate.[2]
(c) The rate of reaction of zinc powder with dilute sulfuric acid is found by measuring the increase in volume of hydrogen gas produced as time increases.
Describe the effect, if any, of each of the following on the rate of this reaction.
-
- The reaction is carried out with large pieces of zinc instead of zinc powder.
All other conditions stay the same.
-
- The reaction is carried out using a catalyst.
All other conditions stay the same.
-
- The reaction is carried out with dilute sulfuric acid of a lower concentration.
All other conditions stay the same. [3] [Total: 11]
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a)(i) sodium nitrate (1)
(and) water (1)
(a)(ii) named suitable indicator e.g. methyl orange / litmus (1)
correct colour in alkali e.g. blue (for litmus) / yellow (for methyl orange) (1)
(a)(iii) ammonia (1)
sodium chloride (1)
(b) 1 mark each for any two of:
-
- evaporate to point of crystallisation / heat to point of crystallisation / evaporate some of the water and leave (1)
- filter crystals / pick out crystals (1)
- dry with filter paper / dry in drying oven
(c) large pieces: (rate) decreases / (reaction gets) slower (1)
catalyst: (rate) increases / (reaction gets) faster (1)
lower concentration: (rate) decreases / (reaction gets) slower (1)