Question
Enzyme activity is affected by temperature and pH.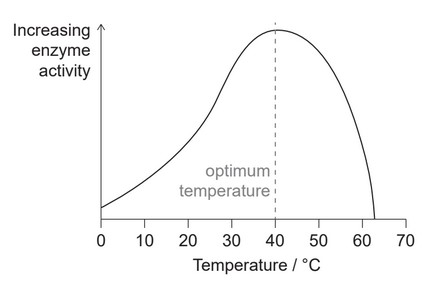
(a) Explain the decrease in activity of the enzyme on either side of the optimum temperature.
(b) In biotechnology, enzymes are used to transfer genes to bacteria. Outline how
two specific enzymes are used for the transfer.
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
a) a. as temperature rises/is higher (than optimal temperature), the enzyme is denatured;
b. as the temperature drops the enzyme molecules have less kinetic energy
OR
fewer successful collisions;
b) a. restriction enzymes/(restriction) endonucleases cut the gene and the bacterial/plasmid/vector
DNA in the same/specific restriction sites
OR
(restriction) endonucleases work by targeting a specific sequence of base pairs in DNA causing
both strands of the DNA to break apart;
b. (DNA) ligase attaches/inserts the gene to the bacterial/plasmid/vector DNA
OR
(DNA) ligase joins the vector and gene by fusing their sugar-phosphate backbones together (with
a covalent phosphodiester bond);
Question
The growing human population has an increasing demand for energy derived from crop plants.
At the same time, increasing droughts that are part of climate change make it difficult to grow
crops in some parts of the world.
(a) Outline energy flow through a community in a natural ecosystem.
(b) Explain how natural selection can cause traits such as drought resistance to develop
in wild plants.
(c) Suggest possible benefits and risks of using genetic modification to develop varieties
of crop plant with traits such as drought resistance.
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
a)
a. communities are made up of populations of different species;
b. plants receive energy from the sun/light;
c. convert it to chemical energy through photosynthesis;
d. chemical energy is stored in organic/C-compounds;
e. the energy is passed to other organisms through feeding / reference to food chain
f. respiration (of plants and animals) converts the chemical energy (of C-compounds) to other useful forms of energy;
g. eventually the chemical energy is lost as heat energy;
h. energy is non-recyclable/lost from a community/ecosystem;
i. energy losses between trophic levels limit food chains/mass of top trophic levels/only about 10% of energy is
transferred;
b)
a. (natural selection occurs if) there is variation in degree of drought resistance among members of a population/same
species;
b. variation is caused by mutations (when changes occur in the DNA/nucleic bases/chromosomes);
c. variation during meiosis occurs (with separation of chromosomes);
d. variation occurs during sexual reproduction (as different alleles combine);
e. some variations make some plants more drought-resistant;
f. example of variations: deeper roots/more storage tissue for water/thicker cuticles/less opening of stomata/other
verifiable variations;
g. these variations let some survive and reproduce better/have more offspring
OR
(these variations) confer selective advantage;
h. these variations/characteristics are passed onto offspring which survive better;
i. natural selection increases the frequency of these characteristics;
j. eventually leads to changes/evolution in the species / more drought-resistant plants;
c)
Benefits:
a. increase crop growth/food productivity;
b. with limited water/ less water is used;
c. increase amount of land available for food production in dry areas;
Risks:
d. these plants may out-compete other species in the community/may cause extinction of some
species/affect the food chains in the community;
e. the modified gene/recombinant DNA may pass to other organisms;
f. more grain requires more nutrients from the soil so its quality may diminish/monoculture issues;
- adminA Level Biology- Exam Style Practice Questions with Answer-Topic Wise-Paper 112 WeeksAll levels24 Lessons0 Quizzes6315 Students$11.00
- adminA Level Biology- Exam Style Practice Questions with Answer-Topic Wise-Paper 212 WeeksAll levels24 Lessons0 Quizzes6316 Students$11.00
- adminA Level Biology- Exam Style Practice Questions with Answer-Topic Wise-Paper 412 WeeksAll levels20 Lessons0 Quizzes6315 Students$11.00
- adminA Level Chemistry- Exam Style Practice Questions with Answer-Topic Wise-Paper 112 WeeksAll levels51 Lessons0 Quizzes6312 Students$11.00
- adminA Level Chemistry- Exam Style Practice Questions with Answer-Topic Wise-Paper 212 WeeksAll levels51 Lessons0 Quizzes6312 Students$11.00