Question
(a) The table shows the percentage by mass of the elements on Earth and in the Universe.
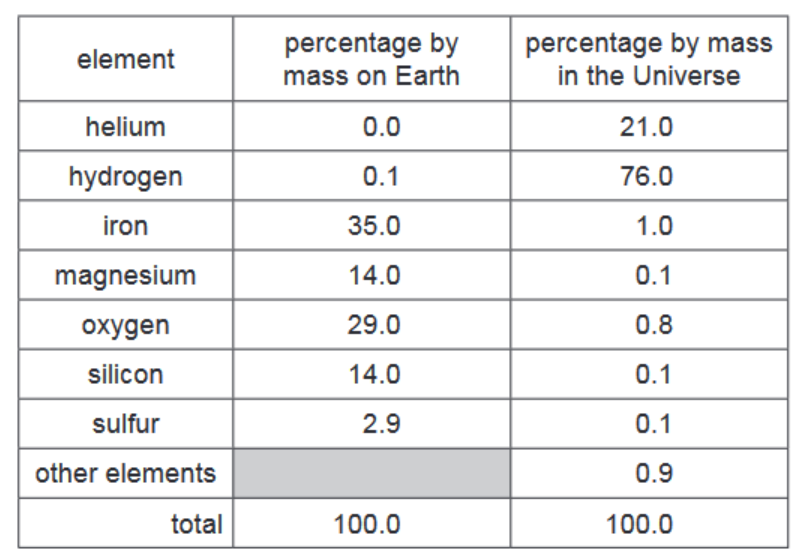
Answer these questions using only the information in the table.
(i) Deduce the percentage by mass of other elements present on Earth.$\%[1]$
(ii) Which non-metallic element is present on Earth in the greatest percentage by mass?[1]
(iii) Give two major differences in the percentage by mass of the elements on Earth and in the Universe.[2]
1
5
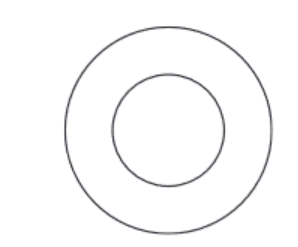
(b) Complete the diagram to show the electron arrangement in an oxygen atom.
(c) Helium, neon and argon are noble gases.
(i) Explain, in terms of the electronic structure, why neon is unreactive.[1]
(ii) State one use of argon.[1] [Total: 7]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a)(i) 5.0%
3(a)(ii) oxygen
3(a)(iii) any two from:
• more hydrogen in Universe (or reverse argument)
• more helium in Universe (or reverse argument)
• more oxygen on Earth (or reverse argument)
• more magnesium on Earth (or reverse argument)
• more iron on Earth (or reverse argument)
• more silicon on Earth (or reverse argument)
• more sulfur on Earth (or reverse argument)
(b) 2 electrons in inner shell AND 6 electrons in outer shell AND no additional shells of electrons
(c)(i) has complete outer (electron) shell / has full outer (electron) shell / outer shell cannot gain or lose electron(s)
(c)(ii) lamps / inert atmosphere (in metal extraction)
Question
This question is about air.
(a) The pie chart shows the proportions of the main gases in clean, dry air.

(i) Name the gases G and H.[2]
gas G
gas H
(ii) The graph shows how the volume of a sample of gas G changes as temperature increases. The pressure is kept constant.

Describe how the volume of gas G changes as temperature increases.[1]
(iii) There is a small percentage of noble gases in the air.
The noble gases are unreactive.
Explain why the noble gases are unreactive in terms of their electronic structure.[1]
(iv) Describe the arrangement and separation of the particles in a gas.[2]
arrangement
separation
(b) Two of the pollutants in air are oxides of nitrogen and lead compounds.
(i) Give one effect of each of these pollutants on health.[2]
oxides of nitrogen
lead compounds
(ii) Name two other pollutants present in air.
State the source of each of these pollutants.[4]
pollutant 1
source of pollutant 1
pollutant 2
source of pollutant 2 [Total: 12]
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a)(i) G is oxygen (1)
H is nitrogen (1)
(a)(ii) volume increases (as temperature increases)
(a)(iii) they have a full outer shell (of electrons) / they have a complete outer shell (of electrons)
(a)(iv) arrangement: irregular / random (1)
separation: far apart (1)
(b)(i) oxides of nitrogen:
breathing difficulties / irritates lungs / irritates eyes / irritates throat / irritates skin / lung problems (1)
lead compounds:
poisonous / toxic / harms nervous system / harms brain (1)
(b)(ii) 1 mark for each correct pollutant and one 1 mark for each correct source e.g.
sulfur dioxide (1)
burning fossil fuels / volcanoes (1)
carbon monoxide (1)
incomplete combustion of carbon containing substance / incomplete combustion of named carbon compound (1)
Question
This question is about elements in the Periodic Table.
(a) The table shows some properties of five elements, P, Q, R, S and T.
Use only the elements shown in the table to answer this question.
State which two of the elements, P, Q, R, S and T, are covalent molecules.
Give two reasons for your answer.
elements …………………………………………………….. and ……………………………………………………..
reason 1 …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
reason 2 …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(b) Element T is on the left-hand side of the Periodic Table.
Suggest whether its oxide is acidic or basic.
Give a reason for your answer.
(c) Krypton is an element in Group VIII of the Periodic Table.
Explain, using ideas about electronic structure, why krypton is unreactive.
(d) Sodium is an element in Group I of the Periodic Table. Iron is a transition element.
Iron has a higher melting point and higher boiling point than sodium.
Give two other ways in which the properties of transition elements differ from the properties of
Group I elements.
1 ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
2 ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(e) The table compares the reactivity of four metals with dilute hydrochloric acid.
Put the four metals in order of their reactivity.
Put the least reactive metal first.
(f) Hot iron reacts with steam. The reaction is reversible.
Complete the equation by writing the symbol for a reversible reaction in the box.
(g) Steel is an alloy of iron.
State the meaning of the term alloy.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a) Q AND S (1)
low melting points (1)
poor conductor (of electricity) / does not conduct (electricity) (1)
(b) basic (oxide) AND
T is a metal / metal oxides are basic
(c) has a complete outer (electron) shell / has a full outer (electron) shell
(d) 1 mark each for any 2 of:
• transition elements have a high(er) density / Group I has a low(er) density
• transition elements form coloured compounds / Group I compounds are not coloured
• transition elements form ions with different charges / Group I forms only one type of ion
• transition elements are good catalysts / Group I elements not catalysts
(e) copper < nickel < iron < calcium (2)
if 2 marks not scored, 1 mark for:
1 consecutive pair reversed / calcium < iron < nickel < copper
(f) \(\leftrightarrow \)
(g) mixture of metal with another element