Question
Match the List-I with List-II.
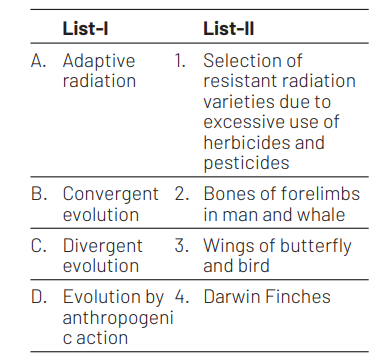
Choose the correct answer from the options given below. [NEET 2021]
A B C D
(a) 4 3 2 1
(b) 3 2 1 4
(c) 2 1 4 3
(d) 1 4 3 2
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
(A) 44$)(\mathrm{B}) \mathrm{H} 3),(\mathrm{CH}-(2),(\mathrm{D})-1)$
Adaptive radiation is a change that occur in organism by adapting according to the environment, e.g. Darwin finches.
Convergent evalution is a process where distant species develop similar structures, e.g. wings of butterfly and birds.
Divergent evolution is a process by which an inbreeding species diverges into two descendant species, e.g. bones of forelimbs in man and whales.
Evolution by anthropogenic action means evolution occurring due to human activities, e.g. selection of resistant varieties due to excessive use of herbicides and pesticides.
Question
Embryological support for evolution was proposed by [NEET (Oct.) 2020]
(a) Ernst Heckel
(b) Karl Ernst von Baer
(c) Charles Darwin
(d) Alfred Wallace
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Embryological support for evolution was proposed by Ernst Haeckel. He proposed biogenetic law in year 1864 . According to this law’structure of ancient origin develops earlier than structure of newer origin. In other words, it states “Ontogeny repeats phylogeny”, i.e. development of structures in an organism follow the same sequence as they evolved in his ancestors.
Question
The phenomenon of evolution of different species in a given geographical area starting from a point and spreading to other habitats is called [NEET (Oct.) 2020]
(a) saltation
(b) co-evolution
(c) natural selection
(d)adaptive radiation
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
The process of evolution of different species in a given geographical area starting from a point and literally radiating to other areas of geography (habitats) is called adaptive radiation.
Question
Embryological support for evolution was disapproved by [NEET (Sep.) 2020]
(a) Alfred Wallace
(b) Charles Darwin
(c) Oparin
(d) Karl Ernst von Baer
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Embryological support for evolution was disapproved by Karl Ernst von Baer. He observed the pattern of embryonic development in different species.
Question
Which of the following refer to correct example(s) of organisms which have evolved due to changes in environment brought about by anthropogenic action? [NEET (Sep.) 2020]
I. Darwin’s Finches of Galapagos islands.
II. Herbicide resistant weeds.
III. Drug resistant eukaryotes.
IV. Man-created breeds of domesticated animals like dogs.
(a) I and III
(b) II, III and IV
(c) Only IV
(d) Only 1
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
The correct option is ( b ) because Herbicide resistant weeds, drug resistant eukaryotes and man-created breeds of domesticated animals like dogs are examples of evolution by anthropogenic action. Darwin’s Finches of Galapagos islands are examples of natural selection, adaptive radiation and founder’s effect.
Question
Flippers of penguins and dolphins are examples of [NEET (Sep.) 2020]
(a) convergent evolution
(b) industrial melanism
(c) natural selection
(d) adaptive radiation
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Flippers of penguins and dolphins are examples of convergent evolution. They have similar function(helps in swimming) but different origin so, they are also called analogous organs. Penguin and dolphins are not closely related to each other but evolved similar traits(flippers) which represent convergent evolution. Hence analogous organs are a result of convergent evolution.
Question
In Australia, marsupials and placental mammals have evolved to share many similar characteristics. This type of evolution may be referred to as [NEET (Odisha) 2019]
(a) adaptive radiation
(b) divergent evolution
(c) cyclical evolution
(d) convergent evolution
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
In Australia, marsupials and placental mammals have evolved to share many similar characteristics. This type of evolution is referred to as convergent evolution.
Convergent evolution is the independent evolution of similar features in species of different lineages. For example, a number of marsupials, each different from the other evolved from an ancestral stock, but all within the Australian island continent. Also, marsupials in Australia resemble placental mammals in the rest of the world, they evolved in isolation after Australia separated from other continents.
Question
In a species, the weight of newborn ranges from 2 to $5 \mathrm{~kg} .97 \%$ of the newborn with an average weight between 3 to $3.3 \mathrm{~kg}$ survive whereas $99 \%$ of the infants born with weights from 2 to $2.5 \mathrm{~kg}$ or $4.5$ to $5 \mathrm{~kg}$ die. Which type of selection process is taking place? [NEET (National) 2021]
(a) Stabilising selection
(b) Disruptive selection
(c) Cyclical selection
(d) Directional selection
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
The given data represents stabilising selection. It eliminates individuals from both ends of a phenotypic distribution and hence maintains the same distribution average. In the given situation, most of the newborn of average weight $3-3.3 \mathrm{~kg}$ survive. Babies having more or less weight had low survival rate. Disruptive selection favours both extremes of continuous variation. Directional selection favours one extreme of continuous variation. Cyclical selection is regarded as a source of polymorphism.
Question
Among the following sets of examples for divergent evolution, select the incorrect option. : [NEET 2018]
(a) Brain of bat, man and cheetah
(b) Heart of bat, man and cheetah
(c) Forelimbs of man, bat and cheetah
(d) Eye of Octopus, bat and man
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Divergent evolution results in homologous structures. These organs have the same fundamental structure but are different in functions. Structural homology is seen in brain, heart and forelimbs of man, bat and cheetah. Eyes of Octopus, bat and man are examples of analogous organs which show convergent evolution. Therefore, option (d) is incorrect.
Question
The similarity of bone structure in the forelimbs of many vertebrates is an example of [NEET 2018]
(a) convergent evolution
(b) analogy
(c) homology
(d) adaptive radiation
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
The similarity of bone structure in the forelimbs of many vertebrates is an example of homology. The homologous organs have the same fundamental structure but are adapted to perform different functions, e.g. forelimbs of man, cheetah, whale and bat. Analogous organs show convergent evolution. These organs have similar functions but are different in their structural details and origin.
Development of different functional structures from a common ancestral form is called adaptive radiation.
Question
Analogous structures are a result of [NEET 2016, Phase I]
(a) convergent evolution
(b) shared ancestry
(c) stabilising selection
(d) divergent evolution
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Analogous structures are a result of convergent evolution. When organisms with completely different organisation, living in the same habitat come to possess superficial resemblance, this is known as convergent evolution.
Question
Which of the following structures is homologous to the wing of a bird? [NEET 2016, Phase I]
(a) Wing of a moth
(b) Hind limb of rabbit
(c) Flipper of whale
(d) Dorsal fin of a shark
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Wings of bird and flipper of whale are modified fore limbs of the two organisms so have same origin wings help in flying and flippers help in swimming, but this perform the different functions.
Question
The wings of a bird and the wings of an insect are [CBSE AIPMT 2015]
(a) homologous structures and represent divergent evolution
(b) analogous structures and represent convergent evolution
(c) phylogenetic structures and represent divergent evolution
(d) homologous structures and represent convergent evolution
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
The wings of a bird and the wings of an insect are analogous structures and represent convergent evolution. Analogous organs have the same function and are superficially alike only. However their fundamental structures are quite different in morphology. anatomy and embryonic origin. Analogy is an example of convergent evolution.
Question
Forelimbs of cat, lizard used in walking forelimbs of whale used in swimming and forelimbs of bats used in flying are an example of [CBSE AIPMT 2014]
(a) analogous organs
(b) adaptive radiation
(c) homologous organs
(d) convergent evolution
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Homologous organs are those organs which have a common fundamental anatomical plan and similar embryonic origin but perform varied functions.
Forelimbs of cat, lizard used in walking, forelimbs of whale used in swimming and forelimbs of bats used in flying are the example for homologous organs. All are the examples of modified forelimbs, with the same type of bones. They have become different due to the adaptations to different habitat.
Question
Which one of the following are analogous structures? [CBSE AIPMT 2014]
(a) Wings of bat and wings of pigeon
(b) Gills of prawn and lungs of man
(c) Thorns of Bougainvillea and tendrils of Cucurbita
(d) Flippers of dolphin and legs of horse
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Analogous organs are the structures of different species having similar or corresponding functions but different structure. They do not belong to the same evolutionary origin. Wings of bat are skin folds stretched mainly between elongated fingers but the wing of birds are feathers covering all along the arm. They look similar because they have a common use for flying, but their origin is not common.
Question
The eyes of Octopus and eyes of cat show different patterns of structure, yet they perform similar function. This is an example of [NEET 2013]
(a) homologous organs that have evolved due to convergent evolution
(b) homologous organs that have evolved due to divergent evolution
(c) analogous organs that have evolved due to convergent evolution
(d) analogous organs that have evolved due to divergent evolution
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
The analogous organs are not anatomically similar structures though they perform similar functions. Hence, analogous structures are $a$ result of convergent evolution, i.e. different structures evolving for the same function and hence, having similarity. Therefore, the eyes of Octopus and eyes of cat are examples of analogous organs, though they are different in structure but similar in function. Homologous organs develop along different directions due to the adaptations to various needs. This is divergent evolution and the structures are homologous.
Question
The process by which organisms with different evolutionary history evolve similar phenotypic adaptations in response to a common environmental challenge, is called [NEET 2013]
(a) natural selection
(b) convergent evolution
(c) non-random evolution
(d) adaptive radiation
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Convergent evolution occurs in unrelated group of organisms. It is the development of similar functional structures but in unrelated groups. The process of evolution of different species in a given geographical area starting from a point and literally radiating to other areas of geography is called adaptive radiation. Natural selection is the basis of evolution.
Question
Evolution of different species in a given area starting from a point and spreading to other geographical areas is known as [CBSE AIPMT 2012]
(a) adaptive radiation
(b) natural selection
(c) migration
(d) divergent evolution
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
The diversification of an ancestral group into two or more species in different habitats is called divergent evolution. When this involves large number of species to occupy different ritches, this is called adaptive radiation. Adaptive radiation is the process of evolution of different species in a given geographical area starting from a species of animals or plants and literally radiating to other areas of geography (habitats). Darwin’s finches represent one of best examples of this phenomenon.
Question
Which one of the following options gives one correct example each of convergent evolution and divergent evolution? [CBSE AIPMT 2012]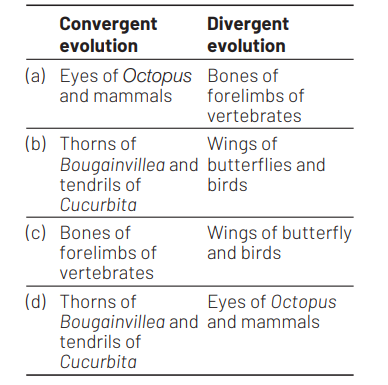
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Convergent evolution involves the independent development of similar structures in organisms that are not directly related. It is represented by analogous organs, e.g. eyes of Octopus and mammals, wings of insects and birds. In divergent evolution, same basic organ becomes adapted by specialisation to perform different functions.
It is represented by homologous organs, e.g. Bones of forelimbs of vertebrates (like seal’s flipper, bat’s wing, cat’s paw horse’s front leg and human hand). thorns of Bougainvillea and tendrils of Cucurbita.
Question
Peripatus is a connecting link between [CBSE AIPMT 2009]
(a) Ctenophora and Platyhelminthes
(b) Mollusca and Echinodermata
(c) Annelida and Arthropoda
(d) Coelenterata and Porifera
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Peripatus is connecting link between Annelide and Arthropoda. It is a living fossil that has similarities to both arthropods (such as absence of external segmentation, unjoined legs, the presence of cuticle, etc) and annelides (internal segmentation, eyes and segmentally arranged nephridia etc.l.
Question
Darwin’s finches are an excellent example of [CBSE AIPMT 2010, 08]
(a) adaptive radiation
(b) seasonal migration
(c) brood parasitism
(d) connecting links
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Adaptive radiation represents evolution of new forms in several directions from the common ancestral type. In 1831 , Darwin got an opportunity to travel by HMS Beagle for a voyage of world exploration. Beagle sailed to the Galapagos islands, here Darwin found a living laboratory of evolution.
The common birds of Galapagos Islands, the finches were markedly different. from the finches of main land. The closely related species of finches had beaks of different shapes and sizes and adapted for feeding on completely different diet showing adaptive radiation. The transitional fossil forms which show characteristic of two different groups of living animals are called connecting links, e.g. Archaeopteryx, Seymouria, etc.
Question
Thorn of Bougainvillea and tendril of Cucurbita are examples of [CBSE AIPMT 2008]
(a) analogous organs
(b) homologous organs
(c) vestigial organs
(d) retrogressive evolution
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Thorns of Bougairwilleo and tendrils of Cucurbita are homologous organs. These are modified branches and are axillary in position. It means axillary branches in Bougoinvillea are modified into thorns for protection from burrowing animals and in Cucurbito they are modified into tendrils for climbing.The analogous organs have almost similar appearance and perform the same function but these develop in totally different groups and are totally different in their basic structure and developmental origin. The phyllode af Ruscus or cladode of Asporagus are analagous to leaves of other plants. The vestigial or rudimentary organs are useless remnants of structures or organs, which might have been large and functional in ancestors, e.g. cutin covered stomata on the stem of cacti plants.
Question
Which one of the following statements is correct? [CBSE AIPMT 2007]
(a) Stem cells are specialised cells.
(b) There is no evidence of the existence of gills during embryogenesis of mammals
(c) All plant and animal cells are totipotent
(d) Ontageny repeats phylogeny
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Recapitulation theory or Biogenetic law states that ontogeny (development of embryo) is recapitulation of phylogeny (ancestral sequence).
Question
What is common to whale, seal and shark? [CBSE AIPMT 2007]
(a) Seasonal migration
(b) Thick subcutaneous fat
(c) Convergent evolution
(d) Homeothermy
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Distantly related animals fas whale, seal and shark) inhabiting similar habitats often develop similar morpholagical features that make them look similar. This is termed adaptive convergence of convergent evolution.
Question
When two species of different geneology come to resemble each other as a result of adaptation, the phenomenon is termed [CBSE AIPMT 2007]
(a) divergent evolution
(b) micro-evolution
(c) CD-evolution
(d) convergent evolution
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
In convergent evalution lineages show similar morphology under the influence of similar environmental factors.
Question
The finches of Galapagos islands provide an evidence in favour of [CBSE AIPMT 2007]
(a) special creation
(b) evolution due to mutation
(c) retrogressive evolution
Answer/Explanation
(d) biogeographical evolution
Ans. (d)
Darwin’s finches of Galapagos islands had common ancestors later on whose beaks modified according to their feeding habits. These provide evidence of geographical distribution.
Question
An important evidence in favour of organic evolution is the occurrence of [CBSE AIPMT 2006]
(a) analogous and vestigial organs
(b) homologous organs only
(c) homologous and analogous organs
(d) homologous and vestigial organs
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
An important evidence in favour of organic evolution is the occurrence of homologous and vestigial organs.
Homologous organs are those which have the common origin and are built on the same fundamental pattern but they perform different functions and have different appearances, e-g. whale’s flipper, bat’s wings, cat’s paws, harse’s front legs, bird’s wings, ax’s front legs and human hands. Vestigial organs in animals are those having no function now, in them, but had important functions in their ancestors. Analogous organs are quite different. in fundamental structure and embryonic origin but perform the same function. The study of analogous organs illustrates the occurrence of convergent evolution.
Question
Which of the following is the relatively most accurate method for dating of fossils? [CBSE AIPMT 2005]
(a) Radio-carbon method
(b) Potassium-argon method
(c) Electron-spin resonance method
(d) Uranium-lead method
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Electron spin resonance method is the most accurate method for dating of fossils. It measures number of charges occupying deep traps in crystal band gap.
Question
Using imprints from a plate with complete medium and carrying bacterial colonies, you can select streptomycin resistant mutants and prove that such mutations do not originate as adaptation. These imprints need to be used [CBSE AIPMT 2005]
(a) on plates with and without streptomycin
(b) on plates with minimal medium
(c) only an plates with streptomycin
(d) only an plates without streptomycin
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Plates having streptomycin allow to propagate only those bacteria which are resistant to the antibiotic. While those plates in which streptomycin is absent, both resistant and non-resistant bacteria can grow normally.
Question
Presence of gills in the tadpole of frog indicates that [CBSE AIPMT 2004]
(a) fishes were amphibian in the past.
(b) fishes evolved from frog-like ancestors
(c) frogs will have gills in future
(d) frogs evolved from gilled ancestors
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
According to biogenetic law of Ernst Haeckel [1866] ontogeny repeats phylogeny. Ontogeny is the life history of an organism while, phylogeny is the evolutionary history of the race of that organism. In other words we can say an organism repeats its ancestral history during its development. Hence, resemblance of amphibian to fish is seen in most systems of the body as both are cold blooded, both respire by gills (as tadpole of frogl both usually lay eggs in water leading to the conclusion that amphibians have originated from fishes.
Question
What kind of evidence suggested that man is more closely related with chimpanzee than with other hominoid apes? [CBSE AIPMT 2004]
(a) Evidence from DNA from sex chromosomes only
(b) Comparison of chromosomes morphology only
(c) Evidence from fossil remains and the fossil mitochondrial DNA alone
(d) Evidence from DNA extracted from sex chromosomes, autosomes and mitochondria
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Chimpanzee is more closely related to man than ather haminoids. It is evidenced by chromosome banding pattern, DNA extracted from sex chromosomes, autosomes and mitochondria. Molecular clock based on mitochondrial DNA are used to date recent events because this DNA mutates 5-10 times faster than nuclear DNA. Some similarities between human and chimpanzee are
(a) DNA matching shows human similarity with chimpanzee.
(b) There is little difference in banding pattern in chromosomes 3 and 6 in human and chimpanzee.
(c) Serum test indicates maximum homolagy between human and chimpanzee.
Question
Age of fossils in the past was generally determined by radio-carbon method and other methods involving radioactive elements found in the rocks. More precise methods, which were used recently and led to the revision of the evolutionary periods for different groups of organisms, include [CBSE AIPMT 2004]
(a) study of carbohydrates/proteins in fossils
(b) study of the conditions of fossilisation
(c) Electron Spin Resonance (ESR) and fossil DNA
(d) study of carbohydrates/proteins in rocks
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Electron Spin Resonance (ESR) measures number of charges occupying deep traps in crystal band gap. The basic principle of ESR is same as those for luminescence, i.e. electrans become trapped and stored as a result of ionising radiations e.9. dating of tooth enamel.
Question
Convergent evolution is illustrated by [CBSE AIPMT 2003]
(a) dogfish and whale
(b) rat and dog
(c) bacterium and protozoan
(d) starfish and cuttle fish
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Canvergent evolution is the acquisition of same or similar characters by distantly related lines of descent. Dogfish (pisces) and whale (mammals) have acquired aquatic characters though distantly related.
Question
Which one of the following describes correctly the homologous structures? [CBSE AIPMT 2003]
(a) Organs appearing only in embryonic stage and disappearing later in the adult
(b) Organs with anatomical similarities, but performing different functions
(c) Organs with anatomical dissimilarities, but performing same functions
(d) Organs that have no function now, but had an important function in ancestors
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Homologous structures are similar in origin but similar or dissimilar in function, such as pectoral fins of fish and forelimbs of horse are similar in structure but different in functions.
Question
Which of the following pair is homologous organ? [CBSE AIPMT 2002]
(a) Wings of birds and locust
(b) Wings of birds(sparrow) and pectoral fins of fish
(c) Wings of bat and butterfly
(d) Legs of frog and cockroach
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Homologous argans are the organs which have the same origin and similar basic structure but may differ in external appearance and function, wings of birds and pectoral fins of fish are examples of the same. Analogous organs are those organs which are anatomically different. but functionally same.
Question
According to fossils discovered up to present time origin and evolution of man was started from [CBSE AIPMT 2002]
(a) France
(b) Java
(c) Africa
(d) China
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
The first Hominid (ancestor from whom humans evolved] arose at a time when a change in weather led to the reduction in the size of the African forests favouring bipedalism.
Question
Sequence of which of the following is used to know the phylogeny? [CBSE AIPMT 2002]
(a) mRNA
(b) rRNA
(c) tRNA
(d) DNA
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
The genes for rRNAs tend to be highly conserved and are, therefore, often employed for phylogenetic studies.
Question
57 Reason of diversity in living being is [CBSE AIPMT 2001]
(a) mutation
(b) gradual change
(c) long term evolutionary change
(d) short term evolutionary change
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Though mutation provides the source of variation, the diversity in living beings is due to the natural selection of variations and consequent evolutionary change over a long period of time.
Question
Similarities in organisms with different genotype indicates [CBSE AIPMT 2001]
(a) micro-evolution
(b) macro-evolution
(c) convergent evolution
(d) divergent evolution
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Increase in resemblance over time of different evolutionary lineages lin one or more phenotypic characters] thereby increasing their phenetic similarities is called convergence or convergent evolution.
Question
Half-life period of $\mathrm{C}^{14}$ is about [CBSE AIPMT 2001]
(a) $ 500 \mathrm{yr}$
(b) $ 5730 \mathrm{yr}$
(c) 50 yr
(d) $5 \times 10^4 \mathrm{yr}$
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
$C^{14}$ takes about 5730 year for half the material to decay.
Question
Darwin’s finches provide an excellent evidence in favour of evolution. This evidence comes from the field of [CBSE AIPMT 2000]
(a) Biogeography
(b) Anatomy
(c) Embryology
(d) Palaeontology
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Biogeography is the study of the geographical distribution of life forms on earth. Darwin undertook a voyage on the ship HMS Beagle. The ship traversed the Southern hemisphere where life is most abundant and varied. Along the way. Darwin found different. forms of life very different from those in England. As he sailed southward along the South America, he found that similar species replaced each other. He thought that related species could have been modified according the environment. His views got confirmed on Galapagos islands (small group of Volcanic islands of the Western coasts of South Americal. Darwin found different modified forms of finches which seemed to have descended from mainland finches as a result of the natural selection.
Question
Which one of the following pair has homologous organs? [CBSE AIPMT 1999]
(a) Pectoral fins of a fish and forelimbs of a horse
(b) Wings of a bat and wings of cockroach
(c) Air sac of fish and lungs of frog
(d) Wings of a bird and wings of a butterfly
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Homologous organs are those organs which are originally and anatomically similar but functionally different. The forelimbs of vertebrates are built on same pentadactyl plan, though they may have different functions, e.g. in birds these are modified for flying.
Question
The age of the fossil of Dryopithecus on the geological time scale is [CBSE AIPMT 1998]
(a) $5 \times 10^2$ yr back
(b) $25 \times 10^6 \mathrm{yr}$ back
(c) $50 \times 10^6$ yr back
(d) $75 \times 10^5$ yr back
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Dryopithecus lived about 20-25 million years ago. Dryopithecus had the combined characters of great apes, ald world monkeys and man. The main structural characteristics of Dryopithecus are broad jaws, large canines, semi-erect walking, 5 cusped molars and absence of brow ridges.
Question
Which one of the following is a living fossil? [CBSE AIPMT 1997]
(a) Pinus longifolia
(b) Dailbergia sissoo
(c) Mirabilis jalapa
(d) Ginkgo bilobo
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Ginkgo biloba is believed to be the oldest living seed plant. Its fossils have been found in rocks as old as Triassic. It still survives with little change over this long periad of time while other members of its group have become extinct.
Question
The homologous organs are those that show similarity in [CBSE AIPMT 1995]
(a) size
(b) origin
(c) function
(d) appearance
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Homologous structures are those which have the same embryonic origin and basic structure, though they may or may not. perform the same function.
Question
Homologous organs are [CBSE AIPMT 1994]
(a) wings of insects and bat
(b) gills of fish and lungs of rabbit
(c) pectoral fins of fish and fore limbs of horse
(d) wings af grasshopper and crow
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Homologous structures are similar in origin but similar or dissimilar in function, as pectoral fins of fish and forelimbs of horse are similar in structure but different in function.
Question
Evolutionary convergence is development of [CBSE AIPMT 1993, 96]
(a) common set of characters in group of different ancestry
(b) dissimilar characters in closely related groups
(c) common set of characters in closely related groups
(d) random mating
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Convergent evolution or adaptive convergence refers to the development of similar adaptive functional structures in unrelated groups of organisms, e.g. wings of insect, bird and bat: Australian marsupials and placental mammals.
Question
Study of fossils is
(a) palaeontology
(b) herpetology
(c) saurology
(d) organic evolution
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Palaeontology is the study of fossils (remains or impressions of ancient forms) and their distribution in rocks of various ages. Study of animal fossils is known as plaeozoology and study of plant fossils is known as palaeobotany.
Question
Humming birds and hawk illustrate [CBSE AIPMT 1988]
(a) convergent evolution
(b) homology
(c)adaptive radiation
(d) parallel evolution
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Adaptive radiation or divergent evolution refers to the formation of different structures from a common ancestral form, e.g. wings of humming birds and hawk, fore limbs of horse, bat and human beings.
