Question
Fig. 3.1 shows a see-saw. The see-saw is horizontal when not in use.
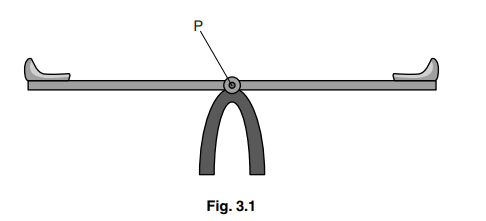
A small child sits on one seat of the see-saw. This creates a turning effect about point P.
(a) Which of these words means the turning effect of a force? Tick one box.
(b) State the scientific name for point P.
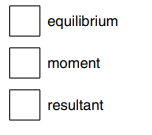
(c) A much heavier boy sits on the other end of the see-saw, as shown in Fig. 3.2.
The heavier boy moves slowly along the see-saw from end B until he reaches point P.
Describe and explain what happens to the see-saw.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a) middle box ticked – moment
(b) pivot/fulcrum
(c) any four from:
• (heavier) boy has greater force/weight/ moment
• when (heavier) boy lifts feet initially tips clockwise
• as boy moves his (clockwise) moment (about P) becomes less
• as distance (of boy’s weight) from the pivot decreases end B moves upward
• see-saw level o.w.t.t.e (when) turning forces balanced/ moments equal
• then end A tips down as anticlockwise moment is greater
Question
(a) A student has a metal object.
i. The student measures the mass of the object.
State the name of the equipment used to measure the mass.
ii. The mass of the metal object is 1260 g. The volume of the metal is 150 \(cm^3\).
Calculate the density of the metal. Include the unit.
density =
iii. The mass of the metal object is given in grams. State the mass in kg.
mass =
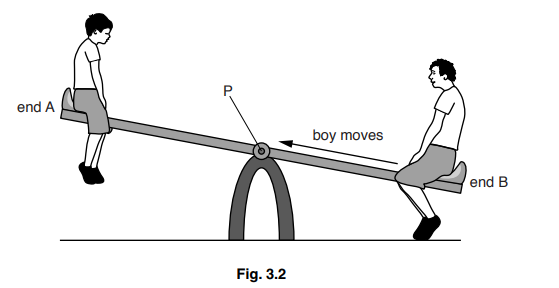
(b) A vase is placed on a table. Forces X and Y act on the vase, as shown in Fig. 1.1
The mass of the vase is 0.25 kg. The vase is not moving.
Calculate the value of force X and the value of force Y.
X…….
Y……..
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a) (i) balance
(ii) density = mass ÷ volume in any form
1260 ÷ 150
8.4
\(g / cm^3\)
(iii) 1.26 (kg)
(b) W = mg in any form
0.25 × 10
2.5 (N)
Both lines have 2.5 (N)
Question
(a) State what is meant by the centre of mass of a body.
(b) Fig. 4.1 shows an athlete successfully performing a high jump.
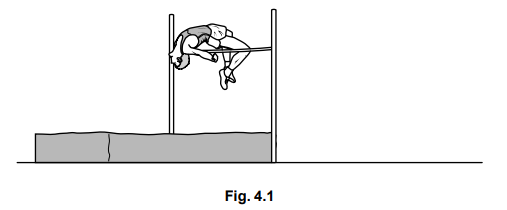
The height of the bar above the ground is 2.0 m. The maximum increase in gravitational potential energy (g.p.e.) of the athlete during the jump is calculated using the expression
g.p.e. = mgh.
Explain why the value of h used in the calculation is much less than 2.0 m.
(c) Fig. 4.2 shows, in order, five stages of an athlete successfully performing a pole-vault.
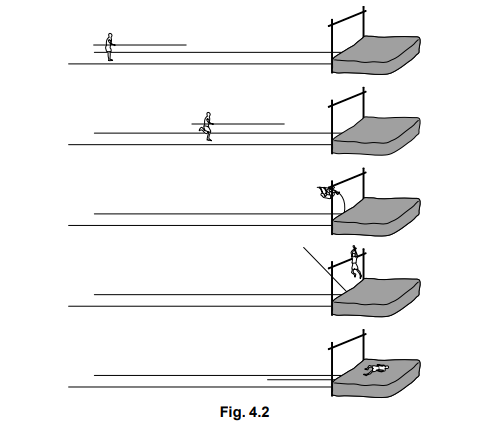
Describe the energy changes which take place during the performance of the pole- vault, from the original stationary position of the pole-vaulter before the run-up, to the final stationary position after the vault.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a) (The point in the body) where (all) the mass / weight / gravity acts / appears to act (owtte)
(b) h is the height through which the centre of mass/rises
OR centre of mass/rises (much) less than 2.0 m
OR centre of mass/of athlete is above the ground level
OR centre of mass/gravity passes under bar
Allow centre of gravity in place of centre of mass
(c) Standing: has chemical energy
Run-up: kinetic energy gained
Pole bent: has strain / elastic energy
Rise: potential energy gained
Fall: kinetic energy gained
On mat: has thermal / heat / sound / strain / elastic energy
