Question
Match the List I with List II. [NEET 2021]
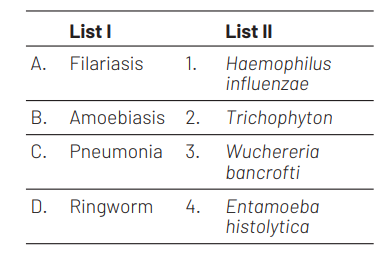
Choose the correct answer from the options given below.
A B C D
(a) 4 1 3 2
(b) 3 4 1 2
(c) 1 2 4 3
(d) 2 3 1 4
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
(A)-(3), (B)-(4), (C )-(1), (D)-(2)
Filariasis or elephantiasis is caused by filarial worm known as Wuchereria bancrofti. It affect the lymphatic vessels of lower limbs resulting in gross deformities. Amoebiasis is a protozoan disease caused by Entamoeba histolytica which parasite the large intestine causing constipation, abdominal pain, etc. Pneumonia is a bacterial disease caused by, Haemophilus influenzae and Sterptococcus pneumoniae bacteria. These bacteria infect the alveoli leading to several problems in respiration. Ringworm is a fungal disease. Trichophyton, Microsporum are responsible for this disease, resulting in appearance of dry scaly lesions on various parts as the symptoms of this disease.
Question
Match the following columns and select the correct option from the codes given below. [NEET (Oct.) 2020]
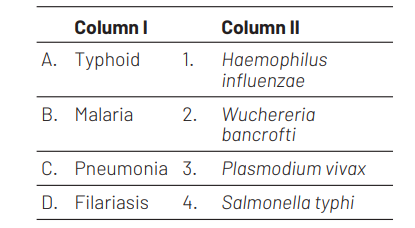
Codes
A B C D
(a) 4 3 1 2
(b) 3 4 2 1
(c) 1 3 2 4
(d) 1 2 4 3
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Option (a) is the correct match which is as follows Typhoid is caused Salmonella typhi. Malaria is caused by Plasmodium vivax. Pneumonia is caused by Haemophilus influenzae. Filariasis is caused by Wuchereria bancrofti.
Question
Match the following diseases with the causative organism and select the correct option. [NEET (Sep.) 2020]
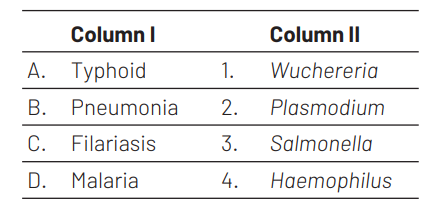
A B C D
(a) 3 4 1 2
(b) 2 1 3 4
(c) 4 1 2 3
(d) 1 3 2 4
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Typhoid is caused by bacterium Salmonella typhi. Typhoid fever is a type of enteric fever. It spreads by drinking water contaminated with the faeces of an infected person. Fever that starts low and increases daily, possibly reaching as high as 104.9 F (40.5 C), muscle aches, sweating, loss of appetite and weight loss, abdominal pain and diarrhoea or constipation are the symptoms of typhoid. Pneumonia is caused by bacterium Haemophilus influenzae. It is a small, Gram-negative, facultative anaerobic organism which causes infection in the upper respiratory tract. The bacteria are usually transmitted by droplets in the air from a sneeze, cough or close conversation with an infected person. Filariasis is a parasitic disease caused by infectious worms called Wuchereria. These spread by blood-feeding insects such as black flies and mosquitoes. Malaria is a life-threatening disease caused by Plasmodium parasite. It’s typically transmitted through the bite of an infected Anopheles mosquito. Infected mosquitoes carry the Plasmodium species. After bite, the parasite is released into the bloodstream where it matures and begin to infect RBCs resulting in symptoms that occur in cycles that last two to three days at a time.
Question
The infectious stage of Plasmodium that enters the human body is [NEET (Sep.) 2020]
(a) sporozoites
(b) female gametocytes
(c) male gametocytes
(d) trophozoites
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
The infectious stage of Plasmodium that enters the human body is sporozoites, present in salivary gland of Anopheles mosquito. The sporozoites grow and multiply in the liver to become merozoites. These merozoites invade the erythrocytes (RBCs) to form trophozoites, schizonts and gametocytes, during which the symptoms of malaria are produced.
Question
Identify the correct pair representing the causative agent of typhoid fever and the confirmatory test for typhoid. [NEET (National) 2019]
(a) Streptococcus pneumoniae / Widal test
(b) Salmonella typhi / Anthrone test
(c) Salmonella typhi / Widal test
(d) Plasmodium vivax/UTI test.
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Typhoid fever is caused by the bacterium Salmonella typhi and widal test is the confirmatory test for typhoid, which is based on antigen antibody reaction. Typhoid fever or enteric fever has the incubation period of 1 to 2 weeks and it is usually transmitted through contaminated food and water.
Question
In which disease does mosquito transmitted pathogen cause chronic inflammation of lymphatic vessels? [NEET 2018]
(a) Ringworm disease
(b) Ascariasis
(c) Elephantiasis
(d) Amoebiasis
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Elephantiasis is a helminthic disease caused by Wuchereria bancrofti. The infestation is transmitted by female Culex mosquitoes from one individual to the others. The worms live in the lymphatic system. Ascariasis is caused by Ascaris lumbricoides. It is an endoparasite of the small intestine of human beings. Amoebiasis is caused by Entamoeba histolytica. It lives in the large intestine of humans. Ringworm is a fungal skin disease.
Question
Which of the following sets of diseases is caused by bacteria? [NEET 2016, Phase II]
(a) Cholera and tetanus
(b) Typhoid and smallpox
(c) Tetanus and mumps
(d) Herpes and influenza
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Cholera and tetanus are diseases caused by bacteria. Cholera is caused by a bacterium Vibrio cholerae and tetanus is caused by a bacterium Clostridium tetani. Mumps, influenza, herpes and smallpox are viral diseases. Typhoid is a bacterial disease but it is not paired with a bacterial disease. Hence, option (a) is correct.
Question
Asthma may be attributed to [NEET 2016, Phase I]
(a) allergic reaction of the mast cells in the lungs
(b) inflammation of the trachea
(c) accumulation of fluid in the lungs
(d) bacterial infection of the lungs
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Asthma is an allergic reaction characterised by spasm of bronchi muscles because of effect of histamine released by mast cells.
Question
Which of the following diseases is caused by a protozoan? [CBSE AIPMT 2015]
(a) Syphilis
(b) Influenza
(c) Babesiosis
(d) Blastomycosis
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Babesiosis is a malaria-like parasitic disease caused by infection with Babesia bigemina, a genus of protozoa piroplasms.
Syphilis — Treponema pallidum (bacterium)
Influenza — Influenza virus Blastomycosis
Blastomyces —dermatitidis (fungus)
Question
Infection of Ascaris usually occurs by [NEET 2013]
(a) drinking water containing egg of Ascaris
(b) eating imperfectly cooked pork
(c) tse-tse fly
(d) mosquito bite
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Infection of Ascaris occurs in a healthy person due to the contaminated water, vegetables, (raw or uncooked) fruits, etc. Mosquitos bite causes malaria due to the entry to Plasmodium parasite into the blood by mosquito. Eating imperfectly cooked pork causes trichinosis disease (parasitic disease). Tse-tse fly causes trypanosomiasis, an infection of the central nervous system.
Question
Widal test is carried out to test [CBSE AIPMT 2012, 10]
(a) malaria
(b)diabetes mellitus
(c) HIV/AIDS
(d) typhoid fever
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Widal test is one of the most reliable diagnostic tests for typhoid fever in developing countries since its introduction (over 100 years ago). This test demonstrates the presence of somatic $(\mathrm{O})$ and flagellar $(\mathrm{H})$ agglutinins to Salmonella typhi in the patients blood serum using suspensions of $\mathrm{O}$ and $\mathrm{H}$ antigens. Antigens of S. paratyphi $A$ and S. paratyphi $B$ are included in most commercial kits.
Question
Common cold differs from pneumonia in, that [CBSE AIPMT 2012]
(a) pneumonia is a communicable disease, whereas the common cold is a nutritional deficiency disease
(b) pneumonia can be prevented by a live attenuated bacterial vaccine, whereas the common cold has no effective vaccine
(c) pneumonia is caused by a virus, while the common cold is caused by the bacterium Haemophilus influenzae
(d) pneumonia pathogen infects alveoli whereas the common cold affects nose and respiratory passage but not the lungs
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Pneumonia is caused by the bacteria Diplococcus pneumoniae which infects the alveoli of lungs. It generally spreads through the sputum of patient. Fever, cold and difficulty in breathing are some common symptoms of pneumonia. It can be treated by the antibiotics. Common cold is caused by a variety of viruses, most commonly by rhinovirus (RNA virus). It spreads through droplet infection. It affects the upper respiratory tract but not the lungs. Nasal and bronchial irritation, sneezing and coughing are some common symptoms of cold.
Question
Ringworm in humans is caused by [CBSE AIPMT 2010]
(a) bacteria
(b) fungi
(c) nematodes
(d) viruses
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Ringworm refers to fungal infections occurring on the surface of the skin. Although the world is full of yeasts, moulds and fungi, only a few cause skin problems. These agents are called the dermatophytes. Some common dermatophytic fungi are Trichophyton rubrum, T. tensurans, $T$. interdigitale, $T$. mentagrophytes, Microsporum, Canis, Albugo candids and Epidermophyton floccosum.
Question
Which of the following is a pair of viral diseases? [CBSE AIPMT 2009]
(a) Ringworm, AIDS
(b) Common cold, AIDS
(c) Dysentery, common cold
(d) Typhoid, tuberculosis
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Common cold and AIDS are viral diseases, occur due to the rhino virus and Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) respectively. Viral diseases can not be treated by the use of antibiotics.
Question
Match the disease in column I with the appropriate items (pathogen/prevention/ treatment) in column II [CBSE AIPMT 2008]
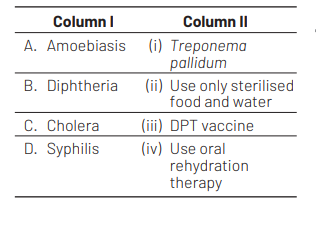
(a) A–(i), B–(ii), C–(iii), D–(iv)
(b) A–(ii), B–(iv), C–(i), D–(iii)
(c) A–(ii), B–(i), C–(iii), D–(iv)
(d) A–(ii), B–(iii), C–(iv), D–(i)
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Amoebiasis is caused by Entamoeba histolytica. Prevention of infection is entirely a matter of hygiene, both personal as well as municipal. Their prevention include use of properly cooked food and sterilized water.
Diphtheria is caused by Corynebacterium diphtheriae. The symptoms are fever, sore throat, severe damage to heart, nerve cell and adrenal glands. The vaccine DPT is used for diphtheria, pertussis and tetanus.
Cholera is caused by Vibrio cholerae, a Gram negative bacterium. It spreads by faecal contamination. The dehydration and loss of mineral salts can cause death. It is treated by use of oral rehydration therapy.
Syphilis is caused by Treponemo pallidum, a spirochaete and spread by sexual contact and is STD.
Question
Sickle-cell anaemia has not been eliminated from the African population because [CBSE AIPMT 2006]
(a) it is controlled by recessive genes
(b) it is not a fatal disease
(c) it provides immunity against malaria
(d) it is controlled by dominant genes
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Sickle-cell anaemia (in which RBCs become sickle-shaped and stiff) is a genetic disorder that is autosomal and linked to a recessive allele. It has not been eliminated from the African population because it provides immunity against malaria. People who are heterozygous for sickle cell allele are much less susceptible for falciparum malaria which is one of the main causes of illness and death in them. Thus, the sickle cell allele is maintained at high levels in populations where falciparum malaria is common.
Question
Both sickle-cell anaemia and Huntington’s chorea are [CBSE AIPMT 2006]
(a) bacteria-related diseases
(b) congenital disorders
(c) pollutant-induced disorders
(d) virus-related diseases
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Both sickle-cell anaemia and Huntington’s chorea are congenital genetic disorders. Sickle-cell anaemia was first reported by James Herrick (1904). In this disease the patient’s haemoglobin level reduced to half of the normal and the RBCs become sickle-shaped. A single mutation in a gene cause sickle-cell anaemia. Huntington’s chorea is caused by autosomal mutation which is dominant. The gene is present on chromosome number 4.
Question
Which one of the following is not correctly matched? [CBSE AIPMT 2004]
(a) Glossina palpalis – Sleeping sickness
(b) Culexpipiens – Filariasis
(c)Aedes aegypti – Yellow fever
(d) Anopheles culicifacies – Leishmaniasis
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Leishmaniasis or kala-azar is caused by a protozoan, Leishmania donovani. It is spread by sand fly. It is also known as dum-dum fever. It’s control includes eradication of vector, and use of antibiotics.
Question
Salmonella is related with [CBSE AIPMT 2001]
(a) typhoid
(b) polio
(c) TB
(d) tetanus
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Salmonella typhi causes typhoid fever. The incubation period is about two weeks. The patient first suffers from high fever of $40^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$ and continual headache. Polio, TB and tetanus are caused by polio virus, Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Clostridium tetani respectively. Polio is being eradicated by polio vaccine. TB and tetanus can be cured by antibiotics.
Question
Which of these is most infectious disease? [CBSE AIPMT 2001]
(a) Hepatitis-B
(b) AIDS
(c) Cough and cold
(d) Malaria
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Hepatitis may be transmitted via blood transfusions, contaminated equipment, unsterile needles (of drug addicts), or any body secretion like saliva, sweat, semen, breast milk, urine, faeces. Infection to healthy persons is prevented by proper vaccinations of hepatitis specially hepatitis-B.
Question
Bovine spongiform encephalopathy is a bovine disease. To which of the following human diseases it is related? [CBSE AIPMT 2000]
(a) Kala-azar
(b) Encephalitis
(c) Cerebral spondylitis
(d) Creutzfeldt Jacob disease
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathy (BSE) is a fatal brain disease known to exists in beef and other dairy cattle in UK, also known as mad cow disease. It is believed to be caused by prions.
Creutzfeldt-Jacob Disease (CJD) is a slow degenerative disease among human affecting central nervous system with dysfunction and degeneration of the brain. Some scientists have suggested that a few people in Britain might have contracted CJD by eating BSE-infected beef.
Question
A patient suffering from cholera is given saline drip because [CBSE AIPMT 1996, 2000]
(a) $\mathrm{Cl}^{-}$ions are important component of blood plasma
(b) $\mathrm{Na}{ }^*$ ions help to retain water in the body
(c) $\mathrm{Na}^{+}$ions are important in transport of substances across membrane
(d) $\mathrm{Cl}^{-}$ions help in the formation of $\mathrm{HCl}$ in stomach for digestion
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Severe diarrhoea, vomiting, watery stools are the chief symptoms of cholera. All these lead to dehydration. The toxin secreted by Vibrio cholerae causes a continuous activation of adenylate cyclase of intestinal epithelial cells. The resultant high concentration of cAMP triggers continual secretion of $\mathrm{Cl}^{-}, \mathrm{HCO}_3^{-}$and water into the lumen of the intestine. Administration of saline not only supports the sodium-potassium pump through which water in cell is restored, but glucose is also symported along with sodium.
Question
Koch’s postulates are not applicable to [CBSE AIPMT 1999]
(a) cholera
(b) leprosy
(c) TB
(d) diphtheria
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
To apply Koch’s postulates, we have to culture the suspected causal organism in vitro. Mycobacterium leprae cannot be cultured in vitro. Hence, Koch’s postulates are not applicable to leprosy because its incubation period is $2-5$ years. Cholera is caused by Vibrio cholerae. TB is caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Diphtheria is caused by Mycobacterium diphtheriae.
Question
Typhoid fever is caused by [CBSE AIPMT 1998]
(a) Giardia
(b) Salmonella
(c) Shigella
(d) Escherichia
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Salmonella typhi causes typhoid fever in human beings. It is characterised by constant fever due to the infection of intestine. Giardia is a flagellate protozoan, lamblia species of this protozoan causes disease giardiasis, a prolonged diarrhoeal disease of humans. Bacterial genus Shigella causes shigellosis or bacillary dysentery. Escherichia coli is a facultative anaerobes, found in the intestine of human beings.
Question
Botulism caused by Clostridium botulinum affects the [CBSE AIPMT 1998]
(a) spleen
(b) intestine
(c) lymph glands
(d) neuromuscular junction
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Clostridium botulinum bacterium causes food poisoning (botulism). Clostridium is an obligate anaerobic endospore-forming Gram positive, rod-shaped bacterium. This bacterium produces an exotoxin which is highly toxic for the synaptic ends of the nerves where it blocks the release of acetylcholine. Later is a chemical necessary for the transmission of nerve impulse across the synapses.
Question
Diphtheria is caused by [CBSE AIPMT 1997]
(a) poisons released by living bacterial cells into the host tissue
(b) poisons released from dead bacterial cells into the host tissue
(c) poisons released by virus into the host tissues
(d) excessive immune response by the host’s body
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Toxins released from Corynebacterium diphtheriae cause diphtheria. Actually. bacterial cells do not contain gene for toxin production, i.e. a phage carries the gene for it. Only those lysogenised cell of C. diphtheriae which carry $\beta$-phage, can produce the toxin and cause diphtheria.
Question
Which of the following disease is now considered nearly eradicated from India? [CBSE AIPMT 1997]
(a) Smallpox
(b) Polio myelitis
(c) Plague
(d) Kala-azar
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Small-pox is an acute highly communicable viral disease. It is caused by virus named Variola virus. Now, it is eradicated from world including India by the mass polio vaccination compaign undertaken by government of India.
Question
Which of the following pair of diseases is caused by virus? [CBSE AIPMT 1996]
(a) Rabies, mumps
(b) Cholera, tuberculosis
(c) Typhoid, tetanus
(d) AIDS, syphilis
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Rabies (hydrophobia) is caused by a virus named as rabies virus. It is a lethal disease. Mumps is an infectious disease causing fever, difficulty in opening the mouth and painful swelling of the parotid glands which lie just below the lobe of the ear. It is caused by a paramyxovirus.
Question
In which one of the following pairs of diseases both are caused by viruses? [CBSE AIPMT 1996]
(a) Tetanus and typhoid
(b) Whooping cough and sleeping sickness
(c) Syphilis and AIDS
(d) Measles and rabies
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Measles and rabies are viral diseases.
Disease Pathogen
Measles Rubeola virus
Rabies Rabies virus.
Question
If all ponds and puddles are destroyed, the organism likely to be destroyed is [CBSE AIPMT 1993]
(a) Leishmania
(b) Trypanosoma
(c) Ascaris
(d) Plasmodium
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Anopheles is the host of malarial parasite Plasmodium is known to occur most favourably in stagnant water, ditches, ponds, moist and damp places. Destruction of all the ponds and puddles, i.e. the breeding places of larva and pupae will cause destruction in the number of Anopheles and Plasmodium.
Question
Give the correct matching of causative agent/germ and disease [CBSE AIPMT 1993]
(a) Anopheles – malaria
(b) Leishmania – sleeping sickness
(c) Glossina – kala-azar
(d) Wuchereria – filariasis
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Wuchereria bancrofti causes filariasis or elephantiasis.
Question
The part of life cycle of malarial parasite Plasmodium vivax, that is passed in female Anopheles is [CBSE AIPMT 1992]
(a) sexual cycle
(b) pre-erythrocytic schisogony
(c) exo-erythrocytic schisogony
(d) post-erythrocytic schisogony
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Sexual phase in the life cycle of Plasmodium occurs in the gut of mosquito. Sexual phase involves the gametocytes, megagametocytes (female) and microgametocytes (male) which reach the stomach of female Anopheles mosquito by sucking human blood.
Question
Who discovered Plasmodium in RBCs of human beings? [CBSE AIPMT 1991]
(a) Ronald Ross
(b) Mendel
(c) Laveran
(d) Stephen
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
In 1880, Charles Laveran discovered Plasmodium, the causative agent of malaria in RBCs of human beings. In 1897, Ronald Ross discovered oocytes of Plasmodium in the stomach of mosquito.
Question
Malignant tertian malarial is caused by [CBSE AIPMT 1991]
(a) Plasmodium falciparum
(b) P. vivax
(c) P. ovale
(d) P. malariae
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Malignant tertian malaria is caused by the malarial parasite, Plasmodium falciparum, whereas, P. vivax causes tertian malaria and benign tertian malaria; $P$. ovale causes mild tertian malaria and $P$. malariae causes Quartan malaria.
Question
In hot summer and cold winter, the number of malaria cases as well as Anopheles declines, reappearance of malaria in humid warm conditions is due to [CBSE AIPMT 1990]
(a) surviving malarial parasites in human carriers
(b) surviving sporozoites in surviving mosquitoes
(c) monkeys
(d) mosquito larvae in permanent waters
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
The reappearance of malaria in humid warm conditions is due to the mosquito larvae in permanent waters.
Question
Amoebiasis is prevented by [CBSE AIPMT 1990]
(a) eating balanced food
(b) eating plenty of fruits
(c) drinking boiled water
(d) using mosquito nets
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Amoebiasis or amoebic dysentery is caused by protozoan parasite Entamoeba histolytica that resides in the upper part of large intestine. It spreads through contaminated water and food containing adult form (trophozoite) or cyst of Entamoeba. Trophozoite damages intestinal wall by enzyme histolysin, reaches blood capillaries and feed on RBCs, bacteria, tissue debris, resulting in abdominal pain, acidic motions with mucus and blood. The disease can be prevented by drinking boiled and clean water and intake of fresh and hygienic food.
Question
The vector for sleeping sickness is [CBSE AIPMT 1989]
(a) house fly
(b) tse-tse fly
(c) sand fly
(d) fruit fly
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Trypanosoma gambiense is the causative agent of African sleeping sickness. Its primary host is man and the secondary (intermediate) host or vector is tse-tse fly (Glossina palpalis).
Question
The infective state of malarial parasite Plasmodium that enters human body is [CBSE AIPMT 1989]
(a) merozoite
(b) sporozoite
(c) trophozoite
(d) minuta form
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Sporozoites are small, spindle-shaped, uninucleate organisms present in the salivary glands of the mosquito. Sporozoites represent the infective stage, which along with saliva inoculates into the blood stream of human and undergo schizogony.
Question
Malaria fever coincides with liberation of [CBSE AIPMT 1989]
(a) cryptomerozoites
(b) metacryptomerozoites
(c) merozoites
(d) trophozoites
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Merozoites are the progeny of sporozoites, formed in the liver of human. These are produced several days after the initial infection, which enter the blood stream and infect erythrocytes.
