Question
Acids have characteristic properties.
(a) Hydrochloric acid reacts with magnesium.
Name the products of this reaction and give the observations…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. [4]
(b) The rate of reaction of iron(II) carbonate with hydrochloric acid can be determined by measuring the time taken to produce $20 \mathrm{~cm}^3$ of carbon dioxide.
A student measured the time taken to produce $20 \mathrm{~cm}^3$ of carbon dioxide at three different temperatures.
In each experiment the student used:
- $1 \mathrm{~g}$ of large pieces of iron(II) carbonate
- dilute hydrochloric acid of the same concentration and volume.
The results are shown in the table.
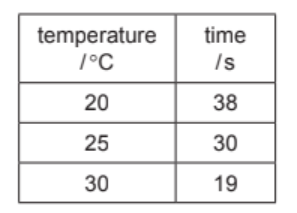
(i) Use the information in the table to describe how the rate of reaction changes with temperature. [1]
(ii) Describe the effect of each of the following on the rate of this reaction at constant
temperature.
● Smaller pieces of iron(II) carbonate are used.
All other conditions stay the same.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
● The concentration of hydrochloric acid is decreased.
All other conditions stay the same.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
[2]
(c) The reaction of iron(II) carbonate with hydrochloric acid is exothermic.
What is meant by the term exothermic?……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. [1]
(d) Rust contains compounds of iron.
State two conditions needed for iron to rust…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. [2]
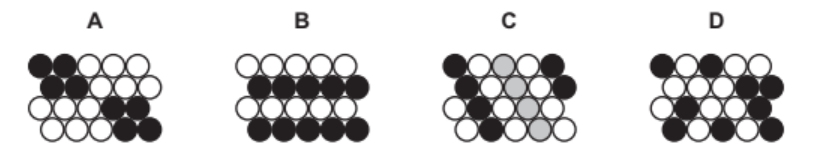
(e) Iron and magnesium are both used in alloys.
Which one of these diagrams, A, B, C or D, best represents an alloy?
 [1] [Total: 11]
[1] [Total: 11]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a) forms magnesium chloride (1)
forms hydrogen (1)
one mark each for any two of:
• reaction is exothermic / (reaction mixture) gets warm
• bubbles / effervesces / fizzes
• magnesium disappears (or gets smaller)
(b)(i) increase in temperature increases rate 1
(b)(ii) (smaller pieces of carbonate) increases the rate
(decreasing concentration) decreases the rate
(c) (reaction) gives out heat / reaction mixture gets warmer 1
(d) water
oxygen / air
6(e) D
Question
This question is about iron and its compounds.
(a) The table shows how easy it is to reduce four metal oxides by heating with carbon.
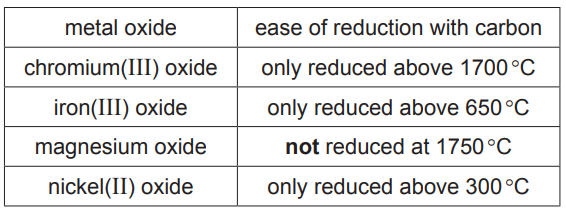
Use this information to put the metals in order of their reactivity. Put the least reactive metal first.[2]
(b) Iron is a transition element. Potassium is an element in Group I of the Periodic Table.
Describe three ways in which the properties of iron differ from those of potassium.[3]
1
2
3
(c) Iron wire burns in oxygen.
Balance the chemical equation for this reaction.[2]
\(…Fe+O_{2}\rightarrow Fe_{3}O_{4}\)
(d) Pure iron can be made by reducing iron(III) oxide, Fe2O3, with hydrogen.
\(Fe_{2}+O_{3}+3H_{2}\rightarrow 2Fe+3H_{2}O\)
How does this equation show that iron(III) oxide is reduced?[1]
(e) When iron reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid, iron(II) chloride is formed.
(i) Describe a test for iron(II) ions.[2]
test
result
(ii) Another chloride of iron has the structure shown.
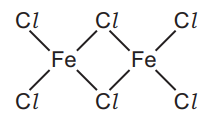
Deduce the molecular formula of this compound showing the number of iron and chlorine atoms.[1]
(f) Some iron nails were placed in bottles under different conditions.
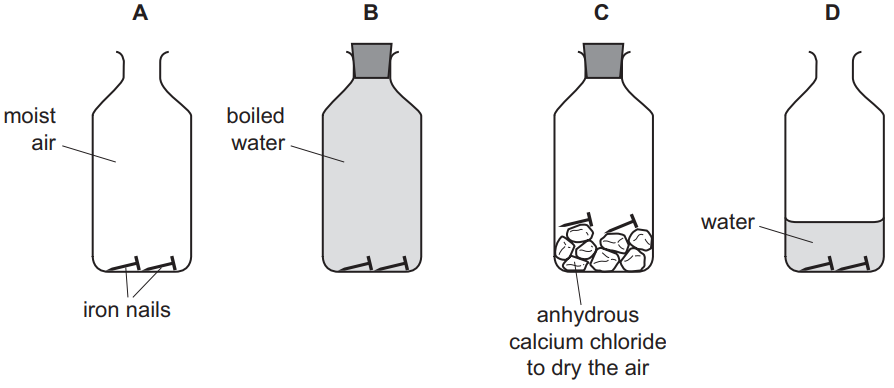
In which bottles will the iron nails not rust?
Give reasons for your answer.[2] [Total: 13]
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a) nickel<iron<chromium<magnesium
IF 2 marks not scored:
1 mark if all reversed / one consecutive pair reversed
(b) One mark each for any 3 of:
- iron has high melting point / boiling point / ORA for K
- iron has high density / ORA for K
- iron has catalytic activity / ORA for K
- iron forms coloured compounds / ORA for K
- iron compounds have variable oxidation states / form ions with different charges / ORA for K
- iron is hard / potassium is soft / iron is strong / potassium is weak
- one suitable difference in chemical properties e.g. iron is less reactive than potassium ORA / potassium reacts with cold water / iron does not react with cold water / iron rusts / potassium does not rust
- iron is magnetic / ORA for K
(c) 3 (Fe)
2 (O2)
(d) it loses oxygen / oxygen is removed from the iron oxide / hydrogen gains the oxygen from the iron oxide
(e)(i) add (aqueous) sodium hydroxide / (aqueous) ammonia AND
green precipitate (2)
IF 2 marks not scored:
1 mark for add (aqueous) sodium hydroxide / (aqueous) ammonia
(e)(ii) Fe2Cl6
(f) B / boiled water
AND
because no air / no oxygen
C / with calcium chloride
AND
because no water
Question
Iron is extracted from the ore hematite in the Blast Furnace.
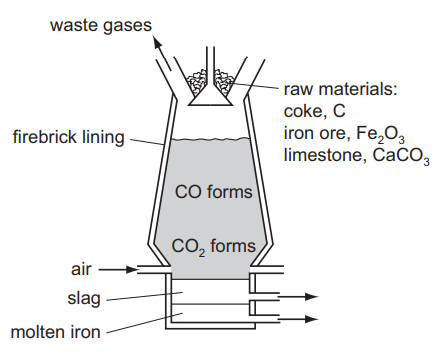
(a) The coke reacts with the oxygen in the air to form carbon dioxide.
C + O2 → CO2
(i) Explain why carbon monoxide is formed higher in the Blast Furnace.[2]
(ii) Write an equation for the reduction of hematite, Fe2O3, by carbon monoxide.[2]
(b) (i) Limestone decomposes to form two products, one of which is calcium oxide. Name the other product.[1]
(ii) Calcium oxide reacts with silicon(IV) oxide, an acidic impurity in the iron ore, to form slag. Write an equation for this reaction.[2]
(iii) Explain why the molten iron and the molten slag form two layers and why molten iron is the lower layer.[2]
(iv) Suggest why the molten iron does not react with the air.[1]
(c) Iron and steel rust. Iron is oxidized to hydrated iron(III) oxide, Fe2O3.2H2O, which is rust.
(i) Name the two substances which cause iron to rust.[1]
(ii) Explain why an aluminum article coated with aluminum oxide is protected from further corrosion but a steel article coated with rust continues to corrode.[1]
(d) There are two electrochemical methods of rust prevention.
(i) The first method is sacrificial protection.
Explain why the steel article does not rust.[4]

The second method is to make the steel article the cathode in a circuit for electrolysis.

(ii) Mark on the diagram the direction of the electron flow. [1]
(iii) The steel girder does not rust because it is the cathode. Reduction takes place at the cathode. Give the equation for the reduction of hydrogen ions.[2] [Total: 19]
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a) (i) insufficient/limited oxygen
or 2C + O2 → 2CO
coke/carbon reacts with carbon dioxide
or C + CO2 → 2CO
(ii) Fe2O3 + 3CO → 2Fe + 3CO2
species (1) balancing (1)
(b) (i) carbon dioxide
(ii) CaO + SiO2 → CaSiO3
[1] each side correct
(iii) (molten) iron higher density (than slag)
(iv) No oxygen in contact with iron or layer of slag prevents hot iron reacting with oxygen/air or (all) oxygen reacts with carbon (so no oxygen left to react with iron)
(c) (i) air/oxygen and water (need both)
(ii) aluminum oxide layer is impervious or non-porous or passive or unreactive or will not allow water/air to pass through it (rust allows passage of water or air or it flakes off)
(d) (i) zinc more reactive (than iron/steel)
loses electrons
electrons move (from zinc) to iron
Zinc reacts (with air and water) or zinc corrodes or zinc is oxidized or zinc is anodic or zinc forms positive ions or zinc forms Zn2+ or iron and steel don’t react with air/water or iron and steel are not oxidized or iron and steel do not
form ions or iron and steel do not lose electrons or iron and steel are cathodic
(ii) R to L in wire
(iii) 2H+ + 2e– → H2
species (1) balancing (1)