Question
(a) Fig. 4.1 shows a smoke cell. The cell contains smoke particles and air molecules. It is lit from the side. A student views the motion of smoke particles in the cell by using a microscope.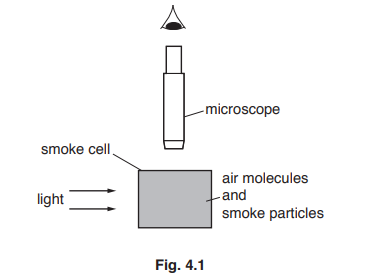
Describe and explain what the student sees when viewing the smoke particles through the microscope.
(b) Drops of water on a warm surface disappear after a short time. State the term used to describe this process. Explain the process, using your ideas about molecules.
name of process
explanation
Answer/Explanation
Answer
(a) Any four from:
specs/dots (of light)
(smoke/air particles) moving
(smoke/air particles) randomly
(because fast moving ) air molecules collide with smoke particles
(producing) Brownian motion
(b) evaporate/evaporation
high(er) energy/enough energy/fast(er) moving molecules OR molecules with great(er) KE
escape (from the water surface)
Question:
A teacher fills a copper can with solid wax and heats the can. She measures the temperature of the wax every minute. She continues heating once the wax has melted and stops heating when
the wax is boiling.
(a) (i) State the term used for the process that transfers thermal energy through the copper.
Answer/Explanation
Ans: conduction
(ii) Fig. 6.1 shows how the temperature of the wax changes as it is heated.
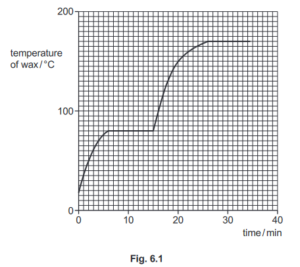
Using the graph in Fig. 6.1, determine:
1. the melting point of the wax ……………………………………………… °C
Answer/Explanation
Ans: 80 (°C)
2. the boiling point of the wax ……………………………………………… °C
Answer/Explanation
Ans: 170 (°C)
3. the time at which the wax starts to boil. ……………………………………………. min
Answer/Explanation
Ans: 26 (minutes)
(b) Describe the molecular structure of the wax in terms of the arrangement, separation and
motion of its molecules when it is a solid and when it is a gas.
solid wax …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
wax as a gas ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Answer/Explanation
Ans: (solid:) particles/molecules any three from:
(are) fixed in place/position/arrangement
regular spacing / pattern / arrangement
vibrating
close together
(gas:) particles/molecules any three from:
(are) moving randomly
at high speed
colliding (with each other/walls)
randomly arranged/no pattern
(relatively) far apart