Question
A student uses a laptop computer. The student notices that the cable connecting the power
adapter for a laptop to the mains electricity supply is damaged as shown in Fig. 10.1.
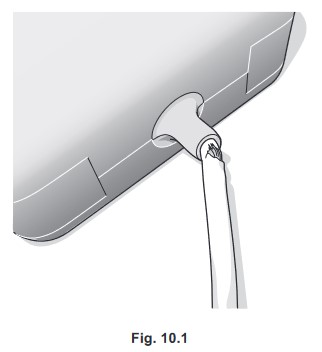
(a) State the hazard of using mains equipment with damaged insulation.
(b) Describe how a fuse protects a mains electrical appliance.
(c) The laptop computer uses a transformer to change the voltage of the mains electricity supply.
The input (primary) voltage is 120 V.
The input (primary) coil has 2000 turns and the output (secondary) coil has 200 turns.
Calculate the output (secondary) voltage from the transformer.
output (secondary) voltage = ……………………………………………… V
(d) State the name of the material used in the core of the transformer.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a) electrocution OR overheating / fire
(b) large current (in fuse)
(causes) fuse / it to melt
isolating appliance from supply OR prevents current in appliance OR breaks circuit
(c) \(V_s\) / \(V_p\) = \(N_s\) / \(N_p\)
\(V_s\) / 120 = 200 / 2000 OR \(V_s\) = 120 × 200 / 2000 OR \(V_s\) = 120 / 10
12 (V)
(d) (soft) iron
Question
Fig. 11.1 shows a relay.
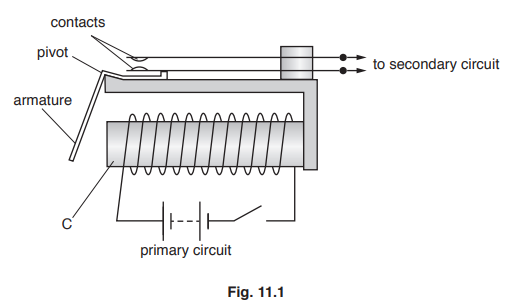
(a) The statements describe the action of a relay. They are not in the correct order.
P Current in the coil creates an electromagnet. Q Secondary circuit is completed.
R Armature pivots, closing the contacts. S Part C attracts the armature.
T The switch in the primary circuit is closed.
Place the statements in the correct order. One has been done for you.
(b) Fig. 11.1 includes the part labelled C, which is made from a metal.
State the name of the metal and explain why this metal is used in the electromagnet.
metal ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
explanation ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a)
T
P
(S)
R
Q
(b) (soft) iron
(forms a) temporary magnet
