Question
(a) (i) State what is meant by the moment of a force about a point.
(ii) Fig. 2.1 shows a large crane on a construction site lifting a block of mass 14 000 kg.
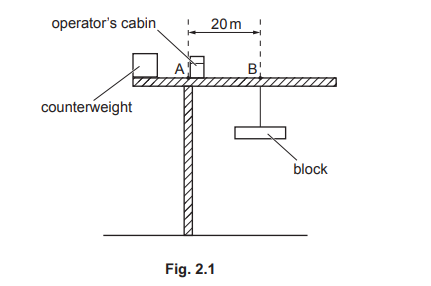
Calculate the moment about A due to the 14 000 kg block suspended from B.
moment =
(b) (i) Speed is a scalar quantity and velocity is a vector quantity. State the difference between a scalar quantity and a vector quantity.
(ii) Write down one other scalar quantity and one other vector quantity.
scalar quantity
vector quantity
(c) Fig. 2.2 shows two forces acting on an object. 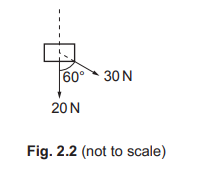
Draw a scale diagram to determine the resultant force acting on the object. State the scale you use.
scale
magnitude of resultant force =
direction of resultant relative to the direction of the 20 N force = …………………………………………………..
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a)(i) (moment of a force) is the turning effect (about a point / pivot)
(a)(ii) 2.8× \(10^6\) Nm
(moment = ) Fd in any form
(b)(i) scalar / speed has magnitude only OR scalar / speed has no direction
vector / velocity has magnitude and direction
(b)(ii) any scalar quantity
any vector quantity
(c) correct triangle or parallelogram drawn
resultant force (including correct arrow)
scale 1 cm = 4 N or 1 cm = 5 N
140 – 47 N AND 33° – 40° (anticlockwise from 20 N)
Question
Fig. 4.1 shows a heavy ball B of weight W suspended from a fixed beam by two ropes P and Q.
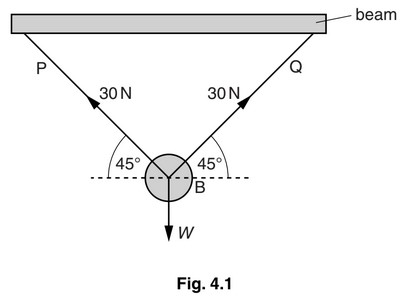
P and Q are both at an angle of 45° to the horizontal. The tensions in P and Q are each 30 N.
(a) In the space below, draw a scale diagram to find the resultant of the tensions in P and Q. Use
a scale of 1.0 cm to represent 5.0 N. Label the forces and show their directions with arrows.
resultant = …………………
(b) State the direction of the resultant.
(c) State the magnitude of W. magnitude of W = ………………………..
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a) 2 lines at 90° to each other of same length labelled 30N or 6cm
both lines 6.0 ± 0.2cm.
arrows on the two lines drawn, either head to tail
OR a complete square shown with diagonal and arrows on adjacent sides
resultant in range 40–45 N
(b) (vertically) upwards
(c) same as value in (a), only if answer to (a) is a force
OR 40–45 N
Question
(a) State the factors which completely describe a vector quantity.
(b) An aeroplane is flying towards the east in still air at 92 m / s. A wind starts to blow at 24 m / s towards the north.
Draw a vector diagram to find the resultant velocity of the aeroplane. Use a scale of 1.0 cm = 10 m / s.
resultant speed =
angle between resultant and easterly direction =
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a) Size / magnitude (NOT distance) and direction
(b) Vectors towards East and North with arrows correct by eye
Complete triangle or rectangle for candidate’s vectors Resultant with correct arrow Resultant 94 to 96m/s by scale OR 95m/s by calculation *Unit penalty applies Angle measured 13.5° – 15.5° OR 15° by calculation
