Question:
Fig. 2.1 shows water stored in a reservoir behind a hydroelectric dam.
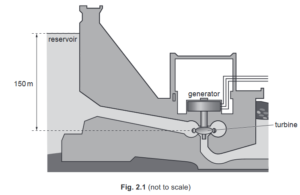
(a) State the form of the energy stored in the water in the reservoir that is used to generate electricity.
Answer/Explanation
Ans: gravitational potential energy
(b) The turbine is 150 m below the level of the water in the reservoir.
Atmospheric pressure is 1.0 × 10 5 Pa. The density of water is 1000 kg / m3 .
(i) Calculate the total pressure in the water at the turbine.
pressure = …………………………………………………
Answer/Explanation
Ans: 1.6 × 10 6 Pa
(p =) hρ g (in any form) or 150 × 1000 × 10 or 1.5 × 10 6
1.5 × 10 6 or 1.0 × 10 5 + {150 × 1000 × 10} or 1.0 × 10 5 + 1.5 × 10 6
or 1.6 × 10N
(ii) The turbine has a cross-sectional area of 3.5 m2 .
Calculate the force exerted on the turbine by the water.
force = …………………………………………………
Answer/Explanation
Ans: 5.6 × 10 6 N
(F =) pA (in any form) or 1.6 × 10 6 × 3.5
(c) The water flows to the turbine through a pipe of constant cross-sectional area.
Explain why the kinetic energy of the water in the pipe remains constant as it flows through the pipe.
Answer/Explanation
Ans: speed (of water) remains constant
otherwise density would decrease or gaps would appear in the water
or volume / density does not change or liquids incompressible or water enters / leaves at constant rate or quantity of water
remains constant
Question
A power station burns waste materials from farm crops to generate electricity.
(a) State and explain whether this process is renewable.
statement
explanation
(b) The power station uses some of its waste thermal energy to heat water for houses in a nearby town.
State one problem of using waste energy in this way if the power station is far from the town.
Suggest a way of reducing this problem.
(c) State two environmental consequences of burning coal to generate electricity.
consequence 1. …………………………………………………………………………………………………………
consequence 2. …………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a) renewable / yes
crops can be regrown (to replace resource) / waste materials don’t run out
(b) water will cool (too much) / thermal energy lost (during transfer)
lag/insulate (pipes) OR transport in a poor conductor of thermal energy
(c) any two from:
• air pollution / harmful gases / acid rain
• \(CO_2\) / greenhouse gases / contribution to global warming
• not renewable
• damage from mining / drilling or any valid environmental consequence of transport of coal
