Question
Many organic compounds contain carbon, hydrogen and oxygen only.
(a) An organic compound V has the following composition by mass.
C, 48.65%; H, 8.11%; O, 43.24%
Calculate the empirical formula of compound V.
empirical formula = …………………………
(b) Compound W has the empirical formula CH4O and a relative molecular mass of 32.
Calculate the molecular formula of compound W.
molecular formula = …………………………
(c) Compounds X and Y have the same general formula.
X and Y are both carboxylic acids.
Compound X has the molecular formula \(C_2H_4O_2\).
Compound Y has the molecular formula \(C_4H_8O_2\).
(i) Deduce the general formula of compounds X and Y.
(ii) Draw the structure of compound Y. Show all of the atoms and all of the bonds.
Name compound Y.
name …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
(iii) Give the name used to describe a ‘family’ of similar compounds with the same general
formula, similar chemical properties and the same functional group.
(d) Propene is an unsaturated hydrocarbon. The formula of propene is shown.
\(CH_3CH=CH_2\)
(i) State the colour change observed when propene is added to aqueous bromine.
from ……………………………………………………. to ……………………………………………………
(ii) Propene can be produced by cracking long chain alkanes.
Pentadecane, \(C_{15}H_{32}\), is cracked to produce an alkane and propene in a 1:2 molar ratio.
Complete the chemical equation for this reaction.
\(C_{15}H_{32}\) → ………………………………… + …………………………………
(iii) Propene can be converted into poly(propene).
Name the type of polymerisation that occurs when propene is converted into poly(propene).
(iv) Complete the diagram to show a section of poly(propene).
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a) 48.65 / 12 8.11 / 1 43.24 / 16 (1)
OR evaluation
4.05 8.11 2.7(0)
divide all by smallest
OR 1.5 : 3 : 1
OR
6 : 3 : 2 (1)
\(C_3H_6O_2\) (1) ALLOW symbols in any order
(b) ( \(M_r\) of \(CH_4O\) = 32)
\(CH_4O\) (1)
(c) (i) \(C_nH_{2n}O_2\)
OR
\(C_nH_{2n+1} COOH\)
(ii) butanoic acid (1)
fully displayed carboxylic acid group (1)
correct structure of butanoic acid showing all atoms and bonds (1)
(iii) homologous series
(d) (i) brown to colourless
(ii) \(C_9H_{20}\) (1)
\(2C_3H_6\) (1)
(iii) addition
(iv) 
any one repeat unit (1)
both repeat units fully correct (1)
Question
(a) Ethane, propane and butane are members of the same homologous series.
(i) Name this homologous series.[1]
(ii) State two ways members of the same homologous series are similar.
1……………………………………………………………………………
2………………………………………………………………….[2]
(b) One mole of ethane, $\mathrm{C}_2 \mathrm{H}_6$, contains $6.02 \times 10^{23}$ molecules.
Calculate how many molecules are in $15 \mathrm{~g}$ of ethane.
number of ethane molecules $=$[1]
(c) Propane reacts with chlorine.
(i) Write the formula of the product which does not contain carbon. [1]
(ii) Draw the structure of an organic product formed. Show all of the atoms and all of the bonds.
(iii) State the name of this type of reaction. ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… [1]
(d) (i) Aqueous bromine was added to a sample of ethene.
Give the colour change seen.
from ……………………………………………………. to …………………………………………………… [2]
(ii) Explain, in terms of bonding, why there is no colour change when aqueous bromine is added to ethane………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. [1]
(e) There are two structural isomers with the formula $\mathrm{C}_4 \mathrm{H}_{10}$.
(i) Draw the structures of both of these isomers, showing all of the atoms and all of the bonds.

(ii) Butane is formed when longer chain hydrocarbons are cracked.
Complete the chemical equation to show the other product when butane is formed by cracking.
$
\mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_{14} \rightarrow \mathrm{C}_4 \mathrm{H}_{10}+\ldots \ldots \ldots \ldots \ldots \ldots \ldots \ldots \ldots \ldots . . \cdots
$
(f) A compound contains $85.7 \%$ carbon and $14.3 \%$ hydrogen by mass.
(i) Calculate the empirical formula of this compound.
Show your working.[3]
(ii) The molecular mass of the compound is 112 .
Calculate the molecular formula of this compound.[1] [Total: 16]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
6(a)(i) alkanes 1
6(a)(ii) one mark each for any two of:
• same chemical properties
• same functional group
• same general formula
• (consecutive members) differ by CH2
• common (allow similar) methods of preparation
• physical properties vary in predictable manner / show trends / gradually change OR example of a physical property
variation i.e. melting point / boiling point / volatility (1)
6(b) $3.01 \times 10^{23}$ (molecules)
6(c)(i) HCl
6(c)(ii)

6(c)(ii) substitution 1
6(d)(i) from: orange (1)
to: colourless (1)
6(d)(ii) contains no double bonds/ethane only contains single bonds
6(e)(i)
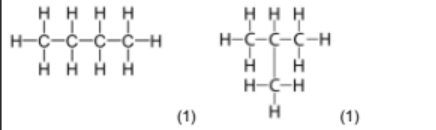
6(e)(ii) $\mathrm{C}_2 \mathrm{H}_4$
6(f)(i) $\begin{aligned} & \left(\mathrm{C}=85.7, \mathrm{H}=14.3, M_{\mathrm{r}} 112\right) \\ & \mathrm{C}=\frac{85.7}{12}=7.14 \quad \mathrm{H}=\frac{14.3}{1}=14.3(1) \\ & (\text { ratio }=7.13: 14.3=1: 2) \\ & \mathrm{CH}_2(2)\end{aligned}$
6(f)(ii) $\mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_{16}$
Question
Ethanol is manufactured by two different processes.
(a) For each process, name the organic reactant and state the type of reaction.
organic reactant ……………………………………….. type of reaction ……………………………………….
organic reactant ……………………………………….. type of reaction ………………………………………. [4]
(b) Alcohols can be oxidised to form carboxylic acids.
Name a suitable oxidising agent for this reaction.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. [1]
(c) Alcohols can be partially oxidised to form aldehydes.
Aldehydes are a homologous series of organic compounds.
Partial oxidation is achieved by reacting an alcohol with the oxidising agent in distillation apparatus as shown.

(i) Name apparatus A. ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… [1]
(ii) On the diagram, use one arrow to show where water enters apparatus A. [1]
(d) The table shows some information about aldehydes.
(i) Complete the table.
 [2]
[2]
(ii) Deduce the general formula of aldehydes. [1]
(e) The structural formula of ethanal is shown.

The C=O group in aldehydes is at the end of the carbon chain.
This is a reactive part of the molecule.
(i) What is the name given to the reactive part of any organic molecule?
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… [1]
(ii) Complete the dot-and-cross diagram to show the electron arrangement of a molecule of ethanal. Inner shells have been drawn.

(f) Propanone belongs to a homologous series called ketones. Ketones have the same $\mathrm{C}=\mathrm{O}$ group as aldehydes but the $\mathrm{C}=\mathrm{O}$ group is not at the end of the carbon chain. Propanone has the same molecular formula as propanal, $\mathrm{C}_3 \mathrm{H}_6 \mathrm{O}$.
(i) What term is used to describe molecules with different structures but with the same molecular formula?[1]
(ii) Suggest the structure of propanone, $\mathrm{C}_3 \mathrm{H}_6 \mathrm{O}$. Show all of the atoms and all of the bonds.[2] [Total: 17]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
5(a) M1 sugar(s)
M2 fermentation
M3 ethene
M4 hydration
5(b) (acidified) potassium manganate(VII)
5(c)(i) (Liebig) condenser
5(c)(ii) arrow at the lower inlet
5(d)(i) methanal
$\mathrm{C}_4 \mathrm{H}_8 \mathrm{O}$
5(d)(ii) $\quad \mathrm{C}_n \mathrm{H}_{2 n} \mathrm{O}$
5(e)(i) functional group
5(e)(ii) M1 $4 \times \mathrm{C}-\mathrm{H}$ dot cross bonds and $1 \mathrm{C}-\mathrm{C}$ dot cross bond M2 $1 \times \mathrm{C}=\mathrm{O}$ dot cross bond M3 non-bonding electrons on $\mathrm{O}$
5(f)(i) (structural) isomers
5(f)(ii) M1 any structure with correct valencies and formula of $\mathrm{C}_3 \mathrm{H}_6 \mathrm{O}$ $\mathrm{M} 2 \mathrm{C}=\mathrm{O}$ bond on second carbon (of a chain of 3 )