Question
Fig. 9.1 shows an electric heating element in a beaker containing water. The heating element is switched on.
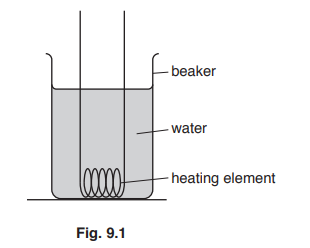
Explain how thermal energy is transferred throughout the water in the beaker. Use ideas about density and expansion in your answer.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Any five, in any order, from
water heats up
molecules gain kinetic energy / move faster/move further apart
water expands OR water volume increases
density (of water) decreases
warm water rises OR cool water falls
convection (current)
Question
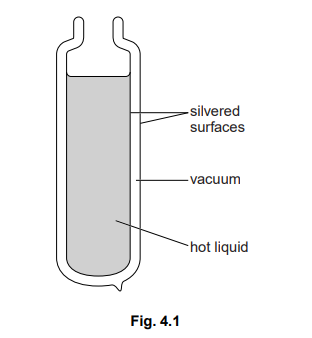
Fig. 4.1 shows a cross-section of a double-walled glass vacuum flask, containing a hot liquid.
The surfaces of the two glass walls of the flask have shiny silvered coatings.
(a) Explain
(i) why the rate of loss of thermal energy through the walls of the flask by conduction is very low,
(ii) why the rate of loss of thermal energy through the walls of the flask by radiation is very low.
(b) Suggest, with reasons, what must be added to the flask shown in Fig. 4.1 in order to keep the liquid hot.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a) (i) mention of vacuum OR glass is a poor conductor OR vacuum/gap between walls has no molecules/atoms/particles
(ii) surface/silver (of walls) is good reflector/poor absorber (of radiation) surface/silver (of walls) is poor emitter (of radiation)
(b) add a stopper/lid/bung/cover/top to reduce/prevent (loss of heat by) convection/ conduction/radiation/evaporation OR to prevent steam/hot vapour leaving made of insulator OR example of insulator to reduce/prevent (loss of heat by) convection/radiation/evaporation OR to prevent steam/hot air leaving