Question
Fig. 3.1 shows a man pulling a truck of logs at a constant speed along a level path from P to Q against a resistive (frictional) force.
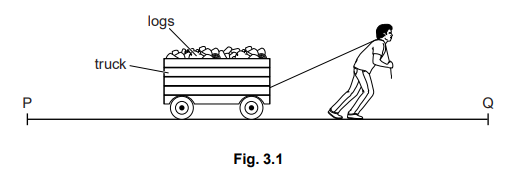
(a) State the two quantities, and their units, that must be measured in order to calculate the work done on the truck. [2]
quantity | unit |
|
|
|
|
(b) State the additional quantity needed in order to calculate the useful power of the man.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. [1]
(c) On another occasion, there is a smaller number of logs in the truck. The resistive force
on the truck is smaller when the truck is pulled from P to Q at the same speed as before.
What effect does this have on
(i). the force exerted by the man,
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(ii). the work done by the man,
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(iii). the useful power of the man?
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….[3]
(d) What form of energy stored in his body does the man use to pull the truck of logs?
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. [1] [Total: 7]
Answer/Explanation
Ans: (a) (frictional/tension/applied) force and newton/N distance and metre/m, centimetre/cm or correct metric unit
(b) time / speed
(c) (i) smaller / less / drops
(ii) smaller / less / drops
(iii) smaller / less / drops
(d) chemical
Question
An archer pulls the string of his bow, and moves the arrow to the position shown in Fig. 4.1.
He then releases the string so that the arrow is fired towards a target.
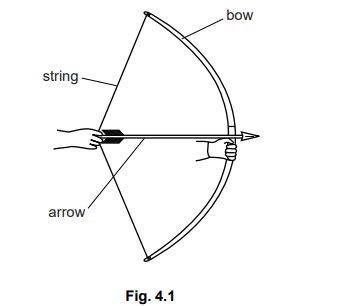
(a) The archer does work on the bow.
When is this work done? Tick one box.
 [1]
[1]
(b) What type of energy is stored in the bow because it is bent?
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. [1]
(c) What type of energy does the arrow have because it is moving?
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. [1]
(d) On another occasion, the archer fires the arrow so that it rises up to a maximum height before falling back down to the ground.
Use words from the following list to complete the sentences below.
gravitational potential, kinetic, thermal, maximum, minimum, zero
As the arrow rises, its…………………………………….. energy increases. At the top of
the flight, this energy is at a……………………………………….. As the arrow falls, this
energy is converted into………………………………………………………. energy.
When it hits the ground,
the energy of the arrow is converted into energy.[4] [Total: 7]
Answer/Explanation
Ans: (a) top box ticked
(b) elastic/strain/potential NOT gravitational PE
(c) kinetic ignore heat
(d) gravitational/gravitational potential/GPE/PE maximum kinetic OR thermal/allow heat thermal allow heater
