Question
(a)
The diagram shows two straight lines intersecting two parallel lines.
Find the values of a, b and c.
a = …………………………………………
b = …………………………………………
c = …………………………………………
(b)
Points R and S lie on a circle with diameter PQ.
RQ is parallel to PS.
Angle RPQ = 58°.
Find the value of x, giving a geometrical reason for each stage of your working.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
x = …………………………………………
(c)
Points A, B and C lie on a circle, centre O.
Angle AOC = 142°.
Find the value of y.
y = …………………………………………
Answer/Explanation
(a) 126
54
117
(b) angle [in a] semicircle is 90
Allied, co-interior [add to 180]
or
Angles in triangle [ = 180] and
alternate oe
32
(c) 109
Question
(a) The interior angle of a regular polygon is 156°.
Calculate the number of sides of this polygon.
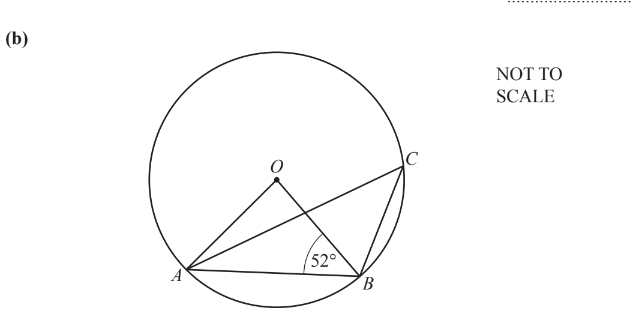
A, B and C lie on a circle, centre O.
Angle OBA = 52°.
Calculate angle ACB.
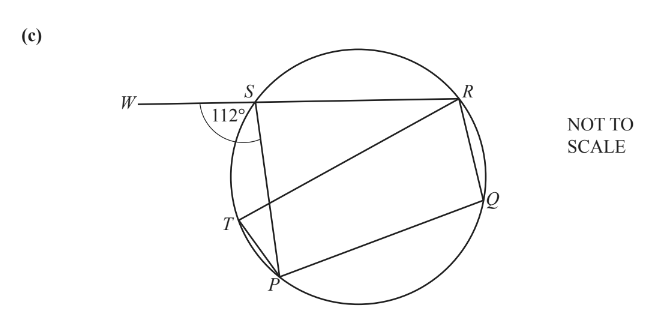
P, Q, R, S and T lie on a circle.
WSR is a straight line and angle WSP = 112°.
Calculate angle PTR.
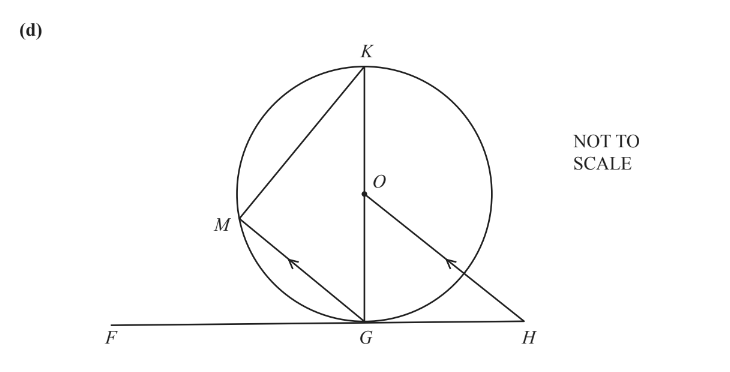
G, K and M lie on a circle, centre O.
FGH is a tangent to the circle at G and MG is parallel to OH.
Show that triangle GKM is mathematically similar to triangle OHG.
Give a geometrical reason for each statement you make.
Answer/Explanation
6(a) 15
6(b) 38
6(c) 68
6(d) Two pairs of equal angles identified
with fully correct reasons
Two or three pairs of angles equal [so similar] oe
Question
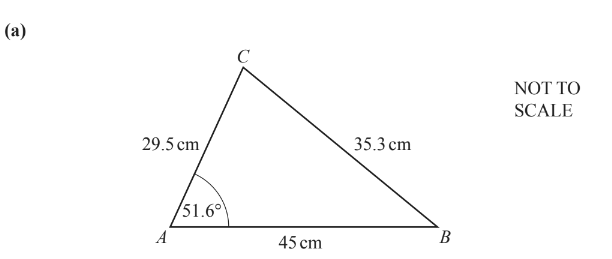
In triangle ABC, AB = 45cm, AC = 29.5cm, BC = 35.3cm and angle CAB = 51.6°.
(i) Calculate angle ABC.
(ii) Calculate the area of triangle ABC.
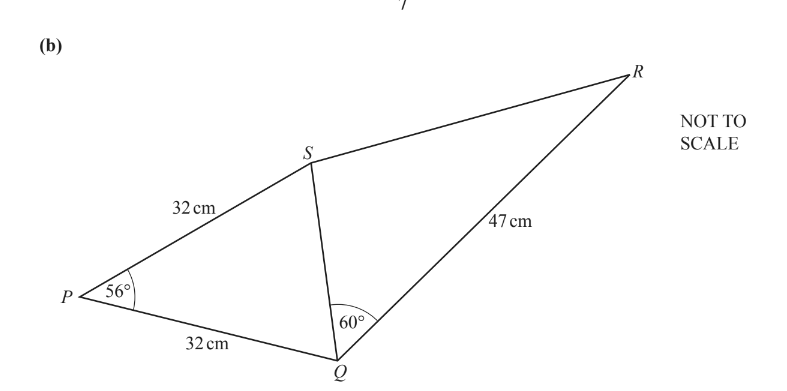
The diagram shows a quadrilateral PQRS formed from two triangles, PQS and QRS.
Triangle PQS is isosceles, with PQ = PS = 32cm and angle SPQ = 56°.
QR = 47cm and angle SQR = 60°.
(i) Calculate SR.
(ii) Calculate the shortest distance from P to SQ.
Answer/Explanation
4(a)(i) 40.9 or 40.91…
4(a)(ii) 520 or 520.0 to 520.2…
4(b)(i) 41.2 or 41.21 to 41.23
4(b)(ii) 28.3 or 28.25 to 28.29…