Question
What is the order of magnitude of the wavelength of visible light?
A. 10-10 m
B. 10-7 m
C. 10-4 m
D. 10-1 m
Answer/Explanation
Ans:B
Visible light which is detectable by the human eye consists of wavelength ranging from approximately . So, the wavelength of light visible to the eye is of the order of
Question
A balloon rises at a steady vertical velocity of 10 m s–1. An object is dropped from the balloon at a height of 40 m above the ground. Air resistance is negligible. What is the time taken for the object to hit the ground?
A 10 s
B 5 s
C 4 s
D 2 s
Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
\(h = ut + \frac{1}{2} at^2\)
Taking upward direction positive
\(-40= 10t + \frac{1}{2}(-10) t^2\)
\(5t^2 -10t -40=0\)
\(t =4\) and \(t = -2\) ( not possible time can’t be negative)
Question
P and Q leave the same point, travelling in the same direction. The graphs show the variation with time t of velocity v for both P and Q.

What is the distance between P and Q when t = 8.0 s?
A 20 m
B 40 m
C 60 m
D 120 m
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Distance travelled by P\(=\frac{1}{2}(2)\times 10+(5\times 20)\)
\(=20+100\rightarrow 120\)
Distance travelled by \(Q=\frac{1}{2}(8)\times 40\)
\(=160\)
so , the difference \(= 160- 120 \rightarrow 40\)
Question
Two identical spheres, each of mass m and speed v, travel towards each other on a frictionless surface in a vacuum.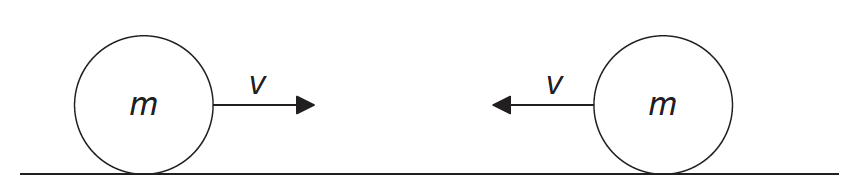
The spheres undergo a head-on elastic collision.
Which statement correctly describes the spheres after the collision?
A. The total momentum of the spheres is 2mv.
B. Each sphere has zero momentum.
C. The total kinetic energy of the spheres is mv2.
D. Each sphere has zero kinetic energy.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
C
Ref: https://www.iitianacademy.com/ib-physics-topic-2-mechanics-2-4-momentum-and-impulse-study-notes/
Before Collision
Total Momentum $=m_1 u_1+m_2 u_2=m u+m(-u)=0$
Total Energy:
$
\frac{1}{2} m_1\left(v_1\right)^2+\frac{1}{2} m_2\left(v_2\right)^2=\frac{1}{2} m v^2+\frac{1}{2} m v^2=m v^2
$