Question
Nitrogen dioxide, NO2, is an atmospheric pollutant and is formed in car engines.
(a) Explain how nitrogen dioxide is formed in car engines. [2]
(b) Nitrogen dioxide causes respiratory problems.
State one other adverse effect of nitrogen dioxide.[1]
(c) Nitrogen dioxide emissions can be reduced by adding an aqueous solution of urea, (NH2)2CO, to car exhaust gases.
The heat of the exhaust gases breaks down the urea into simpler substances.
(i) Name the type of reaction which occurs when a substance is heated and breaks down into simpler substances.[1]
(ii) One molecule of urea breaks down to form one molecule of ammonia and one other molecule.
Complete the chemical equation to show the formula of the other molecule formed in this reaction.
(NH2)2CO → NH3 + [1]
(iii) State the test for ammonia.[2]
test
observations
(d) The ammonia formed reacts with nitrogen dioxide to form nitrogen and water.
(i) Balance the equation for this reaction.
NO2 + NH3 → N2 + 12H2O [2]
(ii) State how the equation shows that the nitrogen in nitrogen dioxide is reduced.[1]
(iii) This reaction is a redox reaction.
State the meaning of the term redox.[1]
(e) 135 moles of urea, (NH2)2CO, is stored in the tank of a car.
Calculate the mass, in kg, of the stored (NH2)2CO.
mass of (NH2)2CO = kg [2]
(f) Another oxide of nitrogen formed in car engines is nitrogen monoxide, NO. A catalytic converter removes NO by reacting it with a gas formed by incomplete combustion of the fuel. Two non‑toxic gases are formed.
(i) Name the gas formed by incomplete combustion of the fuel.[1]
(ii) Name the two non‑toxic gases formed. and [1] [Total: 15]
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
3(a) nitrogen (from air) and oxygen (from air) react
react due to high temperatures (of engine)
3(b) acid rain
3(c)(i) (thermal) decomposition
3(c)(ii) HCNO
3(c)(iii) (damp red) litmus
(litmus) turns blue
3(d)(i) 6NO2 8NH3 7N2
either 6NO2 or 8NH3
all three balanced
3(d)(ii) (nitrogen) loses oxygen
3(d)(iii) reduction and oxidation occur
3(e) Mr urea = 60
135 × 60 = 8100 and g to kg conversion = 8.1(00) kg
3(f)(i) carbon monoxide
3(f)(ii) carbon dioxide and nitrogen
Question
Zinc and copper are elements next to each other in the Periodic Table.
(a) Zinc is obtained from zinc blende in a two-step process.
● In step 1, zinc blende is converted into zinc oxide.
● In step 2, zinc oxide is converted into zinc in a blast furnace.
Outline how each of these steps are done.
In your answer:
● give one chemical equation for each step
● describe how zinc is removed from the blast furnace in step 2.
step 1 ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
chemical equation ……………………………………………………………………………………………………….
step 2 ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
chemical equation ……………………………………………………………………………………………………….
removal of zinc in step 2 ……………………………………………………………………………………………..
(b) Name the alloy formed when zinc is mixed with copper.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(c) Copper is a transition element. It can have variable oxidation states.
State two other chemical properties of transition elements which make them different from
Group I elements.
1 ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
2 ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(d) A compound of copper can be used to test for water.
(i) State the full name of this compound of copper.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(ii) State the colour change that occurs when water is added to this compound of copper.
from …………………………………………………….. to ……………………………………………………….
(e) Aqueous potassium iodide reacts with aqueous copper(II) sulfate to produce iodine.
(i) Balance the chemical equation for this reaction.
![]()
(ii) Deduce the charge on the copper ion in CuI.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(iii) In terms of electron transfer, explain why copper is reduced in this reaction.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(iv) Identify the reducing agent.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
3. (a) roast zinc blende (in air)
2ZnS + \(3O_{2}\) → 2ZnO + \(2SO_{2}\)
add/react with coke
ZnO + C → Zn + CO OR 2ZnO + C → 2Zn + \(CO_{2}\)
(zinc is) distilled
(b) brass
(c) form coloured compounds / ions
act as catalysts
(d) (i) anhydrous copper(II) sulfate
(ii) white
blue
(e) (i) \(4KI+2CuSO_{4}\rightarrow 2CuI+I_{2}+2K_{2}SO_{4}\)
(ii) 1+
(iii) gains electron(s)
(iv) KI / potassium iodide / iodide (ions) / I–
Question
This question is about the halogens and compounds of the halogens.
(a) The properties of some halogens are shown in the table.
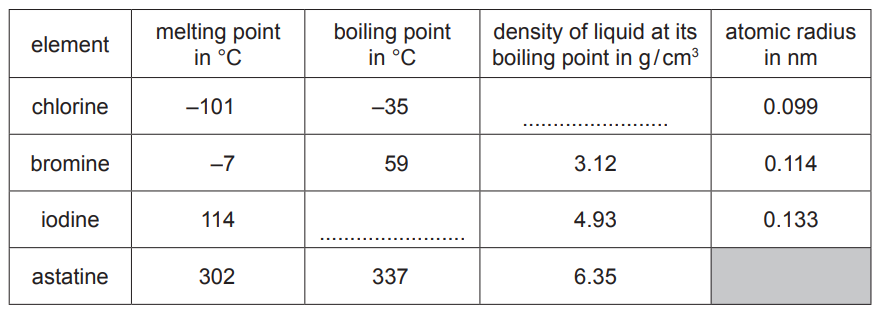
(i) Complete the table to estimate:[2]
-
- the density of liquid chlorine
- the boiling point of iodine.
(ii) Describe the trend in the atomic radius of the halogens down the group.[1]
(iii) Predict the physical state of bromine at 50°C.
Give a reason for your answer.[2]
(b) Bromine reacts with an aqueous potassium salt to form iodine and a different potassium salt.
Complete the word equation for this reaction.

(c) Fluorine is above chlorine in Group VII of the Periodic Table.
(i) Explain, using ideas about the reactivity of the halogens, why chlorine does not react with aqueous sodium fluoride.[1]
(ii) Balance the chemical equation for the reaction of fluorine with ammonia.
__NH3 + __F2 → N2 + 6HF [2]
(iii) A compound of fluorine has the formula XeO3F2.
Complete the table to calculate the relative molecular mass of XeO3F2.
Use your Periodic Table to help you.
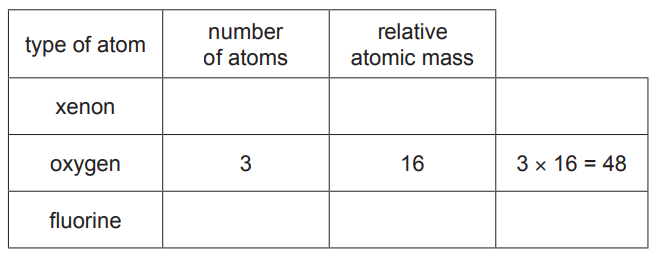
relative molecular mass = [2]
(iv) The compound XeO3F2 readily undergoes reduction.
What is meant by the term reduction?[1][Total: 13]
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a)(i) density of chlorine: any value between 1 g / cm3 and 3 g / cm3 inclusive (1)
boiling point of iodine: any value between 115 °C and 320 °C inclusive (1)
(a)(ii) increases (down the group)
(a)(iii) liquid (1)
50 °C is between the melting point and boiling point / 50 °C is higher than the melting point but lower than the boiling point (1)
(b) potassium iodide (1)
potassium bromide (1)
(c)(i) fluorine more reactive than chlorine ORA
(c)(ii) 2 (NH3) (1)
3 (F2) (1)
(c)(iii) 217 (2)
if 2 marks not scored 1 mark for F = 2 × 19 OR 38 (1)
(c)(iv) removal of oxygen / addition of hydrogen / gain of electrons / decrease in oxidation number