Question
(a) Atoms are made of protons, neutrons and electrons. Atoms of the same element are known as isotopes.
(i) Complete the table.[2]
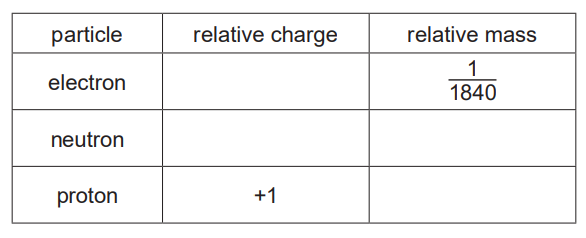
(ii) \(_{12}^{24}\textrm{Mg}\) and \(_{12}^{25}\textrm{Mg}\) are isotopes of magnesium.
Complete the table to show the numbers of electrons, neutrons and protons in these isotopes of magnesium.[2]

(iii) Explain why magnesium ions have a charge of 2+.[1]
(b) Mg2+ ions have the electronic structure 2,8.
Give the formula of the following particles which have the same electronic structure as Mg2+ ions.
-
- a cation (positive ion)
- an anion (negative ion)
- an atom
[3] [Total: 8]
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
2(a)(i)
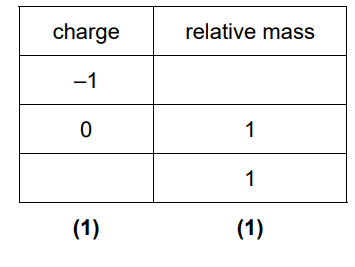
Mark by column
2(a)(ii)

Mark by row
2(a)(iii) (they have) 2 more protons than electrons
OR
(they have) 2 fewer electrons than protons
OR
(they have) 12 protons and 10 electrons
2(b) Na+ or Al 3+ (1)
F– or O2– or N3– (1)
Ne (1)
Question
This question is about copper and its compounds.
(a) Copper has two different naturally occurring atoms, \(^{63}Cu\) and \(^{65}Cu\).
(i) State the term used for atoms of the same element with different nucleon numbers.
(ii) The atomic number of copper is 29.
Complete the table to show the number of protons, neutrons and electrons in the particles
of copper shown.
(iii) Relative atomic mass is the average mass of naturally occurring atoms of an element.
The percentage of the naturally occurring atoms in a sample of copper is shown.
Deduce the relative atomic mass of copper in this sample.
Give your answer to one decimal place.
relative atomic mass = …………………………
(b) Anhydrous copper(II) sulfate is used to test for the presence of water. When this test is positive,
hydrated copper(II) sulfate is formed.
(i) State the colour change seen during this test.
from ……………………………………………………. to ……………………………………………………
(ii) Complete the chemical equation to show the reaction that takes place.
\(CuSO_4 + …………………… \leftrightarrow CuSO_4•5H_2O\)
(iii) State how hydrated copper(II) sulfate can be turned back into anhydrous copper(II) sulfate.
(iv) Describe a test for pure water.
(c) Aqueous copper(II) sulfate contains \(Cu^{2+}\)(aq) ions.
(i) Describe what is seen when aqueous copper(II) sulfate is added to aqueous
sodium hydroxide, NaOH(aq).
(ii) Write the ionic equation for the reaction between aqueous copper(II) sulfate and aqueous
sodium hydroxide.
Include state symbols.
(d) When solid copper(II) nitrate is heated copper(II) oxide, nitrogen dioxide and oxygen are
formed.
\(2Cu(NO_3)_2 → 2CuO + 4NO_2 + O_2\)
Calculate the volume of nitrogen dioxide formed at room temperature and pressure when 4.7g
of \(Cu(NO_3)_2\) is heated.
Use the following steps:
● calculate the mass of one mole of \(Cu(NO_3)_2\)
………………………… g
● calculate the number of moles of \(Cu(NO_3)_2\) used
………………………… moles
● determine the number of moles of nitrogen dioxide formed
………………………… moles
● calculate the volume of nitrogen dioxide formed at room temperature and pressure.
………………………… \(dm^3\)
(e) Write the chemical equation to show the action of heat on sodium nitrate, \(NaNO_3\).
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a) (i) isotopes
(ii) 1 mark for each correct row
(iii) M1 = (70 × 63) + (30 × 65) or [ ( 4410) + (1950) ] or 6360 (1)
M2 = M1 / 100 = 63.6 (1)
OR
M1= (0.7(0) × 63) + (0.3(0) × 65) or [ (44.1(0) ) + (19.5(0)) ] (1)
M2 = 63.6 (1)
(b) (i) M1 white (1)
M2 to (light) blue (1)
(ii) \(5H_2O\)
(iii) heating
(iv) M1 boiling point (1)
M2 is 100 °C
OR
M1 freezing point (1)
M2 is 0 °C (1)
(c) (i) blue precipitate
(ii) Alternative suggestion:
M1 \(Cu(OH)_2\) (as only product) (1)
M2 \(Cu^{2+}\) and 2OH– (as reactants) (1)
M3 state symbols (1)
(d) M1 188
M2 4.7 / 188 = 0.025(0)
M3 0.025(0) × 2 = 0.05(0)
M4 0.05(0) × 24.0 = 1.2
(e) \(2NaNO_3 → 2NaNO_2 + O_2\)
\(NaNO_2\) (1)
rest of equation (1)
Question
This question is about masses, volumes and moles.
(a) Which term is defined by the following statement?[1]
The average mass of naturally occurring atoms of an element on a scale where the 12C atom has a mass of exactly 12 units.
(b) Butane, C4H10, has a relative molecular mass of 58.
Potassium fluoride, KF, has a relative formula mass of 58.
Explain why the term relative molecular mass can be used for butane but cannot be used for potassium fluoride.[2]
(c) A 0.095g sample of gaseous element Y occupies 60.0cm3 at room temperature and pressure.
-
- Determine the number of moles of element Y in 60.0cm3.
moles of element Y = mol
-
- Calculate the relative molecular mass of element Y and hence suggest the identity of element Y.[3]
relative molecular mass =
identity of element Y =
(d) A 1.68g sample of phosphorus was burned and formed 3.87g of an oxide of phosphorus. Calculate the empirical formula of this oxide of phosphorus.
empirical formula = [4]
(e) Another oxide of phosphorus has the empirical formula P2O3.
One molecule of this oxide of phosphorus contains four atoms of phosphorus.
Calculate the mass of one mole of this oxide of phosphorus.
mass = g [2] [Total: 12]
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
4(a) relative atomic mass
4(b) C4H10 is covalent
KF is ionic
4(c) mol of Y = 0.060 / 24.0 = 2.5 × 10–3 or 0.0025
Mr = 0.095 / 2.5 × 10–3 = 38(.0)
fluorine
4(d) mass of O = 3.87 g – 1.68 g = 2.19 (g)
mol of P and mol of O
1.68 / 31 OR 0.054.. 2.19 / 16 OR 0.13..
ratio of P to O
P = 0.054« / 0.054 O = 0.13« / 0.054..
= 1 = 2.5
whole number ratio and P2O5
= 2 = 5
4(e) the formula is P4O6 or (one mole of) P2O3 = 110 (g)
mass = 220 (g)