Question
Fig. 3.1 shows a man pulling a truck of logs at a constant speed along a level path from P to Q against a resistive (frictional) force.
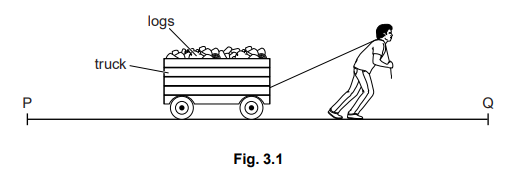
(a) State the two quantities, and their units, that must be measured in order to calculate the work done on the truck. [2]
quantity | unit |
|
|
|
|
(b) State the additional quantity needed in order to calculate the useful power of the man.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. [1]
(c) On another occasion, there is a smaller number of logs in the truck. The resistive force
on the truck is smaller when the truck is pulled from P to Q at the same speed as before.
What effect does this have on
(i). the force exerted by the man,
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(ii). the work done by the man,
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(iii). the useful power of the man?
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….[3]
(d) What form of energy stored in his body does the man use to pull the truck of logs?
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. [1] [Total: 7]
Answer/Explanation
Ans: (a) (frictional/tension/applied) force and newton/N distance and metre/m, centimetre/cm or correct metric unit
(b) time / speed
(c) (i) smaller / less / drops
(ii) smaller / less / drops
(iii) smaller / less / drops
(d) chemical
Question
Fig. 3.1 shows a model of a wind turbine used to demonstrate the use of wind energy to generate electricity. The wind is blowing towards the model, as shown.
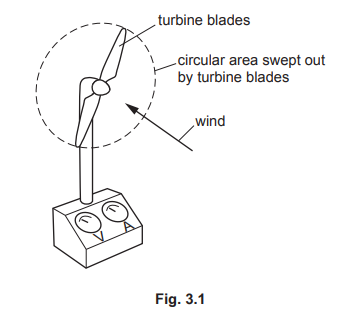
(a) The mass of air passing through the circular area swept out by the turbine blades each second is 7.5 kg. The kinetic energy of the air that passes through this circular area each second is 240 J.
(i) Calculate the speed of the air.
speed =…………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(ii) The kinetic energy of the air drives a generator. State the input power of the air passing through the turbine blades.
input power =…………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(b) The output current of the generator is 2.0 A. The output potential difference (p.d.) of the generator is 11 V.
(i) Calculate the output power of the generator.
output power =……………………………………………………………………………………………………
(ii) Calculate the efficiency of the wind turbine.
efficiency = ………………………………………………………………………………………………………… %
(c) The density of air is 1.3 kg /\(m^3\).
Calculate the volume of air passing through the circular area swept out by the turbine blades each second.
volume =…………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Answer/Explanation
Answer
(a)(i)KE = ½ \(mv^2\)in any form OR \(v^2\)= 2 × KE / m
OR 240 = ½ × 7.5 \(v^2\)
\(v^2\) = 2 × 240 / 7.5 OR (v=) √{2 × 240 / 7.5}
OR (v=) √{2KE / m }
= 8.0 m / s
(ii)240 W
(b)(i) P = VI in any form OR 11 × 2
22 W
(ii) (efficiency =) Po / Pi OR (efficiency =) Po / Pi
OR (efficiency =) (11 × 2 / 240) × 100
{efficiency = (11 × 2 / 240) × 100 =} 9.2 (%)
(c) ρ = m / V in any form OR (V =) m / ρ
OR (V = )7.5 / 1.3
(V = 7.5 / 1.3 =) 5.8 \(m^3\)
