Question
For a particular nonlinear spring, the relationship between the magnitude of the applied force, F, and the stretch of the spring, x, is given by the equation \(F = kx^{1.5}\). How much energy is stored in the spring when is it stretched a distance \(x_1\)
(A) \(\frac{2k_1^{2.5}}{5}\)
(B) \(\frac{kx_1^{1.5}}{5}\)
(C) \(kx_1^{2.5}\)
(D) \(\frac{1}{2}kx_1^2\)
(E) \(1.5 kx_1^{0.5}\)
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
For a spring that is not linear (i.e., does not obey Hooke’s law) the energy stored is not \(\frac{1}{2} kx^2\). The magnitude of the energy stored will be equal to the magnitude of the work done to stretch the spring to \(x_1\)/ the steps to calculate the work are shown below.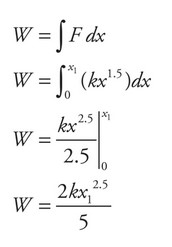
Question
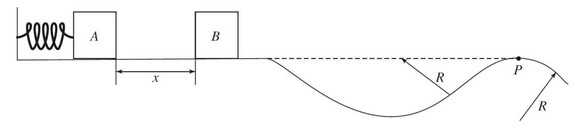
A massless spring with force constant k is attached at its left end to a wall, as shown above. Initially, block A and block B, each of mass M. are at rest on a frictionless, level surface, with block A in contact with spring (but not compressing it) and block B a distance x from block A. Block A is then moved to the left, compressing the spring a distance of d, and held in place while block B remains at rest. First block A is released, then as it passes the equilibrium position it loses contact with the spring. After block A is released it moves forward and has a perfectly inelastic collision with block B and then follows the frictionless, curved path shown above. The radius of the valley and the hill in the diagram are both R. Answer the following in terms of M, k, d, x, g, and R.
(A) Determine the speed of block A just before it collides with block B.
(B) Determine the speed of block B just after the collision occurs.
(C) Determine the change in kinetic energy for the collision.
(D) Determine the normal force on the boxes when they are at position P, the top of the hill.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a) Use Conservation of Energy since all of the energy stored in the spring will be transferred into kinetic energy of block A. Realize the compression of the spring is given as d.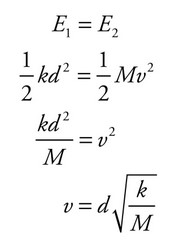
(b) Use Conservation of Linear Momentum for the collision. During a perfectly inelastic collision the two blocks stick together and continue at the same velocity.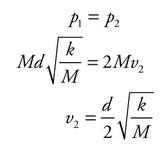
(c) The change in the kinetic energy during the collision is given by \(\Delta K = K_2 – K_1\).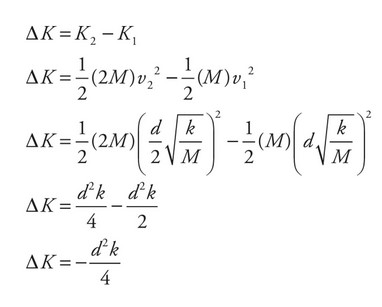
(d) (See diagram on the next page for more details.) The blocks are traveling along a curved path and at the top of the hill they are traveling with the same velocity as in block B since it is at the same elevation. They are also traveling in circular motion at the top of the hill. The gravitational force is pointing toward the center of the circle, so it will be positive and the normal force is pointing away form the center of the circle, so it will be negative.
