Question
The diagram shows a section through part of the leg of an insect and antagonistic muscles X and Y. The tibia moves in the direction shown by the arrow when the muscle is flexing.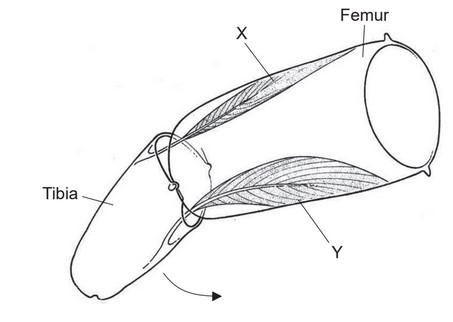
(a) Outline a reason for the muscles being described as antagonistic.
(b) Describe the role of muscle Y.
(c) Outline how the muscle attachment of insects differs from humans.
(d) Explain the role of calcium ions in muscle contraction.
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a)
cause opposite movements / pull in opposite directions / when one contracts the other relaxes;
(b)
a. flexor/flexion;
b. bends/flexes the leg/limb/joint;
(c)
insect muscle is attached inside (the skeleton) and human muscle outside (the skeleton);
insect muscle is attached to exoskeleton and human to endoskeleton/bones;
(d)
a. calcium released from sarcoplasmic reticulum;
b. calcium binds to troponin;
c. causes tropomyosin to move;
d. uncovers binding sites;
Question
(a) Outline how the properties of water make it an effective coolant for the body.
(b) Describe how changes in weather conditions affect the transport and loss of water in plants.
(c) Explain how water balance is restored in mammals when they are dehydrated.
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a)
a. hydrogen bonds hold water molecules together/make water molecules cohere;
b. evaporation requires breaking of hydrogen bonds / heat
needed to break hydrogen bonds
c. water has a high heat of vaporization/high latent heat;
d. evaporation of water/sweat removes heat from/cools the
skin/body;
(b)
a. water (vapor) lost by transpiration/through stomata;
b. transpiration/loss of water from leaves causes transport of water (in xylem);
Temperature:
c. faster/more water loss/transpiration/transport in hotter weather;
d. more heat for evaporation;
Humidity:
e. slower/less water loss/transpiration/transport in more humid weather;
f. faster diffusion of water (vapor) out of the leaf/through the stomata with low humidity
outside;
OR
no evaporation if air is saturated with water vapor/with 100% humidity;
Wind
g. faster/more water loss/transpiration/transport in windy/windier weather;
h. wind/air movement carries away water vapor from around the leaf/stomata;
i. high winds can cause stomatal closure and so reduce transpiration;
Drought
j. drought causes stomata to close so reduces loss/transport;
(c)
a. thirst;
b. more water drunk / more water reabsorbed from feces (in the colon/large intestine);
c. osmoreceptors in the hypothalamus detect dehydration/high solute concentration in blood;
d. ADH secreted;
e. by the pituitary gland;
f. ADH signals to collecting duct/DCT (cells) to increase permeability to water;
g. more aquaporins (in plasma membranes of collecting duct/distal convoluted tubule cells);
h. more water reabsorbed from filtrate (in collecting ducts/distal convoluted tubules);
i. reabsorption by osmosis / reabsorption due to medulla being hypertonic;
j. reabsorbed water passes into the blood/reduces the solute concentration of blood;
k. smaller volume/more concentrated/hypertonic urine formed;
