Question
A load is attached to a spring, as shown in Fig. 3.1. Two arrows indicate the vertical forces acting on the load. The spring and the load are stationary.
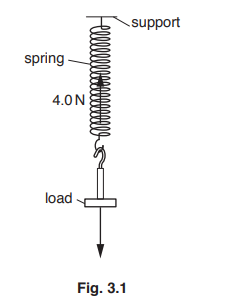
(a) (i) State the name of the force acting vertically downwards.
(ii) The vertical force that acts upwards is 4.0 N.
State the value of the force acting vertically downwards.
force = …………………………………………………………………………………………………. N
(b) The load is pulled downwards and then released. The load moves up and down.
Fig. 3.2 represents the vertical forces acting on the load at some time after it is released.
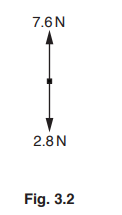
Calculate the resultant force on the load and state its direction.
resultant force =…………………………………………………………………………………………….. N
direction = ………………………………………………………………………………………………
(c) (i) State the principle of conservation of energy.
(ii) Eventually the load stops moving up and down.
Describe and explain why the load stops moving. Use your ideas about conservation of energy.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a)(i) gravity OR weight
(a)(ii) 4.0 (N)
(b) 4.8 (N)
Up(wards)
(c)(i) energy cannot be created or destroyed (but can be transformed)
(c)(ii) PE / KE / elastic energy of load / spring decreases / is transformed
Any one from:
to thermal energy
(which is) dissipated (to surroundings)
Question
Fig. 3.1 shows the load-extension graphs for two springs, A and B.
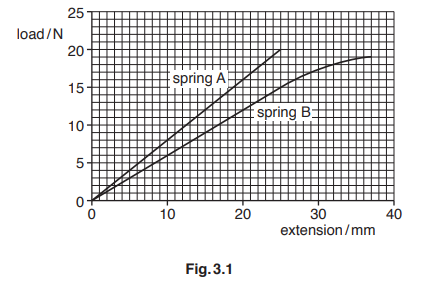
(a) Determine the extension of spring A for a load of 10 N.
extension = ………………………………………….. mm
(b) State which spring is easier to stretch and give a reason for your answer.
spring ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
reason ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(c) A different spring is suspended from the edge of a bench, as shown in Fig. 3.2.
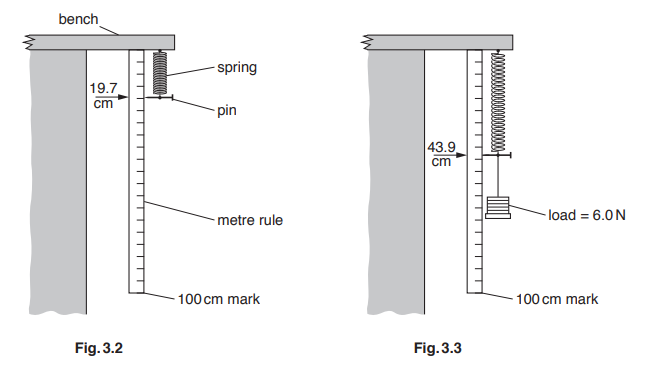
With no load on the spring, the pin points to 19.7 cm on the metre rule, as shown in Fig. 3.2.
When a load of 6.0 N is attached to the spring, the pin points to 43.9 cm, as shown in Fig. 3.3.
(i) Calculate the extension of this spring for a load of 6.0 N.
extension = ……………………………………………. cm
(ii) Describe how a student could use the equipment in Fig. 3.2 to obtain accurate readings for a load-extension graph for this spring.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a) 12.5 (mm)
(b) (spring) B
same load gives greater extension (than spring A) owtte
(c)(i) 43.9 – 19.7 or 24.2 (cm)
(c)(ii) Any two from:
measure the extension for different (number of 1.0 N) loads
repeat each reading (as each (1.0 N) load is removed) AND calculate average (extension for each load)
(take reading from ruler with) eye level with pin
