Question
Nitrogen dioxide, NO2, is an atmospheric pollutant and is formed in car engines.
(a) Explain how nitrogen dioxide is formed in car engines. [2]
(b) Nitrogen dioxide causes respiratory problems.
State one other adverse effect of nitrogen dioxide.[1]
(c) Nitrogen dioxide emissions can be reduced by adding an aqueous solution of urea, (NH2)2CO, to car exhaust gases.
The heat of the exhaust gases breaks down the urea into simpler substances.
(i) Name the type of reaction which occurs when a substance is heated and breaks down into simpler substances.[1]
(ii) One molecule of urea breaks down to form one molecule of ammonia and one other molecule.
Complete the chemical equation to show the formula of the other molecule formed in this reaction.
(NH2)2CO → NH3 + [1]
(iii) State the test for ammonia.[2]
test
observations
(d) The ammonia formed reacts with nitrogen dioxide to form nitrogen and water.
(i) Balance the equation for this reaction.
NO2 + NH3 → N2 + 12H2O [2]
(ii) State how the equation shows that the nitrogen in nitrogen dioxide is reduced.[1]
(iii) This reaction is a redox reaction.
State the meaning of the term redox.[1]
(e) 135 moles of urea, (NH2)2CO, is stored in the tank of a car.
Calculate the mass, in kg, of the stored (NH2)2CO.
mass of (NH2)2CO = kg [2]
(f) Another oxide of nitrogen formed in car engines is nitrogen monoxide, NO. A catalytic converter removes NO by reacting it with a gas formed by incomplete combustion of the fuel. Two non‑toxic gases are formed.
(i) Name the gas formed by incomplete combustion of the fuel.[1]
(ii) Name the two non‑toxic gases formed. and [1] [Total: 15]
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
3(a) nitrogen (from air) and oxygen (from air) react
react due to high temperatures (of engine)
3(b) acid rain
3(c)(i) (thermal) decomposition
3(c)(ii) HCNO
3(c)(iii) (damp red) litmus
(litmus) turns blue
3(d)(i) 6NO2 8NH3 7N2
either 6NO2 or 8NH3
all three balanced
3(d)(ii) (nitrogen) loses oxygen
3(d)(iii) reduction and oxidation occur
3(e) Mr urea = 60
135 × 60 = 8100 and g to kg conversion = 8.1(00) kg
3(f)(i) carbon monoxide
3(f)(ii) carbon dioxide and nitrogen
Question
Zinc is extracted from an ore containing zinc sulfide.
(a) State the name of this zinc ore…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. [1]
(b) This ore is converted to zinc oxide, ZnO.
Zinc oxide is then reacted with carbon.
(i) Write a chemical equation for the reaction of zinc oxide with carbon………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. [1]
(ii) State what type of chemical change happens to the zinc in zinc oxide in this reaction.
Explain your answer.
chemical change …………………………………………………………………………………………………..
explanation ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….[2]
(iii) Explain why aluminium is not extracted from aluminium oxide by heating with carbon………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. [1]
(iv) Suggest an alternative method for the extraction of zinc from zinc oxide……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… [1]
(c) Brass is an alloy of zinc.
Explain, in terms of particles, why brass is harder than pure zinc…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. [3]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
2(a) zinc blende
2(b)(i) $\begin{aligned} & \mathrm{ZnO}+\mathrm{C} \rightarrow \mathrm{Zn}+\mathrm{CO} \\ & \text { or } \\ & 2 \mathrm{ZnO}+\mathrm{C} \rightarrow 2 \mathrm{Zn}+\mathrm{CO}_2\end{aligned}$
2(b)(ii) chemical change: reduction (1)
explanation: oxygen is lost (1)
2(b)(iii) aluminium is more reactive than carbon
2(b)(iv) electrolysis
2(c) exists as layers (1)
(alloy) contains different sized (copper) atoms (1)
makes it more difficult for layers (of atoms) to slide over each slip/shift other (1)
Question
Aluminium is extracted from its ore. The ore is converted into pure aluminium oxide, which then
undergoes electrolysis as shown.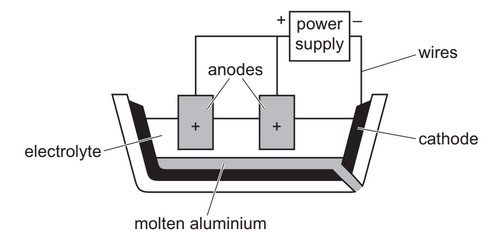
(a) (i) Name an ore of aluminium.
(ii) What is meant by the term electrolysis?
(b) Aluminium oxide has a melting point of about 2000°C, but the electrolysis process operates at
about 900°C.
(i) Name the compound added to aluminium oxide to reduce the operating temperature.
(ii) Suggest one benefit to the environment of reducing the operating temperature.
(iii) Write the ionic half-equation for the reaction taking place at:
the negative electrode (cathode) …………………………………………………………………………….
the positive electrode (anode) ………………………………………………………………………………..
(iv) Explain why the anodes need frequent replacement.
(c) Aluminium oxide reacts with acids and with alkalis.
(i) What term is used to describe an oxide that reacts with acids and with alkalis?
(ii) Aluminium oxide reacts with dilute sulfuric acid to form a salt.
State the name and write the formula of the salt formed.
name …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
formula ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
(iii) Aluminium oxide reacts with dilute sodium hydroxide to form a salt and one other product.
Name the other product.
(iv) Aluminium hydroxide, \(Al(OH)_3\), decomposes when heated to form aluminium oxide and
water.
Write the chemical equation for this reaction.
(v) Suggest the names of two other aluminium compounds that decompose when heated to
form aluminium oxide.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a) (i) bauxite
(ii) breakdown by (the passage of) electricity (1)
of an ionic compound in molten / aqueous (state) (1)
(b) (i) cryolite
(ii) less \(CO_2\) emission
(iii) \(Al^{3+} + 3e^- \rightarrow Al\)
any positive Al species gainig electron(s) (1)
correct species and balance (1)
\(2O^{2–} \rightarrow O_2 + 4e^–\)
any negative O species losing electron(s) (1)
correct species and balance (1)
(iv) anodes or carbon / graphite react with oxygen / \(O_2\) (1)
(form) carbon dioxide (1)
(c) (i) amphoteric
(ii) aluminium sulfate (1) \(Al_2(SO_4)_3\) (1)
(iii) water
(iv) \(2Al(OH)_3 \rightarrow Al_2O_3 + 3H_2O\)
species (1) balance (1)
(v) aluminium carbonate (1)
aluminium nitrate (1)