Question
Statement I The condon ‘AUG’ codes for methionine and phenylalanine.
Statement II ‘AAA’ and ‘AAG’ both codons code for the amino acid lysine.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below. [NEET 2021]
(a) Both statement I and statement II are true
(b) Both statement I and statement II are false
(c) Statement I is true, but statement II is false
(d) Statement I is false, but statement II is true<
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Statement I is false, but statement 11 is true and can be corrected as The codon AUG only codes for methionine. As the codons are universal. From bacteria to mammals AUG only codes for methionine. Some amino acids are coded by more than one codon, hence the cade is degenerate. AAA and AAG both codons code for the amino acid lysine.
Question
Identify the correct statement. [NEET 2021]
(a) In capping, methyl guanosine triphosphate is added to the 3 end of hnRNA
(b) RNA polymerase binds with Rho factor to terminate the process of transcription in bacteria
(c) The coding strand in a transcription unit is copied to an mRNA
(d) Split gene arrangement is characteristic of prokaryotes
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Statement in aption (b) is correct and other statements can be corrected as A heterogeneous nuclear RNA or hnRNA is a primary mRNA transcript that is localised in the nucleus. Capping is a process in which at the $5^{\prime}$ end of hnRNA, a cap of 7-methly guanosine is added. The template strand is a transcription unit is coped to a mRNA.
Split gene arrangement is characteristic of eukaryotes.
Question
What is the role of RNA polymerase-III in the process of transcription in eukaryotes? [NEET 2021]
(a) Transcribes rRNAs(28S, $18 \mathrm{~S}$ and 5.8S)
(b) Transcribes tRNA (5s rRNA and snRNA)
(c) Transcribes precursor of mRNA
(d) Transcribes only snRNAs
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
In eukaryotes, at least three classes of RNA polymerases(Pol I-III) are required for the cellular RNA synthesis. In eukaryote cells, RNA polymerase III (also called Pol III) transcribes DNA to synthesise ribosomal 5 S rRNA, tRNA and other small RNAs. The genes transcribed by RNA Pol III fall in the category of “housekeeping” genes whose expression is required in all cell types and most environmental conditions.
Question
Identify the statement which is incorrect. [NEET (Oet.) 2020]
(a) Sulphur is an integral part of cysteine
(b) Glycine is an example of lipids
(c) Lecithin contains phosphorus atom in its structure
(d) Tyrosine possesses aromatic ring in its structure
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Statement (b) is incorrect. It can be corrected as Glycine is an example of amino acid. It is a neutral amino acid that contains only one amino group and one carboxylic group with non-cyclic hydrocarbon chain.
Question
The first phase of translation is [NEET (Sep.) 2020]
(a) recognition of DNA molecule
(b) amineacylation of tRNA
(c) recognition of an anti-codon
(d) binding of $\mathrm{mRNA}$ to ribosome
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
The first phase of translation is aminoacylation of $t R N A$, i.e. activation of amino acids and the formation of AAtRNA complex. In the presence of an enzyme tRNA synthetase, the amino acid (AA) molecule is activated and then each amino acid is attached to the specific tRNA molecule at 3 ‘/ CCA end to form aminoacyl-tRNA complex. The reaction needs ATP. This process is thus called charging of tRNA or aminoacylation of tRNA.
Question
The specific palindromic sequence which is recognised by EcoRl is [NEET (Sep.) 2020]
(a) 5′-GGAACC- 3
(b) 5′ – CTTAAG – 3′ 3′-CCTTGG – 5 3′ – GAATTC – 5 ‘
(c) 5 – GGATCC – 3
(d) 5′ – GAATTC – 3′ 3′- CCTAGG – 5 ‘ 3’ – CTTAAG – 5
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
The correct option is(d) because the specific palindromic sequence which is recognised by EcoRI is 5′-GAATTC-3′ 3′-CTTAAG-5′.
A palindromic sequence is a sequence made up of nucleic acids within double helix of DNA or RNA that is the same when read from 5 ‘ to 3 ‘ on one strand and 3 to 5 on the other, complementary strand.
Question
The sequence that controls the copy number of the linked DNA in the vector, is termed
(a) Ori site
(b) palindromic sequence
(c) recognition site
(d) selectable marker
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
The sequence that controls the copy number of linked DNA in the vector is called as Ori site. Origin of replication is a sequence from where replication starts and any foreign DNA is linked to this region. Ori site is also responsible for controlling copy number of linked DNA. Therefore, if any person wants to praduce many copies of the target DNA he/she should clone in a vector whose Ori site supports high copy number.
Question
From the following, identify the correct combination of salient features of Genetic code. [NEET (Odisha) 2019]
(a) Universal, Non-ambiguous, Overlapping
(b) Degenerate, Overlapping, Commaless
(c) Universal, Ambiguous, Degenerate
(d) Degenerate, Non-overlapping, Non-ambiguous
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
The correct combination of salient features of Genetic code is degenerate, Non-overlapping, Non-ambiguous. These are explained as one codon codes for only one amino acid, hence genetic code is unambiguous and specific. Some amino acids are coded by more than one codon, hence the code is degenerate. The codon is read in mRNA in a contiguous fashion. There are no punctuations and overlapping.
Question
Which of the following features of genetic code does allow bacteria to produce human insulin by recombinant DNA technology? [NEET (National) 2019]
(a) Genetic code is redundant.
(b) Genetic code is nearly universal
(c) Genetic code is specific
(d) Genetic code is not ambiguous
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Bacteria is able to produce human insulin because genetic code is nearly universal in all organisms. For example, the codon AGG specifies amino acid Arginine in bacteria, animals and plants. But there are also some exceptions to it, e.g. in mitochondria, stop codon UGA specifies amino acid tryptophan.
Question
Match the following RNA polymerases with their transcribed products
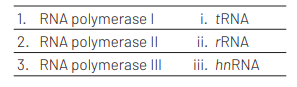
Select the correct option from thefollowing [NEET (Odisha) 2019]
1 2 3
(a) (i) (iii) (ii)
(b) (i) (ii) (iii)
(c) (ii) (iii) (i)
(d) (iii) (ii) (i)
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
The correct matches are
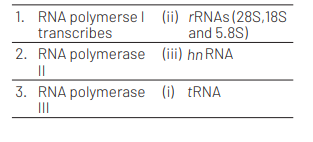
Question
Expressed Sequence Tags (ESTs) refers to [NEET (National) 2019]
(a) polypeptide expression
(b) DNA polymorphism
(c) novel DNA sequences
(d) genes expressed as RNA
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Expressed Sequence Tags (EST) refers to the genes expressed as RNA. These are the DNA sequences that are expressed as mRNA for protein synthesis.
Question
AGGTATCGCAT is a sequence from the coding strand of a gene. What will be the corresponding sequence of the transcribed mRNA? [NEET 2018]
(a) ACCUAUGCGAU
(b) AGGTUTCGCAT
(c) AGGUAUCGCAU
(d) UCCAUAGCGUA
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Coding strand is the one that codes for mRNA. It has same nucleotide sequence as that of mRNA except thymine $(T)$ is replaced by uracil (U) in mRNA. Hence, the corresponding sequence of transcribed mRNA by template or non-coding strand (complementary to RNA) is AGGUAUCGCAU.
Question
If there are 999 bases in an RNA that codes for a protein with 333 amino acids and the base at position 901 is deleted such that the length of the RNA becomes 998 bases, how many codons will be altered? [NEET 2017]
(a) 1
(b) 11
(c) 33
(d) 333
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
33 codons will be altered if the 901 st base is deleted and RNA has only 998 bases instead of 999 bases. Total bases present in RNA $=999$ Bases left after deletion of 901 st base in RNA
$
\begin{aligned}
& =999-901 \\
& =98
\end{aligned}
$
Number of codon present in $98=33$ (Approximately as three codons code for one amino acid).
Question
Which one of the following is the starter codon? [NEET 2016, Phase I]
(a) UGA
(b) UAA
(c) UAG
(d) AUG
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
AUG is the start codon. It also codes for amino acid called methionine which is the first amino acid in a polypeptide chain. UAA, UAG and UGA are stop codons and are meant for termination of polypeptide chain during protein synthesis.
Question
The diagram shows an important concept in the genetic implication of DNA. Fill in the blanks $A$ to $C$. [NEET 2013]
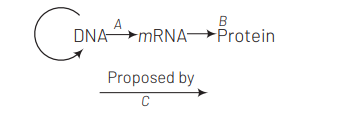
(a) A-transcription, B-replication, C-James Watson
(b) A-translation, B-transcription, C-Erwin Chargaff
(c) A-transcription, B-translation, C-Francis Crick
(d) A-translation, B-extension, C-Rosalind Franklin
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Central dogma is
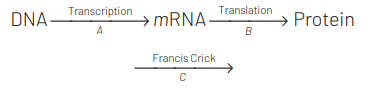
Question
If one strand of DNA has the nitrogenous base sequence as ATCTG, what would be the complementary RNA strand sequence? [CBSE AIPMT 2012]
(a) TTAGU
(b) UAGAC
(c) AACTG
(d) ATCGU
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
If one strand of DNA has the nitrogenous base sequence as ATCTG, the complementary sequence of mRNA will be UAGAC.
Question
What is not true for genetic code? [CBSE AIPMT 2009]
(a) A codon in mRNA is read in a non-contiguous fashion
(b) It is nearly universal
(c) It is degenerate
(d) It is unambiguous
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
The general features of genetic code are
(i) The genetic code is written in linear form, using the ribonucleotide bases that compose mRNA molecule as letters.
(ii) Each word of codon consists of three letters, i.e., the codon is triplet.
(iii) The genetic code inside the cell medium is said to be non-ambiguous.
(iv) The code is degenerate, i.e. a given amino acid can be specified by more than one codons.
(v) The codon contains ‘start’ and ‘stop’ signals.
(vi) The code is said to be commaless.
(vii) The code is non-overlapping.
Question
Which one of the following pairs of codons is correctly matched with their function or the signal for the particular amino acid? [CBSE AIPMT 2008]
(a) GUU, GCU $\quad-\quad$ Alanine
(b) UAG, UGA $\quad-$ Stop
(c)AUG, ACG – Start/methionine
(d) UUA, UCA – Leucine
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
The group of nucleotides that specifies one amino acid is a code word or codon. The nucleotides of mRNA are arranged as a linear sequence of codons, each codon consisting of three successive nitrogenous bases.
Three codons UAG, UAA and UGA are the termination codons. They do not code for any of the amino acids.
In most organisms AUG codon is the start or initiation codon, i.e. the polypeptide chain starts either with methionine or $\mathrm{N}$-formylmethionine.
Leucine – UUA, UUG, CUU, CUC, CUA, CUG.
Alanine – GUC, GCC, GCA, GCG.
GUU – Valine
UCA – Serine.
Question
One gene-one enzyme relationship was established for the first time in [CBSE AIPMT 2007]
(a) Neurospora crassa
(b) Salmonella typhimurium
(c) Escherichia coli
(d) Diplococcus pneumoniae
Answer/Explanation
Anš. (a)
One gene-one enzyme relationship was initially proposed by Beadle and Tatum based on their experiments conducted on Neurospora crassa. They were awarded by Nobel Prize in 1958.
Question
A sequential expression of a set of human genes occurs when a steroid molecule binds to the [CBSE AIPMT 2007]
(a) transfer RNA
(b) messenger RNA
(c) DNA sequence
(d) ribosome
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
The steroid hormone receptor protein complex activate transcription of target gene by binding to sepecific DNA sequence.
Question
One gene-one enzyme hypothesis was postulated by [CBSE AIPMT 2006]
(a) R Franklin
(b) Hershey and Chase
(c) A Garrod
(d) Beadle and Tatum
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
‘One gene-one enzyme’ hypothesis was given by Beadle and Tatum [1948] which states that particular gene controls the synthesis of specific enzyme. Later, it was modified to ‘one gene-one polypeptide hypothesis’ by Yanofsky, et. al, [ 1965]
Question
Amino acid sequence, in protein synthesis is decided by the sequence of [CBSE AIPMT 2006]
(a) tRNA
(b) mRNA
(c) cDNA
(d) rRNA
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
In the process of protein synthesis, the messenger RNA(mRNA) is responsible for carrying the genetic code transcribed from DNA to specialised sites within the cell (called ribosomes) where the information is translated into protein. The sequence of amino acids in a particular protein is determined by the sequence of nucleotides in mRNA. Sequence of tRNA, cDNA or rRNA do not decide the amino acid sequence in protein synthesis.
Question
After a mutation at genetic locus the character of an organism changes due to the change in [CBSE AIPMT 2004]
(a) protein structure
(b) DNA replication
(c) protein synthesis pattern
(d) RNA transcription pattern
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Normally, genetic information flows from DNA $\rightarrow$ mRNA $\rightarrow$ protein. Hence, any change in nucleotides due to the mutation, would result in change in the structure of protein/enzyme which might result in some change in the organism.
Question
The following ratio is generally constant for a given species [CBSE AIPMT 2004]
(a) $A+G / C+T$
(b) $T+C / G+A$
(c) $\mathrm{G}+\mathrm{C} / \mathrm{A}+\mathrm{T}$
(d) $A+C / T+G$
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
The base ratio $A+T / G+C$ may vary from one species to another, but is constant for a given species. It is rarely equal to one and varies between $0.4$ and $1.9$.
Question
In the genetic code dictionary, how many codons are used to code for all the 20 essential amino acids? [CBSE AIPMT 2003]
(a) 61
(b) 60
(c) 20
(d) 64
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Out of 64 codons three (UAA, UAG, UGA) are chain terminating codons the translating mechanism is not able to read these codons and 61 codons are used to code all the 20 essential amino acids.
Question
What would happen if in a gene encoding a polypeptide of 50 amino acids, $25^{\text {th }}$ codon (UAU) is mutated to UAA? [CBSE AIPMT 2003]
(a) A polypeptide of 49 amino acids will be formed
(b) A polypeptide of 25 amino acids will be formed
(c)A polypeptide of 24 amino acids will be formed
(d) Two polypeptides of 24 and 25 amino acids will be formed
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
UAA is the ‘stop’ codon hence, polypeptide chain will not grow after $24^{\text {th }}$ amino acid. In the absence of new initiating codon rest of codons will not be able to translate.
Question
Degeneration of a genetic code is attributed to the [CBSE AIPMT 2003]
(a) entire codon
(b) third member of a codon
(c) first member of a codon
(d) second member of a codon
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
It has seen variously that one tRNA molecule codes for more than one amino acid molecules. This is possible due to the improper pairing of third codon with the first anticodon of tRNA.
Question
During translation initiation in prokaryotes, a GTP molecule is needed in [CBSE AIPMT 2003]
(a) association of $30 S$, mRNA with formyl met tRNA
(b) association of $50 S$ subunit of ribosome with initiation complex
(c) formation of formyl met tRNA
(d) binding of $30 S$ subunit of ribosome with MRNA
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
During the process of translation an initial complex is formed between mRNA, $30 S$ ribosomal sub-unit and methionyl tRNA. This complex is formed due to the association of $I F_1, I F_2, I F_3$ initiation factors and GTP molecule.
Question
Which one of the following triplet codes, is correctly matched with its specificity for an amino acid in protein synthesis or as ‘start’ or ‘stop’ codon? [CBSE AIPMT 2003]
(a) UGU-Leucine
(b) UAC-Tyrosine
(c) UCG-Start
(d) UUU-Stop
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
$\begin{array}{llr}\text { UGU } & \rightarrow & \text { Cistine } \\ \text { UAC } & \rightarrow & \text { Tyrosine } \\ \text { UCG } & \rightarrow & \text { Serine } \\ \text { UUU } & \rightarrow & \text { Phenylalanine } \\ \text { UAG, UGA, UAA } & \rightarrow & \text { Stop codons } \\ \text { UAG } & \rightarrow & \text { Start codon. }\end{array}$
Question
‘Signal hypothesis’ for the biosynthesis of secretory type of proteins was proposed by [CBSE AIPMT 2000]
(a) Camillo Golgi
(b) Blobel and Sabatini
(c) Baltimore
(d) Sheeler and Bianchi
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
A variety of proteins are synthesised on ribosomes. However, these have different destinations. David Sabatini and G. Blobel proposed ‘signal sequence’ hypothesis according to which a short amino acid sequence at the amino terminus of a newly synthesised polypeptide directs a protein to its appropriate sequence.
Question
The transfer RNA molecule in 3D appears [CBSE AIPMT 2000]
(a) L-shaped
(b) E-shaped
(c) Y-shaped
(d) S-shaped
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Kimet al, (1973) suggested L shaped model of $t$ RNA by X-ray diffraction while studying phenyl alanine tRNA of yeast. L shape structure of $t R N A$ is a 3-dimentional(3D) structure of $20 Å$ thickness.
Question
Which is not involved in protein synthesis? [CBSE AIPMT 1994]
(a) Transcription
(b) Initiation
(c) Elongation
(d) Termination
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Transcription is the synthesis of RNA on DNA template. It is not involved in protein synthesis (translation).
Question
In DNA when AGCT occurs, their association is as per which of the following pair? [CBSE AIPMT 1999]
(a) ACGT
(b) AGCT
(c)ATGC
(d) All of these
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
In DNA AGCT is associated with pair ATGC because in a DNA molecule, the purine adenine in either chain is associated with the pyrimidine thymidine on the other. Similarly, purine guanine in either chain is associated with pyrimidine cytosine on the other.
Question
Protein synthesis in an animal cell takes place [CBSE AIPMT 1997]
(a) only in the cytoplasm
(b) in the nucleolus as well as in the cytoplasm
(c) in the cytoplasm as well as in mitochondria
(d) only on ribosomes attached to a nucleus
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Protein synthesis is a complex process it essentially involves DNA for the synthesis of mRNA(transcription) which contains information for the synthesis of proteins (translation). The process of translation takes place on ribosomes which are found in cytoplasm (in attached form on ER) and in mitochondria (in the free form).
Question
The RNA that picks up specific amino acid from amino acid pool in the cytoplasm to ribosome during protein synthesis is called [CBSE AIPMT 1997]
(a) mRNA
(b) tRNA
(c) rRNA
(d) RNA
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
tRNA (soluble RNA = sRNA) is a 70-75 nucleotide long molecule. $80 \%$ of this RNA is double helical, one end of this molecule has $\mathrm{G}$ and other $\mathrm{C}-\mathrm{C}-\mathrm{A}$ sequences. The clover leaf model(2D) of tRNA was given by R Holley [ 1968 ] and Kim et al, [1973] suggested ‘L’shaped model (3D) of tRNA by X-ray diffraction while studying phenyl alanine tRNA of yeast. Each amino acid had its own specific tRNA molecule which transfers it from cytoplasm to the ribosome.
Question
The codons causing chain termination are [CBSE AIPMT 1997]
(a) TAG, TAA, TGA
(b) GAT, AAT, AGT
(c) AGT, TAG, UGA
(d) UAA, UAG, UGA
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
UAA, UAG and UGA act as stop codons (terminator codons) because these are not translated into amino acid. UAA is called ochre, UAG as amber and UGA as opal.
The translation termination triplet is [CBSE AIPMT 1996]
(a) UAU
(b) UAA
(c) UAC
(d) UGC
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Termination codons are three in number they are UAA (ochre) UAG (amber) and UGA (opal).
Question
If the sequence of bases in DNA is ATTCGATG, then the sequence of bases in its transcript will be [CBSE AIPMT 1995]
(a) CAUCGAAU
(b) UAAGCUAC
(c) GUAGCUUA
(d) AUUCGAUG
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Transcription is the process of synthesis of mRNA on DNA template by the complementary bases. As thymine is replaced by uracil in RNA so, the sequence of bases will be UAAGCUAC.
Question
Anticodon is an unpaired triplet of bases in an exposed position of [CBSE AIPMT 1995]
(a) mRNA
(b) rRNA
(c) tRNA
(d) sRNA
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
tRNA possess anticodon stem which includes five paired bases. The anticodon loop consists of 7 unpaired bases. The third, fourth and fifth of which form anticodon. This anticodon permits temporary complementary pairing with three bases on mRNA.
Question
DNA template sequence of CTGATAGC is transcribed over mRNA as [CBSE AIPMT 1994]
(a) GUCTUTCG
(b) GACUAUCG
(c) GAUTATUG
(d) UACTATCU
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
During transcription complementary mRNA is formed on DNA template in which $\mathrm{T}$ is replaced by U. So, the sequence will be GACUAUCG. alled as initiating or starting codon or start signal.
Question
The number of base substitution possible in amino acid codons is [CBSE AIPMT 1994]
(a) 261
(b) 264
(c) 535
(d) 549
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
There are 64 codons out of which 61 codes for amino acid. Each codon possess 3 bases which can undergo transition and transversion, so the number of base substitution possible in amino acid codons is $61 \times 3^2=549$.
Question
Initiation codon of protein synthesis (in eukaryotes) is [CBSE AIPMT 1993, 94, 99, 2000]
(a) GUA
(b) GCA
(c) CCA
(d) AUG
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
At 5′end of mRNA where protein synthesis starts codon AUG is present. So, AUG is called as initiating or starting codon or start signal.
Question
The process of translation is [CBSE AIPMT 1993]
(a) ribosome synthesis
(b) protein synthesis
(c) DNA synthesis
(d) RNA synthesis
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Translation is the process of protein synthesis in which the triplet base sequences of mRNA molecules is converted into a specific sequences of amino acids in a polypeptide chain, this occurs on ribosomes.
Question
Because most of the amino acids are represented by more than one codon, the genetic code is [CBSE AIPMT 1993, 2002]
(a) overlapping
(b)wobbling
(c) degenerate
(d) generate
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Degeneracy means lack of specificity. Presence of more than one meaningful codons for an amino acid is called degeneracy, e.g. methionine and tryptophan has single code for each. The maximum number of codons for an amino acid is six, e.g. serine, arginine and leucine. Degeneracy provides a protection against mutation.
Question
Khorana first deciphered the triplet codons of [CBSE AIPMT 1992]
(a) serine and isoleucine
(b) threonine and histidine
(c) tyrosine and tryptophan
(d) phenylalanine and methionine
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Dr. Hargobind Khorana deciphered first triplet codon of threonine and histidine.
Question
In the genetic dictionary, there are 64 codons as [CBSE AIPMT 1990]
(a) 64 amino acids are to be coded
(b) 64 types of tRNAs are present
(c) there are 44 non-sense codons and 20 sense codons
(d) genetic code is triplet
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
It has been found that a sequence of 3 consecutive bases in a DNA molecule codes for one specific amino acid. So, genetic code is a triplet code and there are 64 triplets which are called codons $(4 \times 4 \times 4=64)$ of nitrogen bases for protein synthesis.
Question
Genetic code consists of [CBSE AIPMT 1988]
(a) adenine and guanine
(b) cytosine and uracil
(c) cytosine and guanine
(d) All of the above
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
The sequence of nitrogen bases on the mRNA which store information for linking the amino acids in a definite sequence during synthesis of proteins is called genetic code. These nitrogen bases include adenine, guanine, cytosine and uracil
