Question
What is the unit of electrical energy in fundamental SI units?
A. kg m2 C–1 s
B. kg m s–2
C. kg m2 s–2
D. kg m2 s–1 A
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
C
Joule is SI unit of work or energy
As work = force x distance
= (mass x acceleration) x distance
\(work=mass \times\frac{distance}{(time)^2}\times distance\)
\(=\frac{mass\times (distance)^2}{time^2}\)
Hence J = \(\frac{kgm^2}{s^2}=kgm^2s^{-2}\)
Joseph runs along a long straight track. The variation of his speed v with time t is shown below.
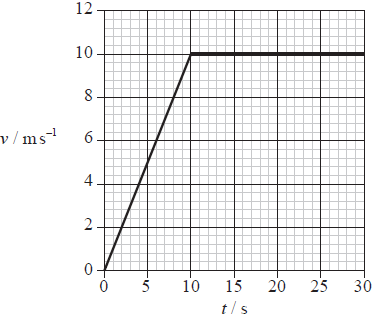
After 25 seconds Joseph has run 200 m. Which of the following is correct at 25 seconds?

Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
C
\(Average speed = \frac{total . distance}{total .time}\)
\(=\frac{200}{25}\rightarrow 8m/s\)
For instantaneous speed we will see the at \(t=25 sec \)
velocity at \(25 sec= 10 m/s\)
A block is attached to a stretched spring and then released. It moves from X to Y along a horizontal frictionless surface in the direction shown. The mass of the spring is negligible.

The equilibrium position of the system is P.
Which of the following is correct with respect to the changes in kinetic energy and potential energy of the block and of the spring as the block moves from X to Y?
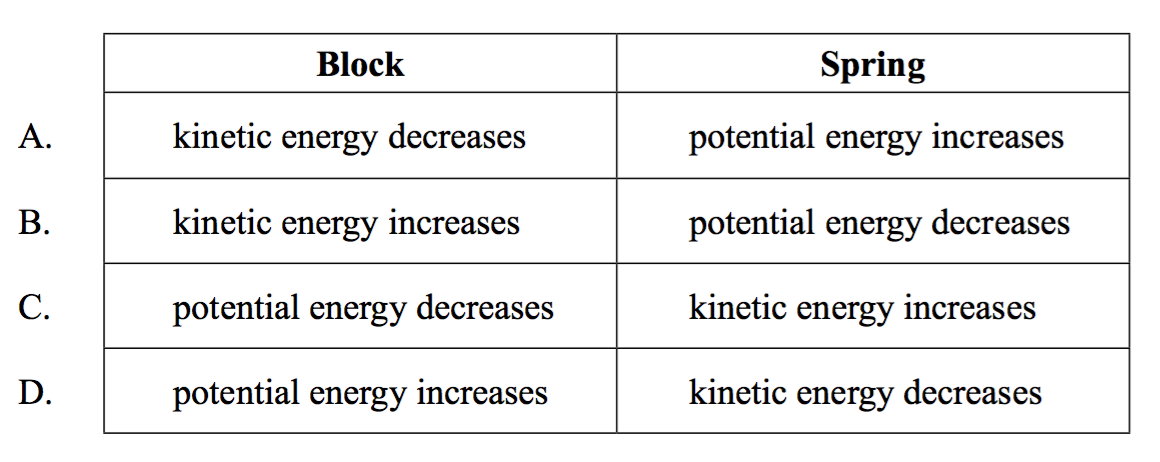
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
B
And kinetic energy will increase.
Two objects m1 and m2 approach each other along a straight line with speeds v1 and v2 as shown. The objects collide and stick together.

What is the total change of linear momentum of the objects as a result of the collision?
A. m1v1 + m2v2
B. m1v1 – m2v2
C. m2v2 – m1v1
D. zero
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
D
The total external force on the system is zero during collision, thus the total linear momentum is always conserved before and after the collision.
\(\Delta P = 0\)