Question
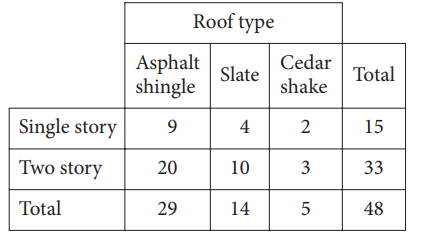
The table above shows the distribution of single-story and two-story houses in a neighborhood classified according to roof type. If one of the houses is selected at random, what is the probability that it will be a single-story house with a slate roof?
- \(\frac{4}{48}\)
- \(\frac{4}{15}\)
- \(\frac{4}{14}\)
- \(\frac{14}{48}\)
Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Question
The table below shows the number of lakes in the United Kingdom classified by alkalinity and depth.
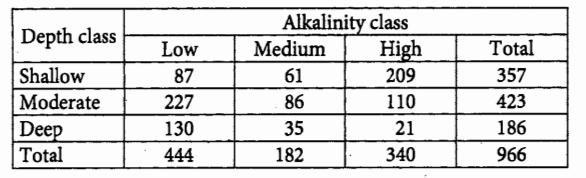
If a lake has high alkalinity, which of the following is closest to the probability that the lake also has a shallow depth?
- 0.22
- 0.37
- 0.59
- 0.61
Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Question
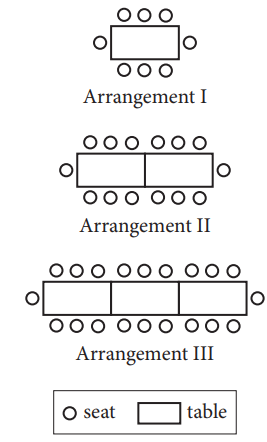
A project coordinator at a banquet hall is given the task of arranging seating for an awards ceremony. The figure above shows the first three possible arrangements of tables and the maximum number of seats in each arrangement. If the number of seats in each successive arrangement is increased by 6 over the preceding arrangement, which of the following represents the maximum number of seats around \(n\) tables?
- \(6n\)
- \(2(3n + 1)\)
- \(6(n + 1)\)
- \(6(n + 3)\)
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question
In a basket of 13 apples, there are 3 McIntosh apples, 4 Gala apples, and 6 Red Delicious apples. If Juanita selects an apple at random, what is the probability that she will not select a Gala apple?
- \(\frac{1}{13}\)
- \(\frac{3}{13}\)
- \(\frac{4}{13}\)
- \(\frac{9}{13}\)
- \(\frac{10}{13}\)
Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Question
Of the 26 cookies in a tin, the most common type is oatmeal. What is the probability that a cookie randomly selected from the tin is not oatmeal?
- \(\frac{1}{26}\)
- \(\frac{6}{13}\)
- \(\frac{1}{2}\)
- \(\frac{25}{26}\)
- It cannot be determined from the information given.
Answer/Explanation
Ans: E
Question
If one of the positive factors of 40 is to be chosen at random, what is the probability that the chosen factor will not be a multiple of 10?
- \(\frac{3}{7}\)
- \(\frac{5}{7}\)
- \(\frac{3}{8}\)
- \(\frac{5}{8}\)
- \(\frac{7}{8}\)
Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Question
0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9
A number is to be chosen at random from the list above. If \(x\) is the probability that the number 3 will be chosen, \(y\) is the probability that the number 5 will be chosen, and \(z\) is the probability that the number 8 will be chosen, which of the following is true?
- \(x=y=z\)
- \(x<y<z\)
- \(z<y<x\)
- \(x=y\) and \(y<z\)
- \(x<y\) and \(y=z\)
Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
