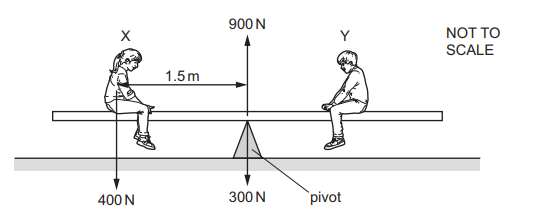
Question
Two people X and Y sit on a see-saw, as shown.
X weighs 400 N and sits 1.5 m from the pivot.
The weight of the see-saw is 300 N and acts through the pivot.
When the see-saw is balanced, the pivot pushes up on the see-saw with a force of 900 N. What is the weight of person Y and how far from the pivot is he sitting?
| weight of Y / N | distance from pivot / m |
A | 200 | 1.5 |
B | 200 | 3.0 |
C | 400 | 1.5 |
D | 400 | 3.0 |
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
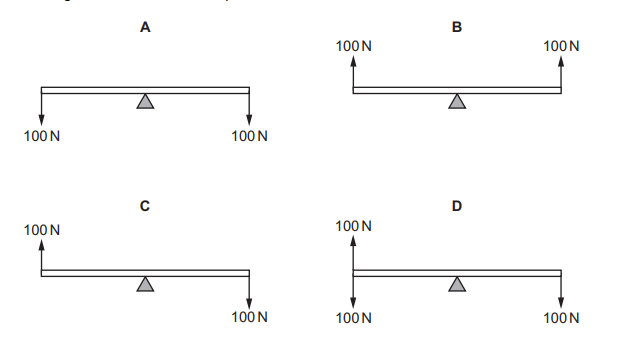
Question
A uniform rod rests on a pivot at its centre. The rod is not attached to the pivot. Forces are then
applied to the rod in four different ways, as shown. The weight of the rod can be ignored.
Which diagram shows the rod in equilibrium?
Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Question
Forces are applied to four identical objects. The lengths of the arrows indicate the magnitude of each force.
Which object is in equilibrium?
A B C D
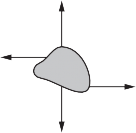
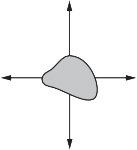
![]()

Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question
The diagram shows a uniform metre rule balanced at its mid-point.
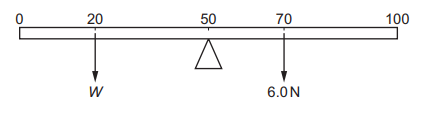
What is the weight W placed at the 20 cm mark?
A 0.25 N
B 4.0 N
C 9.0 N
D 21 N
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Equating the torque by both weights about mid-point
Question
A wooden plank rests in equilibrium on two rocks on opposite sides of a narrow stream.
Three forces P, Q and R act on the plank.
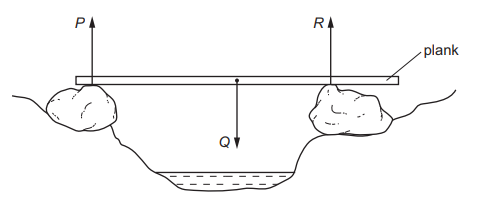
How are the sizes of the forces related?
A P + Q = R
B P + R = Q
C P = Q = R
D P = Q + R
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Given that ,
Question
The diagram shows an object of weight W and an object of weight Z balanced on a uniform metre rule.
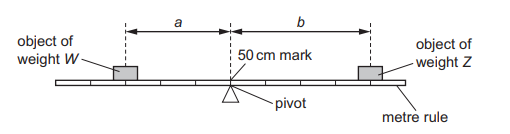
Which equation relating to W, Z, a and b is correct?
A 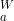 =
= 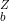
B W × Z = a × b
C W × a = Z × b
D W × (a + b) = Z
Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Question
A hole is drilled in a square tile. The diagram shows the tile hanging freely on a nail.
Where is the centre of mass of the tile?
Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Question
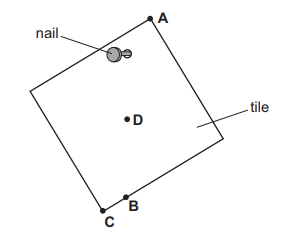
A student sets up the apparatus shown in the diagram to find the centre of mass of the card.
The student makes sure that the card, the string and the bob are all at rest.
What should the student do next?
Mark a horizontal line on the card level with the middle of the string.
Mark the line of the string on the card.
Pull the bob on the string to one side and release it.
Replace the bob with a heavier bob.
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B