Question
Plasmid pBR322 has Pst I restriction enzyme site within gene $a m p^{\mathrm{R}}$ that confers ampicillin resistance. If this enzyme is used for inserting a gene for $\beta$-galactoside production and the recombinant plasmid is inserted in an E.coli strain [NEET 2021]
(a) it will not be able to confer ampicillin resistance to the host cell
(b) the transformed cells will have the ability to resist ampicillin as well as produce $\beta$-galactoside
(c) it will lead to lysis of host cell
(d) it will be able to produce a novel protein with dual ability
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
In plasmid vector $\mathrm{pBR322}$, two unique restriction sites Pstl arid Pvul are located within the $\operatorname{amp}^R$ gene and BamHI, Sall, etc., are located within the tet $^R$ gene. The presence of restriction sites within the marker genes tet $^R$ and $a^{a m p}{ }^R$ permits an easy selection for cells transformed with the I recombinant pBR322. When restriction enzyme BamHI or Sall is used, the DNA insert is placed within the gene tet $^R$ making it non-functional.
If this enzyme is used for inserting a gene for $\beta$-galactoside production and the recombinant plasmid is inserted in an E.coli strain, it will not be able to confer ampicillin resistance to the host cell.
Question
A specific recognition sequence identified by endonucleases to make cuts at specific positions within the DNA is [NEET 2021]
(a) degenerate primer sequence
(b) Okazaki sequences
(c) palindromic nucleotide sequence
(d) poly(A) tail sequence
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Palindromic nucleotide sequence is a specific recognition sequence in a double-standard DNA and RNA molecules that is identified by endonucleases to make cuts at specific positions. The sequence is the same when one strand is read from left to right and the other strand is read from right to left.
Question
Match the following techniques or instruments with their usage. [NEET (Oct.) 2020]
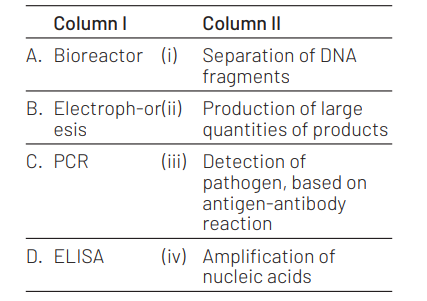
Select the correct option.
A B C D
(a) (iii) (ii) (iv) (i)
(b) (ii) (i) (iv) (iii)
(c) (iv) (iii) (ii) (i)
(d) (ii) (i) (iii) (iv)
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Option (b) is correct match which is as follows Bioreactors are used for the industrial scale production of products. Electrophoresis helps in the separation of DNA fragments based on their size.
PCR helps to amplify or generate large number of copies of nucleic acids. ELISA helps in the detection of pathogens based on the principle of antigen-antibody interaction.
Question
First discovered restriction endonuclease that always cuts DNA molecule at a particular point by recognising a specific sequence of six base pairs is [NEET (Oct.) 2020]
(a) Eco RI
(b) Adenosine deaminase
(c) Thermostable DNA polymerase
(d) Hind II
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Hind II was the first discovered endonuclease. It was isolated by Smith Wilcox and Kelley (1968) from Haemophilus influenzae bacterium. It always cuts bacterium. DNA at particular
point by recognising a specific sequence of six base pairs. It is known as the recognition sequence for Hind II and reads as 5′-GTC GAC-3′, 3′-CAG CTG-5′.
Question
Choose the correct pair from the following. [NEET (Sep.) 2020]
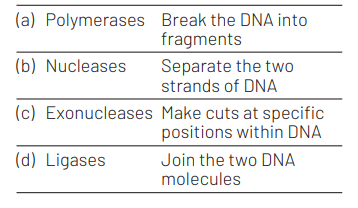
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
The correct pair is option (d). Rest option can be corrected as The main function of DNA polymerase is to synthesise DNA from deoxyribonucleotides, the building blocks of DNA. Nucleases hydrolyse the phosphodiester bonds of DNA and RNA. Exonucleases are a broad class of enzymes that cleave off nucleotides one at a time from the 3’ or 5’ ends of DNA and RNA chains.
Question
Identify the wrong statement with regard to restriction enzymes. [NEET (Sep.) 2020]
(a) They cut the strand of DNA at palindromic sites
(b) They are useful in genetic engineering
(c) Sticky ends can be joined by using DNA ligases
(d) Each restriction enzyme functions by inspecting the length of a DNA sequence
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Statement in option (c) is incorrect. It can be explained as follows. Restriction endonucleases make cuts at specific positions within the DNA known as palindromic sites. They function by inspecting the length of a DNA sequence. They are used in genetic engineering to form recombinant molecules of DNA. DNA ligases join the DNA fragments.
Question
A selectable marker is used to [NEET (Odisha) 2019]
(a) help in eliminating the non-transformants, so that the transformants can be regenerated
(b) identify the gene for a desired trait in an alien organism
(c) select a suitable vector for transformation in a specific crop
(d) mark a gene on a chromosome for isolation using restriction enzyme
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
To facilitate cloning into a vector, the vector requires a selectable marker, which helps in identifying and eliminating non-transformants and selectively permitting the growth of the transformants.
Question
The two antibiotic resistant genes on vector pBR322 are for [NEET (Odisha) 2019]
(a) Ampicillin and Tetracycline
(b) Ampicillin and Chloramphenicol
(c) Chloramphenicol and Tetracycline
(d) Tetracycline and Kanamycin
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
The two antibiotic resistance gene on E.coli cloning vector pBR322 are for ampicillin and tetracycline. Cloning vectors are DNA molecules that carry a foreign DNA segment and replicate
inside host cell. Plasmid in E.coli is a cloning vector
Question
Match the following enzymes with their functions
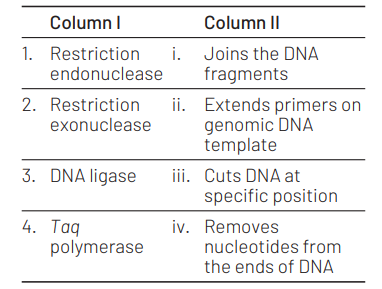
Select the correct option from the following. [NEET (Odisha) 2019]
1 2 3 4
(a) (iii) (i) (iv) (ii)
(b) (iii) (iv) (i) (ii)
(c) (iv) (iii) (i) (ii)
(d) (ii) (iv) (i) (iii)
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
The correct matches are
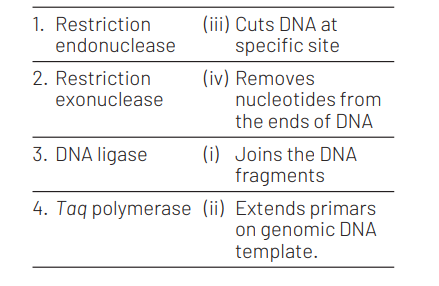
Question
Following statements describe the characteristics of the enzyme Restriction Endonuclease. Identify the incorrect statement. [NEET (National) 2019]
(a) The enzyme binds DNA at specific sites and cuts only one of the two strands
(b) The enzyme cuts the sugar-phosphate backbone at specific sites on each strand
(c) The enzyme recognises a specific palindromic nucleotide sequence in the DNA
(d) The enzyme cuts DNA molecule at identified position within the DNA
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
The statement about restriction enzymes that the enzyme binds DNA at specific sites and cuts only one of the two strands is incorrect.
These enzymes cut both the strands of DNA helix at specific sites in their sugar phosphate backbone. The sequences being recognised by restriction enzymes are called palindromic sequences which have same reading frame in both $5^{\circ} \rightarrow 3$ and $3^{\prime} \rightarrow 5$ directions. Rest statements are correct.
Question
Which of the following is commonly used as a vector for introducing a DNA fragment in human lymphocytes? [NEET 2018]
(a) $\lambda$ phage
(b) Ti-plasmid
(c) Retrovirus
(d) pBR 322
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Usually a retrovirus is used as a vector for introducing a DNA fragment in human cells. They are used as vector in gene therapy to introduce the desired gene so as to replace the functioning of a defected gene,.e.g. Severe Combined Immune Deficiency(SCID) is caused due to defect in the gene for the enzyme adenosine deaminase.
In gene therapy against it, lymphocytes are extracted from the bone marrow of the patient. These are grown in a culture outside the body. A functional ADA cDNA, using a retroviral vector, is then introduced into these lymphocytes. These are reinjected into the patient’s bone marrow. $\lambda$-phage allows cloning of DNA fragments upto $23 \mathrm{~Kb}$ lengths. Ti-plasmid is usually used for plants. pBR-322 is an artificial cloning vector, usually used for bacteria.
Question
A gene, whose expression helps to identify transformed cells is known as [NEET 2017]
(a) selectable marker
(b) vector
(c) plasmid
(d) structural gene
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
A gene whose expression helps to identify transformed cell is known as selectable marker. Usually, the genes encoding resistance to antibiotics, such as tetracycline, amphicillin, etc. are useful selectable markers for, e.g.E. coli. Concept Enhancer Plasmid $p B R^{222}$ has two resistance genes; ampicillin resistance $\left(a m p^{\mathrm{R}}\right.$ ) and tetracyclin resistance $\left(t^{{ }^2}{ }^2\right)$. These are considered as useful selectable markers.
Question
The DNA fragments separated on an agarose gel can be visualised after staining with [NEET 2017]
(a) bromophenol blue
(b) acetocarmine
(c) aniline blue
(d) ethidium bromide
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
The DNA fragments separated on an agarose gel can be visualised after staining with ethidium bromide. It is intercalating agent and a fluorescent agent. The stained DNA fragments are seen as bright orange coloured bands under UV-light.
Thinking process Intercalation is the insertion of molecules between the planar bases of DNA. This process is used as a method for analysing DNA. Intercalation occurs, when ligands of an appropriate size and chemical nature fit themselves in between base pairs of DNA. These ligands are mostly polycyclic, aromatic and planar and therefore often make good nucleic acid stains. Intensively studied DNA intercalator include ethidium bromide, proflavine, etc.
Question
Which of the following is not a feature of the plasmids? [NEET 2016, Phase I]
(a) Circular structure
(b) Transferable
(c) Single-stranded
(d) Independent replication
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Plasmid is extrachromosomal, double stranded, circular DNA, found in bacterial cells and some yeasts.
Discovery of plasmid has led to the revolution in biotechnological research.
Question
Which of the following is a restriction endonuclease? [NEET 2016, Phase I]
(a) Protease
(b) DNase I
(c) RNase
(d) Hind II
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Hind II is a restriction endonuclease. Restriction endonucleases are enzymes used for cutting of DNA at specific locations.
Hindll was the first restriction endonuclease isolated by Smith Wilcox and Kelley in 1968. It was found that it always cut DNA molecules at a particular point by recognising a specific sequence of six base pairs.
Question
Which of the following restriction enzymes produces blunt ends? [NEET 2016, Phase II]
(a) Sall
(b) Eco RV
(c) Xho
(d) Hind III
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Eco RV is a type Il restriction endonuclease isolated from strains of $E$. coli. It creates blunt ends. The enzyme recognises the palindromic 6-base DNA sequence and makes a cut at vertical line. The blunt ends are formed as Coverage site Blunt ends
Question
A foreign DNA and plasmid cut by the same restriction endonuclease can be joined to form a recombinant plasmid using [NEET 2016, Phase II]
(a) Eco RI
(b) Taq polymerase
(c) polymerase-III
(d) ligase
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
DNA ligases (genetic gum) are used in recombinant DNA technology to join two individual fragments of double-stranded DNA by forming phosphodiester bonds between them to produce a recombinant DNA (plasmid).
Question
The cutting of DNA at specific locations became possible with the discovery of [CBSE AIPMT 2015]
(a) restriction enzymes
(b) probes
(c) selectable markers
(d) ligases
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Restriction enzymes are DNA cutting enzymes found in bacteria. A restriction enzyme recognises and cuts DNA only at a particular sequence of nucleotides. For example, the bacterium Haemophilus aegyptius produces an enzyme named Hae lll that cuts DNA wherever, it encounters the sequence.
$
\begin{aligned}
& \text { 5′-G G C C-3′ } \\
& \text { 3′-C C G G-5′ }
\end{aligned}
$
Question
The DNA molecule to which the gene of interest is integrated for cloning is called [CBSE AIPMT 2015]
(a) transformer
(b) vector
(c) template
(d) carrier
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
The DNA molecule to which the gene of interest is integrated for cloning is called vector. It is a DNA molecule used as a vehicle to artificially carry foreign genetic material into another cell, where it can be replicated and/for expressed. A vector containing foreign DNA is termed as recombinant DNA.
Question
Which vector can clone only a small fragment of DNA? [CBSE AIPMT 2014]
(a) Bacterial artificial chromosome
(b) Yeast artificial chromosome
(c) Plasmid
(d) Cosmid
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Plasmid is a small fragment of DNA (about $10 \mathrm{Kbp}$ size) that is physically separate from and can replicate freely of chromosomal DNA within a cell. It can clone small DNA fragments.
Cosmid-45 Kbp
BAC-300-350 Kbp
YAC-1 Mbp/1,000 Kbp-2,500 Kbp)
Question
Commonly used vectors for human genome sequencing are [CBSE AIPMT 2014]
(a) T-DNA
(b) BAC and YAC
(c) Expression vectors
(d) T/A cloning vectors
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Commonly used vector for human genome sequencing are BAC(Bacterial Artificial Chromosome)and YAC. BAC is a DNA construct, based on a functional fertility plasmid (F plasmid) used for transforming and cloning in bacteria(E. coli)and YAC are genetically engineered chromosomes derived from the DNA of the yeast, (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) which is then ligated into a bacterial plasma.
Question
The colonies of recombinant bacteria appear white in contrast to blue colonies of non-recombinant bacteria because of [NEET 2013]
(a) Non-recombinant bacteria containing $\beta$-galactosidase
(b) Insertional inactivation of $\alpha$-galactosidase in non-recombinant bacteria
(c) Insertional inactivation of $\alpha$-galactosidase in recombinant bacteria
(d) Inactivation of glycosidase enzyme in recombinant bacteria
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
The colonies of recombinant bacteria appear white in contrast to blue colonies of non-recombinant bacteria because of insertional inactivation of alpha galactosidase in recombinant bacteria. Alpha galactosidase is a glycoside hydrolase enzyme that hydrolyse the terminal alpha galactosyl moieties from glycolipids and glycoprotein. It is encoded by the GLA gene. $\beta$-galactosidase is an exoglycosidase, which hydrolyses the $\beta$-glycosidic bond formed between a galactose and its organic moiety.
Question
The given figure is the diagrammatic representation of the E. coli vector $p B R 322$. Which one of the given options correctly identifies its certain component(s)? [CBSE AIPMT 2012]
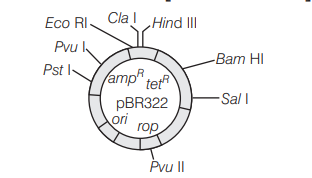
(a) ori–original restriction enzyme
(b) rop–reduced osmotic pressure
(c) Hind III, Eco RI-selectable markers
(d) $a m p^R$, tet $t^R$-antibiotic resistance genes
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
$a m p^{\mathrm{R}}$ and tet ${ }^{\mathrm{R}}$ are the antibiotic resistant genes. Ori represents the site of origin of replication, rop represents the proteins that take part in the replication of plasmid. Hind III, Eco RI are the recognition sites of restriction endonucleases.
Question
A single strand of nucleic acid tagged with a radioactive molecule is called [CBSE AIPMT 2012]
(a) vector
(b) selectable marker
(c) plasmid
(d) probe
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Probes are 15-30 bases long radioactive labelled oligonucleotides (RNA or DNA) used to detect complementary nucleotide sequences, used for disease diagnosis, etc.
Question
For transformation, microparticles coated with DNA to be bombarded with gene gun are made up of [CBSE AIPMT 2012]
(a) silver or platinum
(b) platinum or zinc
(c) silicon or platinum
(d) gold or tungsten
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Biolistics or gene gun is a direct or vectorless way used to introduce alien DNA into host cells. In this method of gene transfer, high velocity micro-particles of gold or tungsten, coated with DNA are bombarded on the plant cells.
Question
Which one of the following is a case of wrong matching? [CBSE AIPMT 2012]
(a) Somatic hybridisation-Fusion of two diverse cells
(b) Vector DNA – Site for tRNA synthesis
(c) Micropropagation – In vitro production of plants in large numbers
(d) Callus – Unorganised mass of cells produced in tissue culture
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Out of the following the statement (b) is wrong because a vector is a DNA molecule used as a vehicle to transfer foreign genetic material into desired cell. The tRNA is synthesised in the nucleus on a DNA tempelate. Only $0.025 \%$ of total DNA content codes for tRNA.
Question
Given below is a sample of portion of DNA strand giving the base sequence on the opposite strands. What is so, special shown in it? [CBSE AIPMT 2011]
$
\begin{array}{r}
5^{\prime} \text { – GAATTC – } 3^{\prime} \\
3^{\prime} \text { – CTTAAG – 5′ }
\end{array}
$
(a) Replication completed
(b) Deletion mutation
(c) Start codon at the $5^{\prime}$ end
(d) Palindromic sequence of base pairs
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Palindromic DNA is a base sequence of DNA, which reads the same forward or backward. It has similar sequence in both the strands. Different types of palindromic sequences are recognised by restriction endonucleases.
Question
There is a restriction endonuclease called Eco Rl. What does ‘co’ part in it stand for? [CBSE AIPMT 2011]
(a) Colon
(b) Coelom
(c) Coenzyme
(d) Coli
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Restriction endonuclease recognises a particular palindromic sequence and degrades the same. It was so, called because it restricted the growth of bacteriophage in the bacterium (e.g. E. coli). The convention for naming these enzymes is the first letter of the name comes from the bacterial genus; the second two letters come from the species, and the fourth letter from strain, e.g. Eco Rl comes from Escherichia coli RY13. Roman numbers following the names indicate the order in which the enzymes were isolated.
Question
Which one of the following is used as vector for cloning genes into higher organisms? [CBSE AIPMT 2010]
(a) Baculovirus
(b) Salmonella typhimurium
(c) Rhizopus nigricans
(d) Retrovirus
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Retroviruses are RNA containing animal viruses that replicate through a DNA intermediate. Retroviruses in animals have the ability to transform normal cells into cancerous cells. A better understanding of the act of delivering genes by pathogen in these eukaryotic hosts has generated knowledge to transform these tools of pathogen into useful vectors for delivering genes of interest of humans. Retroviruses have been disarmed and are now used to deliver desirable genes into animal cells.
Question
Restriction endonucleases are enzymes which [CBSE AIPMT 2010, 06, 02, 01, 98, 95]
(a) make cuts at specific positions within the DNA molecule
(b) recognise a specific nucleotide sequence for binding of DNA ligase
(c) restrict the action of the enzyme DNA polymerase
(d) remove nucleotides from the ends of the DNA molecule
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Restriction endonuclease recognises a specific DNA base sequence (recognition sequence or recognition site, restriction sequence or restriction site) and cleaves both the strands of DNA at or near that site. The enzyme cuts the DNA, generating restriction fragments with overhanging ends or blunt ends.
Question
The linking of antibiotic resistance gene with the plasmid vector became possible with [CBSE AIPMT 2008]
(a) DNA polymerase
(b) exonucleases
(c) DNA ligase
(d) endonucleases
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
The linking of antibiotic resistance gene with the plasmid vector became possible with the enzyme DNA ligase, which acts on cut DNA molecules and joins their ends. This makes a new combination of circular autonomously replication DNA created in vitro and is known as recombinant DNA.
Question
Which one of the following is commonly used in transfer of foreign DNA into crop plants? [CBSE AIPMT 2009]
(a) Trichoderma harzianum
(b) Meloidogyne incognita
(c) Agrobacterium tumefaciens
(d) Penicillium expansum
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
The uptake of foreign DNA or transgenes by plant cells is called transformation. A variety of techniques have been used to introduce transgenes into plant cells, these can be grouped into the following two categories (i) Agrobacteriummediated and (ii) direct gene transfers. Agrobacterium tumefaciens mediated transformation eliminates the need for regeneration from tissue explants.
Question
Restriction endonucleases [CBSE AIPMT 2004]
(a) are present in mammalian cells for degradation of DNA when the cell dies
(b) are used in genetic engineering for ligating two DNA molecules
(c) are used for in vitro DNA synthesis
(d) are synthesised by bacteria as part of their defense mechanism
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Restriction endonucleases are found in bacteria and are synthesised by bacteria as a part of their defense mechanism. They function in restricting the multiplication of viruses in bacterial cells by cutting up the genetic material of invading virus.
Question
Manipulation of DNA in genetic engineering became possible due to the discovery of [CBSE AIPMT 2003]
(a) restriction endonuclease
(b) DNA ligase
(c) transcriptase
(d) primase
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Manipulation of DNA in genetic engineering became possible due to the discovery of restriction endonuclease. These are isolated from bacterial cells, and are tools for molecular biologists.
Several hundred restriction enzymes are now known, each with a specific sequence requirement dictating where it will cut DNA. Therefore, digesting DNA with a restriction enzyme creates a characteristic set of fragments, which can be isolated by electrophoresis and subsequently analysed.
Question
A mutant strain of $\mathrm{T}_4$-bacteriophage R-II, fails to lyse the $E$. coli but when two strains $\mathrm{R}-\mathrm{I}^{\mathrm{x}}$ and $\mathrm{R}-1^y$ are mixed then they lyse the E. coli. What may be the possible reason? [CBSE AIPMT 2002]
(a) Bacteriophage transforms in wild
(b) It is not mutated
(c) Both strains have similar cistrons
(d) Both strains have different cistrons
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
The possible reason is that both strains have different cistron because the enzymes required forlysing $E$. coll could not be synthesised by the mutant strain. Two different strains had cistrons for synthesising different enzymes which acted together.
Question
In bacteria, plasmid is [CBSE AIPMT 2002]
(a) extrachromosomal material
(b) main DNA
(c) non-functional DNA
(d) repetitive gene
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Plasmid is a piece of circular DNA
molecule (mostly in bacteria but in yeast also) which is not part of the normal chromosomal DNA of a cell, and is capable of replicating independently.
Question
Plasmid is [CBSE AIPMT 2000, 01]
(a) fragment of DNA which acts as vector
(b) fragment which joins two genes
(c) mRNA which acts as carrier
(d) autotrophic fragment
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
A plasmid is a piece of DNA, mostly in bacteria (but also in yeast) not forming a part of normal chromosomal DNA of a cell, but capable of replicating independently of it. These often act as vehicles for gene transfer.
Question
Plasmids are suitable vectors for gene cloning becauseu [CBSE AIPMT 2000]
(a) these are small circular DNA molecules which can integrate with host chromosomal DNA
(b) these are small circular DNA molecules with their own replication origin site
(c) these can shuttle between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
(d) these often carry antibiotic resistance genes
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Plasmids replicate autonomously. These carry a signal situated at their replication origin which determines how many copies are to be made and this number can be artificially increased for cloning a given gene.
Question
Which of the following is related to genetic engineering? [CBSE AIPMT 1999]
(a) Mutation
(b) Plasmid
(c) Plastid
(d) Heterosis
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Plasmids are used as vectors in genetic engineering.
Question
Recombinant DNA is obtained by cleaving the pro-DNA by [CBSE AIPMT 1998]
(a) primase
(b) exonucleases
(c) ligase
(d) restriction endonuclease
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Recombinant DNA is obtained by cleaving the pro-DNA by restriction endonucleases. They can cleave DNA at specific base sequences called restriction sites.
Question
Genetic engineering is possible, because [CBSE AIPMT 1998]
(a) the phenomenon of transduction in bacteria is well understood
(b) we can see DNA by electron microscope
(c) We can cut DNA at specific sites by endonucleases like DNAs-1
(d) restriction endonucleases purified from bacteria can be used in vitro
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Genetic engineering is the manipulation of genetic material of an organism using enzyme restriction endonuclease.
Nathans and Smith (1970) isolated the first restriction endonuclease. Jackson, Symons and Paul Berg (1972) successfully generated recombinant DNA molecules in vitro.
Question
Two bacteria found to be very useful in genetic engineering experiments are [CBSE AIPMT 1998]
(a) Nitrosomonas and Klebsiella
(b) Escherichia and Agrobacterium
(c) Nitrobacter and Azotobacter
(d) Rhizobium and Diplococcus
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
The most important tool in genetic engineering of plants has been the Ti plasmid of soil bacterium, Agrobacterium tumefaciens. E. coli has also been extensively used for genetic engineering in animals, like in production of humulin, somatotropin, etc.
